17 ruby date time
0 likes528 views
This document discusses working with dates and times in Ruby. It provides examples of getting the current date and time, extracting components of dates and times like year, month, day, and formatting dates and times in different formats. It also covers time arithmetic, timezones, and daylight savings time.
1 of 4
Download to read offline
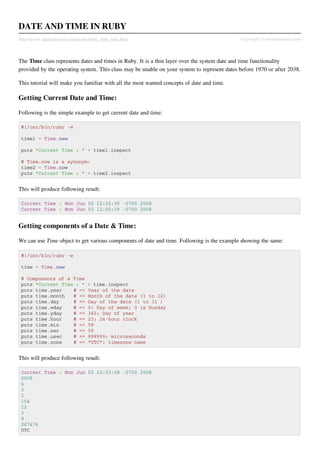
![Time.utc, Time.gm and Time.local Functions:
These two functions can be used to format date in standard format as follows:
# July 8, 2008
Time.local(2008, 7, 8)
# July 8, 2008, 09:10am, local time
Time.local(2008, 7, 8, 9, 10)
# July 8, 2008, 09:10 UTC
Time.utc(2008, 7, 8, 9, 10)
# July 8, 2008, 09:10:11 GMT (same as UTC)
Time.gm(2008, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11)
Following is the example to get all components in an array in the following format:
[sec,min,hour,day,month,year,wday,yday,isdst,zone]
Try the following:
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w
time = Time.new
values = time.to_a
p values
This will generate following result:
[26, 10, 12, 2, 6, 2008, 1, 154, false, "MST"]
This array could be passed to Time.utc or Time.local functions to get different format of dates as follows:
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w
time = Time.new
values = time.to_a
puts Time.utc(*values)
This will generate following result:
Mon Jun 02 12:15:36 UTC 2008
Followin is the way to get time represented internally as seconds since the (platform-dependent) epoch:
# Returns number of seconds since epoch
time = Time.now.to_i
# Convert number of seconds into Time object.
Time.at(time)
# Returns second since epoch which includes microseconds
time = Time.now.to_f
Timezones and daylight savings time:
You can use a Time object to get all the information related to Timezones and daylight savings as follows:
time = Time.new
# Here is the interpretation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/17rubydatetime-130204175543-phpapp01/85/17-ruby-date-time-2-320.jpg)


Ad
Recommended
How to work with dates and times in swift 3
How to work with dates and times in swift 3allanh0526
Ěý
This document discusses working with dates and times in Swift 3. It covers the Date, DateComponents, DateFormatter, Calendar, Locale, and TimeZone classes. It shows how to create and format dates, extract date components, perform date calculations like adding/subtracting days/weeks, and compare dates. Key aspects covered include converting between dates and strings, building dates from components, and getting the difference between dates in seconds or days.Mathcad day number in the year and solar declination angle
Mathcad day number in the year and solar declination angleJulio Banks
Ěý
The document describes a procedure to calculate the day number of a given date and its application to determine the solar declination angle, δ. It outlines the computation method for the day of the year and reveals that the solar declination ranges from +23.45° on June 21 to -23.45° on December 21. An example calculation shows that June 1 corresponds to the 152nd day of the year.What Year Is It: things you shouldn't do with timezones
What Year Is It: things you shouldn't do with timezonesAram Dulyan
Ěý
This document discusses common issues with working with timezones in Django projects and provides recommendations. It notes that Django handles converting datetimes to the current timezone in templates and form inputs, but does not handle per-user timezones without additional code. It demonstrates functions from Django's timezone module for working with aware datetimes, filtering records by date while accounting for timezones, and calculating future datetimes that respect daylight saving time changes. It also recommends the dateutil library for working with date arithmetic across years and months.Python Lecture 12
Python Lecture 12Inzamam Baig
Ěý
This lecture discusses Python's datetime and OS modules. It shows how to use datetime to work with dates, times, and datetimes, including creating, formatting, and manipulating them. It also demonstrates various OS module functions for working with directories and files, such as getting/changing the current directory, listing contents, creating/removing directories, renaming files, checking file attributes, and more.Gem and I: Runt
Gem and I: Runtcglee
Ěý
Runt is a Ruby gem for building temporal expressions to describe recurring events or dates. It allows defining expressions like "every week" or "Tuesdays and Thursdays except holidays". Temporal expressions can be used to generate dates in a range or test if a date is included. The gem provides classes to describe weekly, monthly, or yearly intervals as well as days of the week. Complex expressions can be built by combining interval classes with operators like &, |, and -.Will the computer world collapse in 2038?
Will the computer world collapse in 2038?Joris Berthelot
Ěý
The document discusses the potential "Y2K38 bug" that could cause issues for computers and software in 2038 due to timestamps being stored using 32-bit integers, which will reach their maximum value and roll over on January 19th, 2038. This will cause time values to incorrectly jump back to 1901. The solutions proposed include switching systems to 64-bit architectures, updating programs to handle 64-bit timestamps, and updating core time libraries. Overall, the conclusion is that there is no need to panic as there is still plenty of time to implement solutions and prepare for this issue.Y2 k38.
Y2 k38.Presentaionslive.blogspot.com
Ěý
The Y2K38 problem refers to an issue that will occur in systems that store time as a 32-bit signed integer representing seconds since January 1st, 1970. This will overflow on January 19th, 2038 when the number becomes too large for 32 bits. After this point, times will wrap around and be interpreted as dates in 1901 instead of future dates, causing systems to fail. The solution is to update systems to use 64-bit integers or unsigned 32-bit integers to store time and avoid this overflow.16 ruby hashes
16 ruby hashesWalker Maidana
Ěý
Hashes in Ruby are collections of key-value pairs similar to arrays but where indexing is done using keys of any object type rather than integers. Keys and values can be any object including arrays. Hashes have many built-in methods for accessing, modifying, and traversing key-value pairs including fetch, delete, each, keys, values, merge, and more. Creating a hash can be done using Hash.new or Hash[] and default values can be set.15 ruby arrays
15 ruby arraysWalker Maidana
Ěý
Ruby arrays are ordered collections that can hold any object type. They are indexed starting at 0, can dynamically grow in size, and provide many built-in methods. Some key characteristics of Ruby arrays include:
1) They are ordered and associate each element with an integer index. Negative indices count backward from the end.
2) Arrays can be created and initialized in several ways such as with Array.new or [].
3) Arrays provide over 70 built-in methods for accessing, modifying, and manipulating array elements like fetch, push, pop, insert, delete, and more.Ruby File I/O
Ruby File I/OSarah Allen
Ěý
The document discusses input/output (IO) and file handling in Ruby. It explains that the IO class is the basis for all input and output, and that the File class allows reading and writing files as it is a subclass of IO. It then provides examples of how to open, read, write, iterate over, and get metadata from files and directories in Ruby.19 ruby iterators
19 ruby iteratorsWalker Maidana
Ěý
This document discusses two Ruby iterators: each and collect. The each iterator returns each element of an array or hash and executes a block of code for each. Collect returns a new array containing the return values of its block for each element or just returns the original collection. Examples demonstrate using each to print array elements and collect to multiply array elements by 10 and return a new array.14 ruby strings
14 ruby stringsWalker Maidana
Ěý
This document provides information about Ruby strings, including:
- Strings can be created using single or double quotes, and support escape characters
- Strings support expression interpolation using #{expression}
- Methods like gsub, slice, and split can be used to manipulate and extract parts of strings
- Built-in string methods allow tasks like changing case, formatting strings, searching/matching substrings
- Strings have methods for operations like concatenation, comparison, indexing, and conversion between other types18 ruby ranges
18 ruby rangesWalker Maidana
Ěý
Ranges in Ruby can represent sequences, conditions, and intervals. Ranges use the ".." and "..." operators to define inclusive and exclusive sequences. Ranges can iterate over their values, test membership, find minimum/maximum values, and reject values. Ranges are also used as conditional expressions to check if a value falls within the start and end points, and in case statements to check different ranges.20 ruby input output
20 ruby input outputWalker Maidana
Ěý
The document discusses Ruby file input/output (I/O) and directory functionality. It covers Ruby classes like IO, File, and Dir that provide methods for reading, writing, opening, closing, renaming, and deleting files. It also discusses creating and navigating directories. Some key file I/O methods include read, write, gets, puts, readline, sysread, and syswrite. Directory methods include chdir, pwd, entries, mkdir, and delete. The document provides examples of using these various Ruby file and directory functions.8 Key Life and Leadership Lessons
8 Key Life and Leadership LessonsStanford Graduate School of Business
Ěý
This document discusses 8 key life and leadership lessons shared in the 2016 Stanford GSB View From The Top guest speaker series. It explores takeaways from leaders who spoke at Stanford about their experiences and advice. The document aims to provide insights for developing leadership skills.Date and time manipulation
Date and time manipulationShahjahan Samoon
Ěý
The document discusses working with dates and times in Java. It covers the Date class, Calendar class, formatting dates, parsing strings into dates, and performing date/time operations and comparisons. The Date class represents a specific instant in time and provides methods for getting dates, comparing dates, and formatting dates. The Calendar class provides methods for converting between dates and calendar fields like month, day, year, and manipulating calendar fields. Formatting dates can be done using SimpleDateFormat, printf, or other methods.Fun times with ruby
Fun times with rubyGeoff Harcourt
Ěý
This document discusses time and time zones in Ruby and Rails. It explains why time is important and difficult, describes UTC and time zone offsets, and provides best practices for using time in Rails applications, including storing times in UTC and converting to local times for display. It also covers parsing times from users, testing with time, and caching pages that display times.Python time
Python timeJanu Jahnavi
Ěý
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Python's time and date modules, discussing various functions such as time(), gmtime(), localtime(), strptime(), and strftime(). It covers how to convert between epoch time and human-readable formats, as well as the use of directives for date formatting. Additionally, it illustrates practical examples of time manipulation, time comparison, and the use of time.sleep() for thread execution control.Ruby Time & Date
Ruby Time & DateJesus Castello
Ěý
Ruby's Time class allows you to work with dates and times. It can store both a date and time, get the current time, and perform time arithmetic like adding seconds. The strftime method formats times for output and strptime parses dates from strings. Rails adds functionality via ActiveSupport, including methods like 3.days.ago that return TimeWithZone objects. Formatting, parsing, and arithmetic on Time objects lets you easily manage dates and times in Ruby.SessionSeven_WorkingWithDatesandTime
SessionSeven_WorkingWithDatesandTimeHellen Gakuruh
Ěý
This document provides an overview of working with dates and times in R. It discusses recognizing date-time objects in R, getting the current date and time, and creating date-time objects using the POSIXct and POSIXlt classes. Methods for converting character and numeric data to date-time objects are presented, along with extracting parts of date-time objects and performing computations. The goal is to introduce the reader to key date and time functionality in base R.Java 8 Date and Time API
Java 8 Date and Time APISualeh Fatehi
Ěý
This document summarizes Sualeh Fatehi's presentation on the Java 8 Date and Time API. It discusses problems with previous date and time APIs in Java, introduces concepts like epochs, calendar systems, time zones, and ISO-8601. It provides examples of using the new API classes like LocalDate, LocalTime, Instant, and Duration. Design principles of the new API emphasize clarity, immutability, and rejecting invalid values. The API separates machine and human views of time and supports internationalization.Joda-Time & JSR 310 – Problems, Concepts and Approaches
Joda-Time & JSR 310 – Problems, Concepts and ApproachesJustin Lin
Ěý
The document discusses issues related to date and time handling in programming, specifically addressing problems with Joda-Time and JSR-310. It highlights the complexities of date manipulation, the distinctions between human and machine interpretations of time, and introduces key concepts like instant, duration, and chronology. The document also compares Joda-Time with JSR-310 while suggesting that both can simplify date and time management in software development.Brand New Date and Time API
Brand New Date and Time APIKenji HASUNUMA
Ěý
The document discusses the JSR 310 Date and Time API, which provides a new date and time API for Java based on the ISO 8601 standard. It introduces key classes like LocalDate, LocalDateTime, and ZonedDateTime. It describes representations of dates, times, durations, and periods. It also covers conversions between different date/time objects, formatting, and support for different chronologies.Brand new Date and Time API
Brand new Date and Time APIKenji HASUNUMA
Ěý
1. The document discusses the new Date and Time API (JSR 310) for Java, which is based on the ISO 8601 standard.
2. It provides details on date, time, duration, and period representations, conversions between different date/time objects, and examples of using the API.
3. The API includes classes like LocalDate, LocalDateTime, OffsetDateTime, ZonedDateTime, Instant, Duration, and Period to represent dates, times, durations, and periods.Date time
Date timeapeiron
Ěý
The document discusses dates and times, noting that they are not always as simple as having 60 seconds in a minute and 24 hours in a day due to factors like leap seconds and daylight saving time. It recommends using the DateTime module to handle date and time calculations since it accounts for these complexities and exceptions. The DateTime module can construct objects from various inputs, manipulate dates through arithmetic, and output dates in different formats.Php date & time functions
Php date & time functionsProgrammer Blog
Ěý
The document discusses PHP's date and time functions, emphasizing the importance of standard date formats for accurate calculations and comparisons. It details various functions like checkdate(), date(), and time(), explaining their usage and the Unix timestamp system, which tracks time as seconds since January 1, 1970. Additionally, it highlights challenges such as time zone variations and the impending 2038 overflow issue affecting 32-bit timestamps.Time manipulation lecture 2
Time manipulation lecture 2Mudasir Syed
Ěý
This document discusses various PHP functions for manipulating dates and times - getdate(), strtotime(), and date().
Getdate() returns an associative array of date/time values for a given timestamp. Strtotime() parses an English textual datetime into a Unix timestamp. Date() formats a timestamp based on a format string, with different format specifiers for dates, times, years, months, and more. Examples are provided for using these functions.doc
docPlanetExpressATX
Ěý
This document provides information about epoch time and tools for converting between epoch timestamps and human-readable dates. It defines epoch time as the number of seconds since January 1st, 1970 UTC and provides examples of converting epoch timestamps to dates in several programming languages and databases. It also describes how to convert from a date string to an epoch timestamp.jkfdlsajfklafj
jkfdlsajfklafjPlanetExpressATX
Ěý
This document provides information about epoch time and tools for converting between epoch timestamps and human-readable dates. It defines epoch time as the number of seconds since January 1st, 1970 UTC and provides examples of converting epoch timestamps to dates in several programming languages and databases. It also describes how to convert from a date string to an epoch timestamp.Introduction to Date and Time API 3
Introduction to Date and Time API 3Kenji HASUNUMA
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to Java's Date and Time API. It discusses key classes like LocalDate, LocalDateTime, and ZonedDateTime that represent dates, times, and timestamps. It covers common operations like getting/setting fields, conversions between types, formatting/parsing, and comparisons. The document also explores more advanced topics such as clocks, durations, periods, zone IDs, and the internal representations used by the API.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (7)
15 ruby arrays
15 ruby arraysWalker Maidana
Ěý
Ruby arrays are ordered collections that can hold any object type. They are indexed starting at 0, can dynamically grow in size, and provide many built-in methods. Some key characteristics of Ruby arrays include:
1) They are ordered and associate each element with an integer index. Negative indices count backward from the end.
2) Arrays can be created and initialized in several ways such as with Array.new or [].
3) Arrays provide over 70 built-in methods for accessing, modifying, and manipulating array elements like fetch, push, pop, insert, delete, and more.Ruby File I/O
Ruby File I/OSarah Allen
Ěý
The document discusses input/output (IO) and file handling in Ruby. It explains that the IO class is the basis for all input and output, and that the File class allows reading and writing files as it is a subclass of IO. It then provides examples of how to open, read, write, iterate over, and get metadata from files and directories in Ruby.19 ruby iterators
19 ruby iteratorsWalker Maidana
Ěý
This document discusses two Ruby iterators: each and collect. The each iterator returns each element of an array or hash and executes a block of code for each. Collect returns a new array containing the return values of its block for each element or just returns the original collection. Examples demonstrate using each to print array elements and collect to multiply array elements by 10 and return a new array.14 ruby strings
14 ruby stringsWalker Maidana
Ěý
This document provides information about Ruby strings, including:
- Strings can be created using single or double quotes, and support escape characters
- Strings support expression interpolation using #{expression}
- Methods like gsub, slice, and split can be used to manipulate and extract parts of strings
- Built-in string methods allow tasks like changing case, formatting strings, searching/matching substrings
- Strings have methods for operations like concatenation, comparison, indexing, and conversion between other types18 ruby ranges
18 ruby rangesWalker Maidana
Ěý
Ranges in Ruby can represent sequences, conditions, and intervals. Ranges use the ".." and "..." operators to define inclusive and exclusive sequences. Ranges can iterate over their values, test membership, find minimum/maximum values, and reject values. Ranges are also used as conditional expressions to check if a value falls within the start and end points, and in case statements to check different ranges.20 ruby input output
20 ruby input outputWalker Maidana
Ěý
The document discusses Ruby file input/output (I/O) and directory functionality. It covers Ruby classes like IO, File, and Dir that provide methods for reading, writing, opening, closing, renaming, and deleting files. It also discusses creating and navigating directories. Some key file I/O methods include read, write, gets, puts, readline, sysread, and syswrite. Directory methods include chdir, pwd, entries, mkdir, and delete. The document provides examples of using these various Ruby file and directory functions.8 Key Life and Leadership Lessons
8 Key Life and Leadership LessonsStanford Graduate School of Business
Ěý
This document discusses 8 key life and leadership lessons shared in the 2016 Stanford GSB View From The Top guest speaker series. It explores takeaways from leaders who spoke at Stanford about their experiences and advice. The document aims to provide insights for developing leadership skills.Similar to 17 ruby date time (20)
Date and time manipulation
Date and time manipulationShahjahan Samoon
Ěý
The document discusses working with dates and times in Java. It covers the Date class, Calendar class, formatting dates, parsing strings into dates, and performing date/time operations and comparisons. The Date class represents a specific instant in time and provides methods for getting dates, comparing dates, and formatting dates. The Calendar class provides methods for converting between dates and calendar fields like month, day, year, and manipulating calendar fields. Formatting dates can be done using SimpleDateFormat, printf, or other methods.Fun times with ruby
Fun times with rubyGeoff Harcourt
Ěý
This document discusses time and time zones in Ruby and Rails. It explains why time is important and difficult, describes UTC and time zone offsets, and provides best practices for using time in Rails applications, including storing times in UTC and converting to local times for display. It also covers parsing times from users, testing with time, and caching pages that display times.Python time
Python timeJanu Jahnavi
Ěý
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Python's time and date modules, discussing various functions such as time(), gmtime(), localtime(), strptime(), and strftime(). It covers how to convert between epoch time and human-readable formats, as well as the use of directives for date formatting. Additionally, it illustrates practical examples of time manipulation, time comparison, and the use of time.sleep() for thread execution control.Ruby Time & Date
Ruby Time & DateJesus Castello
Ěý
Ruby's Time class allows you to work with dates and times. It can store both a date and time, get the current time, and perform time arithmetic like adding seconds. The strftime method formats times for output and strptime parses dates from strings. Rails adds functionality via ActiveSupport, including methods like 3.days.ago that return TimeWithZone objects. Formatting, parsing, and arithmetic on Time objects lets you easily manage dates and times in Ruby.SessionSeven_WorkingWithDatesandTime
SessionSeven_WorkingWithDatesandTimeHellen Gakuruh
Ěý
This document provides an overview of working with dates and times in R. It discusses recognizing date-time objects in R, getting the current date and time, and creating date-time objects using the POSIXct and POSIXlt classes. Methods for converting character and numeric data to date-time objects are presented, along with extracting parts of date-time objects and performing computations. The goal is to introduce the reader to key date and time functionality in base R.Java 8 Date and Time API
Java 8 Date and Time APISualeh Fatehi
Ěý
This document summarizes Sualeh Fatehi's presentation on the Java 8 Date and Time API. It discusses problems with previous date and time APIs in Java, introduces concepts like epochs, calendar systems, time zones, and ISO-8601. It provides examples of using the new API classes like LocalDate, LocalTime, Instant, and Duration. Design principles of the new API emphasize clarity, immutability, and rejecting invalid values. The API separates machine and human views of time and supports internationalization.Joda-Time & JSR 310 – Problems, Concepts and Approaches
Joda-Time & JSR 310 – Problems, Concepts and ApproachesJustin Lin
Ěý
The document discusses issues related to date and time handling in programming, specifically addressing problems with Joda-Time and JSR-310. It highlights the complexities of date manipulation, the distinctions between human and machine interpretations of time, and introduces key concepts like instant, duration, and chronology. The document also compares Joda-Time with JSR-310 while suggesting that both can simplify date and time management in software development.Brand New Date and Time API
Brand New Date and Time APIKenji HASUNUMA
Ěý
The document discusses the JSR 310 Date and Time API, which provides a new date and time API for Java based on the ISO 8601 standard. It introduces key classes like LocalDate, LocalDateTime, and ZonedDateTime. It describes representations of dates, times, durations, and periods. It also covers conversions between different date/time objects, formatting, and support for different chronologies.Brand new Date and Time API
Brand new Date and Time APIKenji HASUNUMA
Ěý
1. The document discusses the new Date and Time API (JSR 310) for Java, which is based on the ISO 8601 standard.
2. It provides details on date, time, duration, and period representations, conversions between different date/time objects, and examples of using the API.
3. The API includes classes like LocalDate, LocalDateTime, OffsetDateTime, ZonedDateTime, Instant, Duration, and Period to represent dates, times, durations, and periods.Date time
Date timeapeiron
Ěý
The document discusses dates and times, noting that they are not always as simple as having 60 seconds in a minute and 24 hours in a day due to factors like leap seconds and daylight saving time. It recommends using the DateTime module to handle date and time calculations since it accounts for these complexities and exceptions. The DateTime module can construct objects from various inputs, manipulate dates through arithmetic, and output dates in different formats.Php date & time functions
Php date & time functionsProgrammer Blog
Ěý
The document discusses PHP's date and time functions, emphasizing the importance of standard date formats for accurate calculations and comparisons. It details various functions like checkdate(), date(), and time(), explaining their usage and the Unix timestamp system, which tracks time as seconds since January 1, 1970. Additionally, it highlights challenges such as time zone variations and the impending 2038 overflow issue affecting 32-bit timestamps.Time manipulation lecture 2
Time manipulation lecture 2Mudasir Syed
Ěý
This document discusses various PHP functions for manipulating dates and times - getdate(), strtotime(), and date().
Getdate() returns an associative array of date/time values for a given timestamp. Strtotime() parses an English textual datetime into a Unix timestamp. Date() formats a timestamp based on a format string, with different format specifiers for dates, times, years, months, and more. Examples are provided for using these functions.doc
docPlanetExpressATX
Ěý
This document provides information about epoch time and tools for converting between epoch timestamps and human-readable dates. It defines epoch time as the number of seconds since January 1st, 1970 UTC and provides examples of converting epoch timestamps to dates in several programming languages and databases. It also describes how to convert from a date string to an epoch timestamp.jkfdlsajfklafj
jkfdlsajfklafjPlanetExpressATX
Ěý
This document provides information about epoch time and tools for converting between epoch timestamps and human-readable dates. It defines epoch time as the number of seconds since January 1st, 1970 UTC and provides examples of converting epoch timestamps to dates in several programming languages and databases. It also describes how to convert from a date string to an epoch timestamp.Introduction to Date and Time API 3
Introduction to Date and Time API 3Kenji HASUNUMA
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to Java's Date and Time API. It discusses key classes like LocalDate, LocalDateTime, and ZonedDateTime that represent dates, times, and timestamps. It covers common operations like getting/setting fields, conversions between types, formatting/parsing, and comparisons. The document also explores more advanced topics such as clocks, durations, periods, zone IDs, and the internal representations used by the API.Time manipulation lecture 1
Time manipulation lecture 1 Mudasir Syed
Ěý
This document discusses various concepts related to time manipulation in PHP, including timestamps, date functions, and time functions. It provides definitions and examples of timestamps, Unix timestamps, UTC, GMT, epochs, and functions like mktime(), date(), and time(). It explains how timestamps work as the number of seconds since January 1, 1970 UTC and how functions like mktime() and date() can be used to generate and format timestamps to work with dates and times. It also discusses potential issues with Unix timestamps and the year 2038 problem. Assignments involving tracking time on pages and displaying text up to a selected time are provided at the end.Formattime
Formattimeyclimyingching
Ěý
FORMATTIME converts a serialized date into a formatted string by expanding various date and time tokens in the provided text. The tokens include elements like $second, $minute, $hour, $day, $month, $year, and $weekday to represent different components of the date. It also includes tokens like $isoweek that represent ISO 8601 week numbers, which can be formatted in multiple ways like $isoweek($year) or $isoweek($year-W$wk).Data i czas dla programistĂłw
Data i czas dla programistĂłwThe Software House
Ěý
The document provides an overview of various date and time concepts relevant for programmers, including formats like ISO 8601, Unix timestamps, and leap seconds. It emphasizes the importance of proper date handling and distinguishes between different time zones and daylight saving time variations. Additionally, it offers practical advice on measuring elapsed time in programming and suggests using monotonic clocks for accurate time measurement.Java 8 date & time api
Java 8 date & time apiRasheed Waraich
Ěý
The document summarizes the new Java 8 Date & Time API. It discusses problems with the old Date and Calendar classes, including inconsistent behavior and lack of thread safety. It then overviews the new API, which was influenced by Joda-Time and aims to distinguish machine and human views of time. Key aspects covered include Instant, LocalDate, Duration, and formatting/parsing utilities. The new API provides a more clear and consistent model for working with dates and times in Java.Dates and Times
Dates and TimesMichael Parker
Ěý
The document discusses various standards and concepts related to timekeeping, including solar time, mean solar days, Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), time zones, leap seconds, Unix time, and Network Time Protocol (NTP). It explains how UTC approximates solar time, how time zones define offsets from UTC, and how leap seconds are inserted to keep UTC synchronized with solar time.Ad
More from Walker Maidana (16)
13 ruby modules
13 ruby modulesWalker Maidana
Ěý
Ruby modules allow grouping of related methods and constants in a namespace to avoid naming collisions. Modules can be included in classes using the 'include' statement, providing a way for classes to inherit functionality from multiple modules, implementing a form of multiple inheritance known as a mixin. Modules define a namespace and methods are called using the module name and a period. The 'require' statement loads module files so their contents can be used.12 ruby blocks
12 ruby blocksWalker Maidana
Ěý
Ruby allows defining reusable blocks of code that can be invoked from methods using the yield statement. A block consists of code enclosed in curly braces and is associated with a method of the same name. The yield statement passes control to the block and can optionally pass parameters to the block. Ruby files can also define BEGIN and END blocks to specify code to run as the file loads and after program execution completes, respectively.11 ruby methods
11 ruby methodsWalker Maidana
Ěý
Ruby methods are used to bundle repeatable statements into a single unit. Method names should begin with a lowercase letter. Methods should be defined before calling them. Methods can accept parameters with default values. Variables can be returned from methods. The return statement is used to return values explicitly. Methods can take a variable number of parameters using *. Class methods can be accessed without instantiating an object. The alias statement creates an alias for a method or variable. The undef statement cancels a method definition.10 ruby loops
10 ruby loopsWalker Maidana
Ěý
The document discusses various loop constructs in Ruby including while, until, for, break, next, redo, and retry. The while and until loops execute code repeatedly as long as or until a conditional is true. The for loop iterates over each element in an expression. break exits the current loop, next skips to the next iteration, redo restarts the current iteration, and retry restarts the entire loop from the beginning.09 ruby if else
09 ruby if elseWalker Maidana
Ěý
The document discusses different conditional statements in Ruby including if/else, unless, case. The if/else statement executes code based on whether a conditional is true or false. Unless executes code if the conditional is false. Case compares an expression to expressions in when clauses using === and executes matching code. Examples are provided for each statement.08 ruby comments
08 ruby commentsWalker Maidana
Ěý
Ruby supports single-line comments starting with # and multiline comments using =begin and =end. Single-line comments extend from # to the end of the line. Multiline comments can span multiple lines between =begin and =end tags. Trailing comments should be aligned and separated from code for clarity.07 ruby operators
07 ruby operatorsWalker Maidana
Ěý
The document summarizes Ruby operators including arithmetic, comparison, assignment, logical, bitwise, range, ternary and defined? operators. It provides examples of common operators like addition, subtraction, logical AND, assignment, range inclusion and method definition checking. Operators in Ruby are generally method calls that allow succinct operation on operands.06 ruby variables
06 ruby variablesWalker Maidana
Ěý
The document discusses the different types of variables in Ruby including global variables, instance variables, class variables, local variables, constants, pseudo-variables, and literals. It provides examples of how to declare and use each variable type in Ruby code. It also covers the basic data types like integers, floats, strings, arrays, hashes, and ranges that can be used as literals in Ruby.05 ruby classes
05 ruby classesWalker Maidana
Ěý
The document discusses Ruby classes and objects. It defines a class as a blueprint from which individual objects are created. A class contains data members like attributes and functions/methods. Objects are instances of a class and are created using the new method. The document provides examples of defining a Vehicle class with attributes like wheels, horsepower etc. and methods like speeding, driving. It also discusses creating Customer objects, initializing them using an initialize method, and calling their methods.04 ruby syntax
04 ruby syntaxWalker Maidana
Ěý
The document discusses Ruby syntax including: writing a simple Ruby program with the .rb extension; whitespace and line endings in Ruby programs; Ruby identifiers, reserved words, and comments; here documents for multi-line strings; and the BEGIN and END statements for code execution before and after the main program. Key points are that whitespace is generally ignored, semicolons and newlines end statements, identifiers are case sensitive, reserved words can't be used as names, here documents use line terminators to build strings, and BEGIN and END blocks allow code execution at the start and end of a Ruby program.03 ruby environment
03 ruby environmentWalker Maidana
Ěý
This document provides an overview of setting up a Ruby development environment. It discusses installing Ruby on Unix and Windows systems, common command line options, important environment variables, popular Ruby editors like VIM and RubyWin, and how to use the Interactive Ruby shell (IRb) for testing code. The next step outlined is writing initial Ruby programs after confirming a working environment is established.01 index
01 indexWalker Maidana
Ěý
This document provides an overview and introduction to the Ruby programming language. Ruby is a scripting language designed by Yukihiro Matsumoto that can run on Windows, Mac OS, and UNIX systems. The tutorial is intended for beginners and assumes some basic knowledge of computer programming but no experience with Ruby is required. It provides links to additional reference materials on Ruby including quick references, lists of useful functions and tools, resources for learning Ruby, and tutorials for Ruby on Rails web development.00 ruby tutorial
00 ruby tutorialWalker Maidana
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the Ruby programming language. It discusses that Ruby is an object-oriented scripting language created by Yukihiro Matsumoto, and can run on various platforms like Windows, Mac OS, and UNIX. It also summarizes key Ruby concepts like Interactive Ruby Shell (IRb), syntax, data types, variables, and predefined variables.02 ruby overview
02 ruby overviewWalker Maidana
Ěý
Ruby is a pure object-oriented programming language created in 1993 by Yukihiro Matsumoto. It has features similar to Smalltalk, Perl, and Python. Ruby is freely available, open-source, and easy to learn. It can be used to create web applications, CGI scripts, and programs that connect to databases. The next chapter will cover obtaining, installing, and setting up Ruby.21 ruby exceptions
21 ruby exceptionsWalker Maidana
Ěý
Ruby provides mechanisms like begin/rescue/ensure to handle exceptions gracefully. The begin block contains code that could raise exceptions, rescue clauses specify the types of exceptions to handle, and ensure ensures some code is always executed. Exceptions can be raised manually using raise and caught using catch/throw. Common exception classes include StandardError, while custom exceptions should inherit from Exception.Tutorial ruby eustaquio taq rangelWalker Maidana
Ěý
1. O documento é um tutorial de Ruby que ensina sobre a linguagem, incluindo como instalá-la, tipos básicos, estruturas de controle e iteradores.
2. É dividido em seções como instalação, tipos básicos, expressões regulares, arrays, hashes, tratamento de exceções e iteradores.
3. O tutorial é licenciado sob Creative Commons permitindo compartilhamento e modificações desde que creditado e não usado comercialmente.Ad
17 ruby date time
- 1. DATE AND TIME IN RUBY http://www.tutorialspoint.com/ruby/ruby_date_time.htm Copyright © tutorialspoint.com The Time class represents dates and times in Ruby. It is a thin layer over the system date and time functionality provided by the operating system. This class may be unable on your system to represent dates before 1970 or after 2038. This tutorial will make you familiar with all the most wanted concepts of date and time. Getting Current Date and Time: Following is the simple example to get current date and time: #!/usr/bin/ruby -w time1 = Time.new puts "Current Time : " + time1.inspect # Time.now is a synonym: time2 = Time.now puts "Current Time : " + time2.inspect This will produce following result: Current Time : Mon Jun 02 12:02:39 -0700 2008 Current Time : Mon Jun 02 12:02:39 -0700 2008 Getting components of a Date & Time: We can use Time object to get various components of date and time. Following is the example showing the same: #!/usr/bin/ruby -w time = Time.new # Components of a Time puts "Current Time : " + time.inspect puts time.year # => Year of the date puts time.month # => Month of the date (1 to 12) puts time.day # => Day of the date (1 to 31 ) puts time.wday # => 0: Day of week: 0 is Sunday puts time.yday # => 365: Day of year puts time.hour # => 23: 24-hour clock puts time.min # => 59 puts time.sec # => 59 puts time.usec # => 999999: microseconds puts time.zone # => "UTC": timezone name This will produce following result: Current Time : Mon Jun 02 12:03:08 -0700 2008 2008 6 2 1 154 12 3 8 247476 UTC
- 2. Time.utc, Time.gm and Time.local Functions: These two functions can be used to format date in standard format as follows: # July 8, 2008 Time.local(2008, 7, 8) # July 8, 2008, 09:10am, local time Time.local(2008, 7, 8, 9, 10) # July 8, 2008, 09:10 UTC Time.utc(2008, 7, 8, 9, 10) # July 8, 2008, 09:10:11 GMT (same as UTC) Time.gm(2008, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11) Following is the example to get all components in an array in the following format: [sec,min,hour,day,month,year,wday,yday,isdst,zone] Try the following: #!/usr/bin/ruby -w time = Time.new values = time.to_a p values This will generate following result: [26, 10, 12, 2, 6, 2008, 1, 154, false, "MST"] This array could be passed to Time.utc or Time.local functions to get different format of dates as follows: #!/usr/bin/ruby -w time = Time.new values = time.to_a puts Time.utc(*values) This will generate following result: Mon Jun 02 12:15:36 UTC 2008 Followin is the way to get time represented internally as seconds since the (platform-dependent) epoch: # Returns number of seconds since epoch time = Time.now.to_i # Convert number of seconds into Time object. Time.at(time) # Returns second since epoch which includes microseconds time = Time.now.to_f Timezones and daylight savings time: You can use a Time object to get all the information related to Timezones and daylight savings as follows: time = Time.new # Here is the interpretation
- 3. time.zone # => "UTC": return the timezone time.utc_offset # => 0: UTC is 0 seconds offset from UTC time.zone # => "PST" (or whatever your timezone is) time.isdst # => false: If UTC does not have DST. time.utc? # => true: if t is in UTC time zone time.localtime # Convert to local timezone. time.gmtime # Convert back to UTC. time.getlocal # Return a new Time object in local zone time.getutc # Return a new Time object in UTC Formatting Times and Dates: There are various ways to format date and time. Here is one example showing few: #!/usr/bin/ruby -w time = Time.new puts time.to_s puts time.ctime puts time.localtime puts time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") This will produce following result: Mon Jun 02 12:35:19 -0700 2008 Mon Jun 2 12:35:19 2008 Mon Jun 02 12:35:19 -0700 2008 2008-06-02 12:35:19 Time Formatting Directives: These directives in the following table are used with the method Time.strftime. Directive Description %a The abbreviated weekday name (Sun). %A The full weekday name (Sunday). %b The abbreviated month name (Jan). %B The full month name (January). %c The preferred local date and time representation. %d Day of the month (01 to 31). %H Hour of the day, 24-hour clock (00 to 23). %I Hour of the day, 12-hour clock (01 to 12). %j Day of the year (001 to 366). %m Month of the year (01 to 12). %M Minute of the hour (00 to 59). %p Meridian indicator (AM or PM). %S Second of the minute (00 to 60).
- 4. %U Week number of the current year, starting with the first Sunday as the first day of the first week (00 to 53). %W Week number of the current year, starting with the first Monday as the first day of the first week (00 to 53). %w Day of the week (Sunday is 0, 0 to 6). %x Preferred representation for the date alone, no time. %X Preferred representation for the time alone, no date. %y Year without a century (00 to 99). %Y Year with century. %Z Time zone name. %% Literal % character. Time arithmetic: You can do simple arithmetic with time as follows: now = Time.now # Current time past = now - 10 # 10 seconds ago. Time - number => Time future = now + 10 # 10 seconds from now Time + number => Time future - now # => 10 Time - Time => number of seconds
