1.pdf
- 1. INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING Dr. Ali Hussein Muqaibel ver 2.4 DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 1
- 2. OUTLINES ï§ What Does Communication (or Telecommunication) Mean? ï§ Importance of Communications (by electrical signals) ï§ So What will We Study in This Course? ï§ Examples of Todayâs Communication Methods ï§ Simplex vs. Duplex Communications DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 2
- 3. WHAT DOES COMMUNICATIONS (OR TELECOMMUNICATIONS) MEAN? The transfer of some form of information from one place (known as the source of information) to another place (known as the destination of information) using some system to do this function (known as a communication system). What is the difference between communication and communications? DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 3
- 4. Teleconferencing, teleshopping, telebanking, internet, computer networks, mobile,...etc Examples of Todayâs Communication Methods All of the following are electric (or electromagnetic) communication systems ï§ Satellite (Telephone, TV, Radio, Internet, âĶ ) ï§ Microwave (Telephone, TV, Data, âĶ) ï§ Optical Fibers (TV, Internet, Telephone, âĶ ) ï§ Copper Cables (telephone lines, coaxial cables, twisted pairs, âĶ etc) DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 4 IMPORTANCE OF COMMUNICATIONS (BY ELECTRICAL SIGNALS) coaxial twisted pairs Optical Fibers
- 5. WHAT WILL WE STUDY IN THIS COURSE? The basic methods that are used for communication in todayâs world and the different systems that implement these communication methods. Upon the successful completion of this course, you should be able to: 1) identify the different communication techniques 2) know the advantages and disadvantages of each technique, 3) show the basic construction of the systems that implement these communication techniques. (Check the syllabus for course description, outcomes and objectives) DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 5
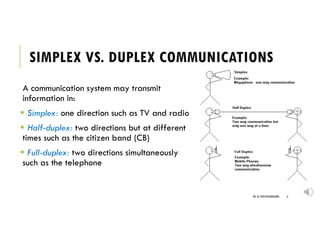
- 6. SIMPLEX VS. DUPLEX COMMUNICATIONS A communication system may transmit information in: ï§ Simplex: one direction such as TV and radio ï§ Half-duplex: two directions but at different times such as the citizen band (CB) ï§ Full-duplex: two directions simultaneously such as the telephone DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 6