150110188-SUBSTATION-AUTOMATION.pdf
- 1. Introduction to Substation Automation MV Girish, Commissioning engineers training, 2011-01-21 and IEC61850
- 2. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 2 Conventional Control & Protection 220 kV Switch Yard Double Busbar Control Building 400 kV Switch Yard 1/2 Circuit Breaker Control Board Cable Trenches Protection panels
- 3. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 3 Modern Substation Automation 220 kV line protection 400 kV line protection Interbay bus Gateway GPS Printers Eth. Switch Interbay bus Monitoring & control from remote Local control Bay control 220 kV Bay control 400 kV Transformer protection Bay Units Busbar protection Central Unit
- 4. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 4 Modern Substation Automation -Q1 -Q0 -Q8 -Q9 -Q2 Process Level Bay Level Station Level ABB Network Partner AG C E COM581 Network Control Center NCC Inter Bay Bus
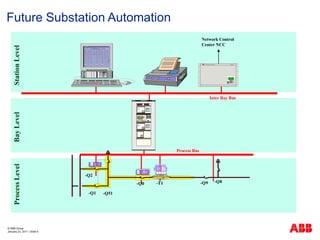
- 5. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 5 Future Substation Automation ABB Network Partner AG C E COM581 Network Control Center NCC PISA PISA A PISA B PISA A -Q1 -Q2 -Q51 -Q0 -T1 -Q9 -Q8 Process Level ? LOCAL REMOTE SET OPERATION M M M Bay Level Station Level Process Bus Inter Bay Bus
- 6. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 6 Technical requirements for the standard Long term stability The standard shall be future proof, i.e. it must be able to follow the progress in communication technology as well as evolving system requirements. Interoperability The ability for IEDŌĆÖs from one or several manufacturer to exchange information and use the information for the their own functions. Free allocation The standard shall support different philosophies and allow a free allocation of functions e.g. it must work equally well for centralized (RTU like) or decentralized (SCS like) systems.
- 7. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 7 How to solve all these Technical requirements? ’é¦ Interoperability ! ’é¦ Free allocation ! ’é¦ Long term stability ! What features in a Substation and in a Substation Automation System ’é¦ are changing slowly ? ’é¦ are changing fast ? What belongs really to the ’é¦ the functions ? ’é¦ the communication ? ’é¦ to both ?
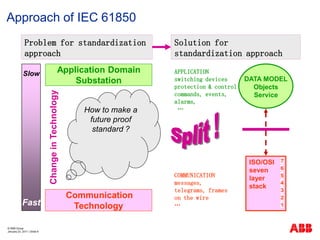
- 8. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 8 Approach of IEC 61850 DATA MODEL Objects Service APPLICATION switching devices protection & control commands, events, alarms, ŌĆ” Application Domain Substation Communication Technology Problem for standardization approach Slow Fast Change in Technology How to make a future proof standard ? Solution for standardization approach ISO/OSI seven layer stack COMMUNICATION messages, telegrams, frames on the wire ŌĆ” 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 9. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 9 Data model ’āś The data model is an object model close to user ’āś It provides all services for the domain S/S and SA ’āś It provides a high degree of freedom for optimization ’āś It supports the more convenient use of object lists instead of signal lists
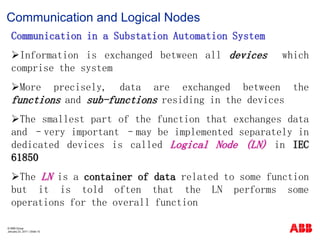
- 10. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 10 Communication and Logical Nodes Communication in a Substation Automation System ’āśInformation is exchanged between all devices which comprise the system ’āśMore precisely, data are exchanged between the functions and sub-functions residing in the devices ’āśThe smallest part of the function that exchanges data and ŌĆōvery important ŌĆōmay be implemented separately in dedicated devices is called Logical Node (LN) in IEC 61850 ’āśThe LN is a container of data related to some function but it is told often that the LN performs some operations for the overall function
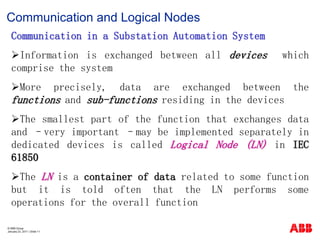
- 11. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 11 Communication and Logical Nodes Communication in a Substation Automation System ’āśInformation is exchanged between all devices which comprise the system ’āśMore precisely, data are exchanged between the functions and sub-functions residing in the devices ’āśThe smallest part of the function that exchanges data and ŌĆōvery important ŌĆōmay be implemented separately in dedicated devices is called Logical Node (LN) in IEC 61850 ’āśThe LN is a container of data related to some function but it is told often that the LN performs some operations for the overall function
- 12. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 12 Examples of Logical Nodes close to the user Secondary technology Control Q0/CSWI Q8/CSWI Q9/CSWI Bay-HMI IHMI Distance Protection PDIS LN function-related in the substation Circuit Breaker Q0_L1/XCBR Gas density mon. Q0_L1/SIMG Primary technology Isolator Q9_L1/XSWI Gas density mon. Q9_L1/SIMG Earthing Switch Q8_L1/XSWI Gas density mon. Q8_L1/SIMG
- 13. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 13 Examples of LNs in devices (IEDs) Device Example: Combined Protection and Control Unit Device Example: Circuit Breaker Device Example: Station Workplace XCBR (Circuit Breaker) TCTR (Current Transformer) TVTR (Voltage Transformer) CSWI (Switch Controller) PDIS (Distance Protection) IHMI (Human Machine IF) Device Example: Combisensor
- 14. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 14 The groups of LNs provided by IEC 61850 ’é¦ L System LN (2*) ’é¦ P Protection (28) ’é¦ R Protection related (10) ’é¦ C Control (5) ’é¦ G Generic (3) ’é¦ I Interfacing and archiving (4) ’é¦ A Automatic control (4) ’é¦ M Metering and measurement (8) ’é¦ S Sensor and monitoring (4) ’é¦ X Switchgear (2) ’é¦ T Instrument transformers (2) ’é¦ Y Power transformers (4) ’é¦ Z Further power system equipment (15) Examples ŌĆó PDIF: Differential protection ŌĆó RBRF: Breaker failure ŌĆó XCBR: Circuit breaker ŌĆó CSWI: Switch controller ŌĆó MMXU: Measurement unit ŌĆó YPTR: Power transformer Group identification by First letter *) Number in brackets indicates the number of LNs provided allocated to this group
- 15. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 15 The model hierarchy (example) Property ’é» Attribute Value Attribute Value Logical Device (LD) ’éŁ Grouping Physical Device (IED) defined as Server ’éŁ Implementation Logical Node (LN) Data (Object) Data ’é» Bay Unit (name not standardized) Control (name not standardized) CSWI (Switch Control) Pos (Position) ctlVal (Control Value/Command) off/on stVal (Status Value) Intermediate-state/off/on/bad-state
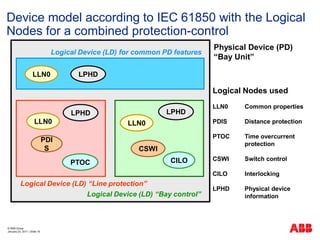
- 16. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 16 Device model according to IEC 61850 with the Logical Nodes for a combined protection-control LLN0 CSWI Logical Device (LD) ŌĆ£Line protectionŌĆØ Logical Device (LD) ŌĆ£Bay controlŌĆØ Physical Device (PD) ŌĆ£Bay UnitŌĆØ CILO LLN0 Logical Device (LD) for common PD features LPHD LPHD PDI S PTOC LLN0 LPHD Logical Nodes used LLN0 Common properties PDIS Distance protection PTOC Time overcurrent protection CSWI Switch control CILO Interlocking LPHD Physical device information
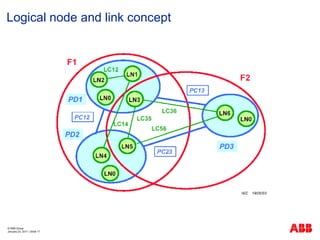
- 17. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 17 Logical node and link concept
- 18. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 18 From Signal List to Object List LN XCBR Circuit Breaker LN IHMI Station HMI LN CSWI Switch Controller Complete ? Complete regarding mandatory data ! Object list ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. Signal list
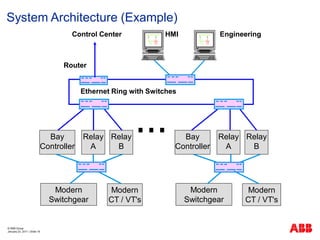
- 19. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 19 System Architecture (Example) Control Center HMI Engineering Router Relay A Bay Controller Modern Switchgear Modern CT / VT's Relay B Relay A Bay Controller Modern Switchgear Modern CT / VT's Relay B Ethernet Ring with Switches
- 20. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 20 IEC 61850 Documentation Mapping to real Comm. Networks (SCSM) Part 8-1: Mapping to MMS and to ISO/IEC 8802-3 Part 9-1: Sampled Values over Serial Unidirectional Multidrop Point-to-Point link Part 9-2: Sampled values over ISO 8802-3 Part 7-2: Abstract Communication Services (ACSI) Part 7-1: Principles and Models Abstract Communication Services Part 7-4: Compatible Logical Node Classes and Data Classes Part 7-3: Common Data Classes Data Models Part 10: Conformance Testing Testing Part 1: Introduction and Overview System Aspects Part 2: Glossary Part 3: General Requirements Part 4: System and Project Management Part 5: Comm. Requirements for Functions and Device Models Configuration Part 6: Configuration Language for electrical Substation IEDs
- 21. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 21 Engineering Engineering features ’é¦ Formal description for device and system structures needed ’é¦ Substation Configuration description Language provides the formal description ’é¦ Engineering process
- 22. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 22 Engineering For the formal description is provided by the Substation Configuration description Language (SCL) ’é¦ based on XML ’é¦ defined in part 6 of the standard (IEC 61850-6) ’é¦ usable for ’é¦ IED Configuration Description (ICD) files ’é¦ System Configuration Description (SCD) file ’é¦ System functional specification (SSD) the engineering information is exchangeable between tools !!!
- 23. ┬® ABB Group January 23, 2011 | ║▌║▌▀Ż 23 SCL exchange during the engineering process IED Configurator IED DB File transfer local File transfer remote IED Capabilities (LN, DO, etc) File transfers and parameterization with IEC61850 services Engineering environment SA system IED IED IED IED Substation Gateway Association, relation to Single line diagram, preconfigured, reports, etc. Engineering Workplace System Configurator