190620-Composite Structures - Introduction (By SNB).pptx
- 1. Composite Structures - Introduction BY, SHASHANK N BABU
- 2. What are Composite Structures? ŌĆó General ŌĆō Any members composed of more than one material. ŌĆó Combination of Steel ŌĆō Concrete. Why? Steel is efficient in tension while concrete is efficient in compression. Uses? Buildings, Bridges
- 3. Major Types ŌĆó COMPOSITE BEAMS - SIMPLY SUPPORTED ŌĆó COMPOSITE BEAMS - CONTINUOUS ŌĆó COMPOSITE COLUMNS ŌĆó COMPOSITE SLABS ŌĆó COMPOSITE JOINTS
- 4. Codes Associated with Design ŌĆó IS 11384 ŌĆō 1985 ŌĆō Code of Practice for Composite Construction in Structural Steel and Concrete. ŌĆó This standard deals with the design and construction of Composite beams ( simply supported ) made up of structural steel units and cast in-situ concrete. ŌĆó Eurocode 4: Design of composite steel and concrete structures (2004) ŌĆó EN 1994-1-1 : General rules and rules for buildings ŌĆó EN 1994-1-2 : Structural fire design ŌĆó EN 1994-2 : General rules and rules for bridges
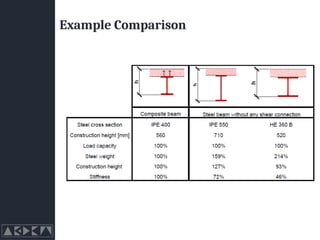
- 5. Advantages ŌĆó Architectural ŌĆó In addition to reductions in the dimensions of the beams ŌĆó longer spans ŌĆó thinner slabs ŌĆó Economical ŌĆó Reduction of height reduces the total height of the building ŌĆó Functionality ŌĆó Big Bonus is Fire Safety, Modern steel and composite structures can provide fire resistance by using principles of reinforced concrete structures in which the concrete protects the steel because of its high mass and relatively low thermal conductivity. (IS Codes do not cover this at all)
- 7. Examples in Real Life Millennium Tower (Vienna - Austria) Citibank Duisburg, Germany
- 8. Examples in Real Life Grand Palladium, Mumbai Eicher Corporate Office, Gurgaon
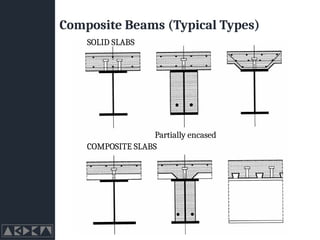
- 10. Composite Beams (Typical Types) Partially encased SOLID SLABS COMPOSITE SLABS
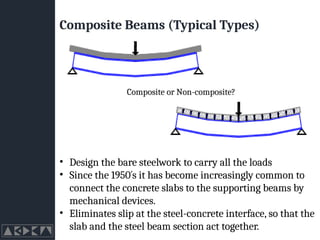
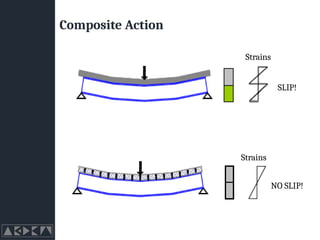
- 11. Composite Beams (Typical Types) Composite or Non-composite? ŌĆó Design the bare steelwork to carry all the loads ŌĆó Since the 1950┬┤s it has become increasingly common to connect the concrete slabs to the supporting beams by mechanical devices. ŌĆó Eliminates slip at the steel-concrete interface, so that the slab and the steel beam section act together.
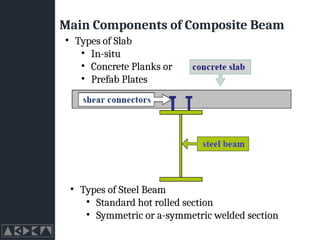
- 12. Main Components of Composite Beam ŌĆó Types of Steel Beam ŌĆó Standard hot rolled section ŌĆó Symmetric or a-symmetric welded section ŌĆó Types of Slab ŌĆó In-situ ŌĆó Concrete Planks or ŌĆó Prefab Plates
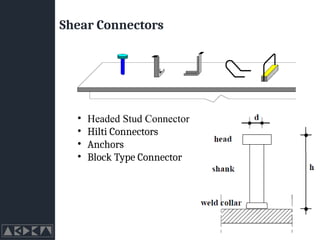
- 14. Shear Connectors
- 15. Shear Connectors ŌĆó Headed Stud Connector ŌĆó Hilti Connectors ŌĆó Anchors ŌĆó Block Type Connector
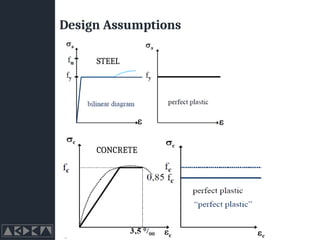
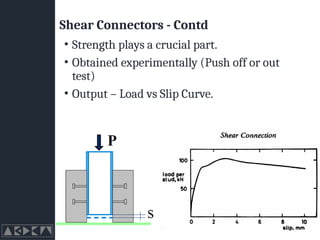
- 18. Shear Connectors - Contd ŌĆó Strength plays a crucial part. ŌĆó Obtained experimentally (Push off or out test) ŌĆó Output ŌĆō Load vs Slip Curve.
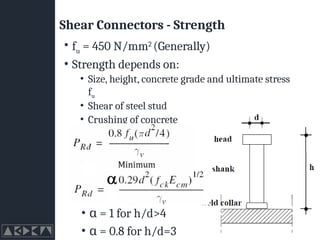
- 19. Shear Connectors - Strength ŌĆó fu = 450 N/mm2 (Generally) ŌĆó Strength depends on: ŌĆó Size, height, concrete grade and ultimate stress fu ŌĆó Shear of steel stud ŌĆó Crushing of concrete ŌĆó ╬▒ = 1 for h/d>4 ŌĆó ╬▒ = 0.8 for h/d=3
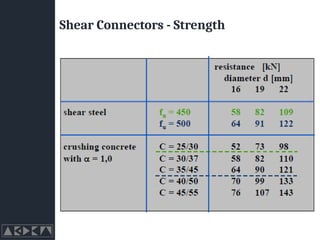
- 20. Shear Connectors - Strength
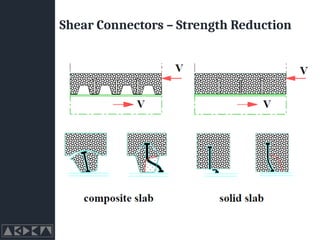
- 21. Shear Connectors ŌĆō Strength Reduction
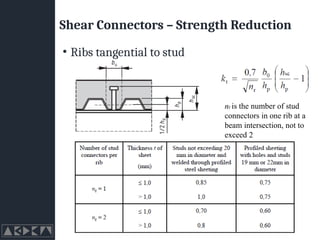
- 22. Shear Connectors ŌĆō Strength Reduction ŌĆó Ribs tangential to stud nr is the number of stud connectors in one rib at a beam intersection, not to exceed 2
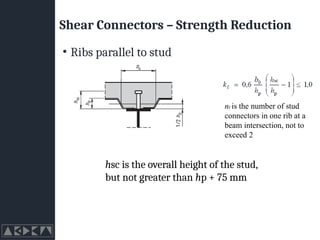
- 23. Shear Connectors ŌĆō Strength Reduction ŌĆó Ribs parallel to stud nr is the number of stud connectors in one rib at a beam intersection, not to exceed 2 hsc is the overall height of the stud, but not greater than hp + 75 mm
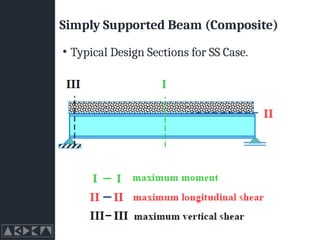
- 24. Simply Supported Beam (Composite) ŌĆó Typical Design Sections for SS Case.
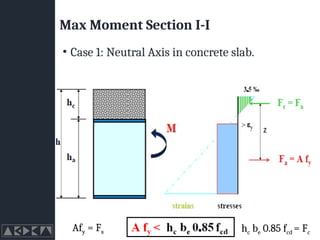
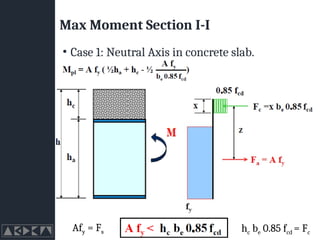
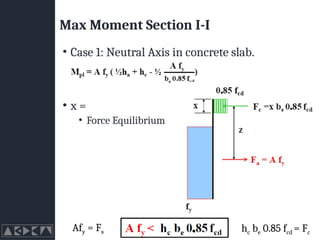
- 25. Max Moment Section I-I ŌĆó Case 1: Neutral Axis in concrete slab. hc be 0.85 fcd = Fc Afy = Fs
- 26. Max Moment Section I-I ŌĆó Case 1: Neutral Axis in concrete slab. hc be 0.85 fcd = Fc Afy = Fs
- 27. Max Moment Section I-I ŌĆó Case 1: Neutral Axis in concrete slab. ŌĆó x = ŌĆó Force Equilibrium hc be 0.85 fcd = Fc Afy = Fs
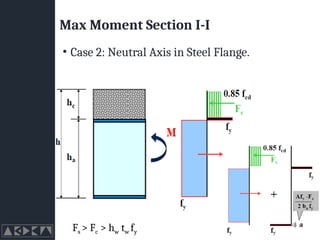
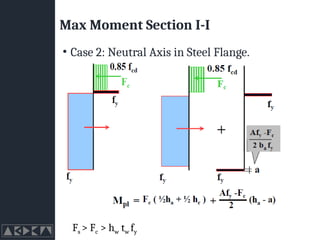
- 28. Max Moment Section I-I ŌĆó Case 2: Neutral Axis in Steel Flange. Fs > Fc > hw tw fy
- 29. Max Moment Section I-I ŌĆó Case 2: Neutral Axis in Steel Flange. Fs > Fc > hw tw fy
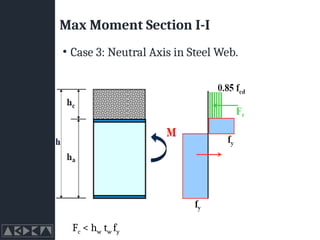
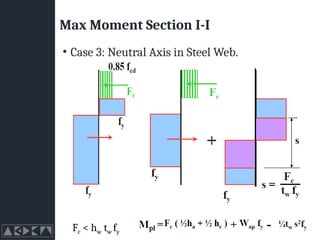
- 30. Max Moment Section I-I ŌĆó Case 3: Neutral Axis in Steel Web. Fc < hw tw fy
- 31. Max Moment Section I-I ŌĆó Case 3: Neutral Axis in Steel Web. Fc < hw tw fy
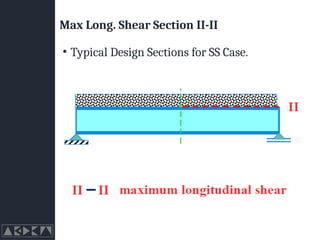
- 32. Max Long. Shear Section II-II ŌĆó Typical Design Sections for SS Case.
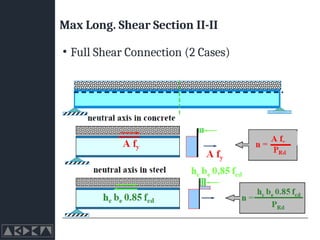
- 33. Max Long. Shear Section II-II ŌĆó Full Shear Connection (2 Cases)
- 34. Next Part ŌĆó Partial Shear Connection ŌĆó Maximum Vertical Shear Design ŌĆó Deflection