2 bsn innv&entre
- 1. 1. Introduction The banking sector comprises licensed institutions namely commercial banks, finance companies, merchant banks, discount houses and money brokers which bare licensed under the Banking and Financial Institutions Act 1989 (BAFIA) and supervised by BNM. (Chapter 3: Banking Sector-Bank Negara Malaysia, 2001-2010) 1.1 History of Banking Industries in Malaysia The first commercial bank to established in the country was a branch of a British exchange bank called The Chartered Merchantile Bank of India, London and China (Later renamed as the Merchantile bank) in Penang in 1859. This was followed by the Chartered bank establishing a branch in Penang in 1875. (Amended Chapter 1 Financial System and Principles of Credit April 2005 updates) The led to the development of financial Institutions is to overcome all the disadvantages of direct lending and borrowing, the need of intermediaries to do such transaction such as deposit the surplus unit of monies and deficit unit to borrow monies. In Kuala Lumpur, the Capital of Malaysia Kwong Yik (Selangor) Banking Corporation was the first incorporated here in July 1913. On January 1959, Bank Negara Malaysia is led from the establishment of the Central Bank of Malaya Ordinance and by June 1967 the currency issuing authority was handed to Bank Negara Malaysia. 1.1.1 General Overview of Banking Industries in Malaysia Referring to the Certified Credit Professional study materials, the banking system in Malaysia comprises the Central Bank, which is Bank Negara Malaysia, commercial banks including banking and finance companies and other financial institutions such as discount houses, merchant banks, the representative offices of foreign banks and the offshore banks in the International Offshore Financial Centre of Labuan. (Amended Chapter 1 Financial System and Principles of Credit April 2005 updates) 1
- 2. According to the material also, the regulatory framework in which banks and financial institutions in Malaysia operate is primarily governed by the Banking and Financial Institutions Act 1989 (BAFIA) and the regulation made thereunder. The BAFIA is intended, inter-alia, to preserve the soundness and stability of the banking and financial system in the country. (Amended Chapter 1 Financial System and Principles of Credit April 2005 updates) In relation to the regulatory BAFIA is a body of enforcement to the Finance Companies Act 1969 and the Banking Act 1973 arose largely due to inadequacies in the law to prevent cooperative and others, except banks, from taking deposit from the public, (Amended Chapter 1 Financial System and Principles of Credit April 2005 updates) As at end-2000, there were 31 commercial banks (of which 14 are fully foreign-owned), 19 finance companies, 12 merchant banks and 7 discount houses. Upon completion of the merger programme among domestic banking institutions, the number of domestic banking institutions will be significantly reduced to 10 domestic banking groups consisting of 10 commercial banks, 10 finance companies and 9 merchant banks. (Chapter 3: Banking SectorBank Negara Malaysia, The Financial Sector Masterplan, 2001-2010) 2
- 3. 2. 3
- 4. 3. Findings: Innovation According to Davis (2008), Innovation happens under certain conditions and does not happen under other cultural conditions. The conditions can be described and they can be replicated. Organizational leaders create the culture of innovation by their, systems, policies and actions. They are responsible for creating or destroying innovation in organizations. Drucker (1985), Entrepreneurs need to search purposefully for the sources of innovation, the changes and their symptoms that indicate opportunities for successful innovation. And they need to know and to apply the principles of successful innovation. 3.1 Theory of Innovation Drucker (2006), Innovation is the specific instrument of entrepreneurship. The act that endows resources with a new capacity to create wealth. Innovation, indeed, creates a resource. There is no such thing as a “resource” until man finds a use for something in nature and thus endows it with economic value (Innovation and Entrepreneurship, HarperBusiness; Reprint Edition May 9, 2006) In relation to the banking innovation the World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 4262 has stated, Innovation is changing the structure and enhancing the capabilities of organizations. Moreover, institutional innovations are sharpening market incentives for entrepreneurial activity and technology trading which take new ideas, products and practices into the commercial domain. (Yusuf 2007, P.1) 3.1.1 Concept of Innovation In relation to the concept of innovation Geroski (1995) has defined, innovation counts are at least direct (if imperfect) measures of innovative output, and, since it is the consequences (and not the causes) of innovation which are of interest here, they are the natural measures to 4
- 5. focus on. Patents are less clearly identifiable as a measure of innovative output, not least because they seem to be highly correlated with input measures like R&D and are typically taken out well before the knowledge which they describe is embodied in a particular product or process. (Geroski 1995, p.8) Thomas L.Wheelen & J. David Hunger (2012), On the other hand, environmental uncertainty is an opportunity because it creates a new playing field in which creativity and innovation can play a major part in strategic decisions. (Strategic Management And Business Policy 13th Edition 2012, P.98) Innovation consists of two different type of innovation to focus on. One, Ireland, R. D., Covin, J. G. and Kuratko, D. F. (2009) has define, Radical innovation is the launching of inaugural breakthroughs such as personal computer, Post-it® notes, disposable diapers, and overnight mail deliver. These innovations take experimentation and determined vision, which are not necessarily managed but must be recognized and nurtured. On the other hand Incremental innovation refers to the systematic evolution of a product or service into newer or larger markets….the incremental innovation will take over after a radical innovation introduces breakthrough. The structure, marketing, financing, and formal system of a corporation can help implement incremental innovation. (Ireland, R. D., Covin, J. G. and Kuratko, D. F. (2009), Conceptualizing Corporate Entrepreneurship Strategy. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice) 3.1.1.1 Innovation in Distribution Channels As in the industrial system in general, there are two basic driving forces behind the appearance of innovations in distribution channels, namely competition and "entrepreneurial spirit". In order to sustain their viability and competitiveness, and/or because they see entrepreneurial opportunities, firms experiment with new ways of doing business. (Nyberg 1998, p.74) 5
- 6. 3.1.1.2 Innovation in Technology Rapidly emerging innovations will deliver the possibility of smart phones able to use product bar codes to access product-related information and phones able to act as ewallets, as either a prepaid card for small purchases or a fully functioning credit debit card unit. (Hollensen 2012, p.401) Scientists today are working on a startling range of new technologies that will revolutionize products and production processes. with superior ease-of-use, seamless integration, and innovative industrial design. (Kotler 2002, P.150) 3.1.2 Innovation as the Bottom Line Denning (2012), innovation become an integral part of 100% of what the company does, not just 20%. As a result, experimentation is harnessed for the commercial purposes of the firm. Companies with this mental model have shown a consistent ability to innovate and to disrupt their own businesses with innovation. (http://www.forbes.com/sites/stevedenning/2012/02/14/whats-your-mental-model-ofinnovation/) 3.1.2.1 Innovation Adoption Model Belch and Belch (2003), The innovation adoption model evolved from work on the diffusion of innovations. This model represents the stages a consumer passes through in adopting a new product or service. Like the other models, it says potential adopters must be moved through a series of steps before taking some action (in this case, deciding to adopt a new product). 3.1.2.2 Challenges to Innovation Model Belch and Belch (2003), The steps preceding adoption are awareness, interest, evaluation, and trial. The challenge facing companies introducing new products is to create awareness 6
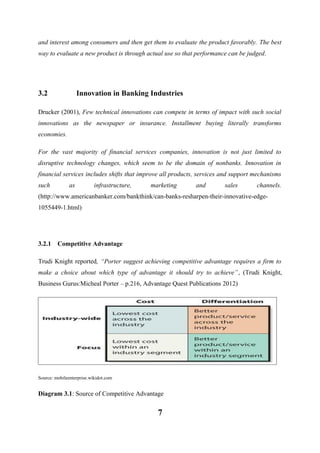
- 7. and interest among consumers and then get them to evaluate the product favorably. The best way to evaluate a new product is through actual use so that performance can be judged. 3.2 Innovation in Banking Industries Drucker (2001), Few technical innovations can compete in terms of impact with such social innovations as the newspaper or insurance. Installment buying literally transforms economies. For the vast majority of financial services companies, innovation is not just limited to disruptive technology changes, which seem to be the domain of nonbanks. Innovation in financial services includes shifts that improve all products, services and support mechanisms such as infrastructure, marketing and sales channels. (http://www.americanbanker.com/bankthink/can-banks-resharpen-their-innovative-edge1055449-1.html) 3.2.1 Competitive Advantage Trudi Knight reported, “Porter suggest achieving competitive advantage requires a firm to make a choice about which type of advantage it should try to achieve”, (Trudi Knight, Business Gurus:Micheal Porter – p.216, Advantage Quest Publications 2012) Source: mobileenterprise.wikidot.com Diagram 3.1: Source of Competitive Advantage 7
- 8. 3.2.1.1 Differentiation Advantage In relation to Competitive Advantage, Differentiation is aimed at the broad mass market and involves the creation of a product or service that is perceived throughout its industry as unique. The company or business unit may then charge a premium for its product. This specialty can be associated with design or brand image, technology, features, a dealer network, or customer service. (Wheelen & Hunger, Strategic Management and Business Policy – p.186, 13th edition 2012) 3.3 Impact of Innovation towards Competitive Advantage Journal of technology management & innovation has reported, Innovate is recognized today as one of the main aspects leading to a competitive advantage amongst firms. A regional context that supports innovation and entrepreneurial initiative encourages competitiveness. (http://www.scielo.cl/) According to the journal also, Innovation reflects the tendency of a firm to lend its support to new ideas, novelty, experimentation and the creative processes that may result in new products, services or technological processes (Lumpkin and Dess 1996; cited by Marques and Ferreira) 8
- 9. 4. Recommendation Hippel (1988), Many functional relationships can exist between innovator and innovation in addition to user, supplier, and manufacturer. For example, firms and individuals can benefit from innovations as innovation distributors, insurers, and so forth. (The Source of Innovation, New York Oxford Oxford University Press, 1988) There are many way to stay relevant the market by continuously reviving the passion to innovate. In view of the current findings it is important to focus on certain factors which critically contribute towards the success of implementation the competitive advantage. However, the Bank Simpanan Nasional (BSN) is recommended to look on factors which will be explained in this section. Hippel (1988) has reported, universal belief that large businesses do not and cannot innovate is not even a half-truth; rather, it is a misunderstanding. In the first place, there are plenty of exceptions, plenty of large companies that have done well as entrepreneurs and innovators...Citibank, America’s and the world’s largest nongovernmental financial institution, well over a century old, has been a major innovator in many areas of banking and finance. (The Source of Innovation, New York Oxford Oxford University Press, 1988) 9
- 10. 5. Conclusion This study has explained the central importance how innovation can contribute to competitive advantage towards the organization bottom-line. BSN as market leader that focusing to a rural area in Malaysia. Here, this assignment has ability for BSN capture the target audience and provide continuous interest in the function of banking new line of distribution channel using an innovative and engaging market strategy. This study also found, generally the innovation can help the establishment of niche market. It is believable that using the right tools and opportunity, innovation has can enable organization creating value towards their products, services or process. BSN would have a strong innovation strategy which is enough to achieve the vision their existing and potential market. From time to time, innovation strategies could be develop and modifying the corporate strategies by adapting the innovation business model. However, innovation needs passion, creativity and critically mind with financial, legal, managerial, technical in the process to produce a quality, adding value and the importance is the fine result is not easy to imitate. This will require cost, skill, and fine resources to implement the process and result. The main resources and strength to stay relevant in the industries is the entrepreneurship minded in each of the organization members like 3M® does. 10