2 d gel electrophresis
- 1. 2D GEL ELECTROPHRESIS ANN MARY MATHEW M.Sc. 1st YEAR BGS051705 11-03-2018
- 2. WHAT IS SDS-PAGE? WHATIS THE PRINCIPLE OF SDS-PAGE? HOW WE SEPARATE TWO PROTEINS WITH SAME MOLECULAR WEIGHT ?
- 3. Two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-D electrophoresis) is a powerful and widely used method for the analysis of complex protein mixtures extracted from cells, tissues, or other biological samples. Based on two independent properties : The second-dimension step, SDS- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), separates proteins according to their molecular weights (Mr, relative molecular weight). the first-dimension step, isoelectric focusing (IEF), separates proteins according to their isoelectric points (pI);
- 4. WHAT IS IEF ? WHY IEF? pH<pI pH=pI pH>pI
- 5. EXPERIMENTAL PROCESS : SAMPLE PREPARATION IPG STRIP REHYDRATION IEF IPG STRIP EQUILIBRATIION SDS-PAGE VISUALIZATION ANALYSIS
- 7. 1. SAMPLE PREPARATION • Must break all non-covalent protein-protein, protein- DNA, proteinlipid interactions, disrupt S-S bonds • Must prevent proteolysis, accidental phosphorylation, oxidation, cleavage, deamidation • Must remove substances that might interfere with separation process such as salts, polar detergents (SDS), lipids, polysaccharides, nucleic acids • Must try to keep proteins soluble during both phases of electrophoresis process
- 8. CELL DISRUPTION Gentle Lysis Method – Osmotic lysis, Freeze thaw lysis, Detergent lysis, Enzymatic lysis. Vigorous Lysis Method – Sonication, Grinding, Mechanical homogenization, PROTEASE INHIBITORS -PMSF(phenyl methylsulfonyl fluride), AEBSF(aminoethyl benzylsuonyl fluride),1mM EDTA etc.. PRECIPITATION - Ammonium sulfate, TCA, acetone, TCA in acetone etc.. CONTAMINANT REMOVAL – Filtration, Centrifugation, Chromatography, Solvent Extraction
- 9. PROTEIN SOLUBILIZATION – 8 M Urea (neutral chaotrope) – 4% CHAPS (zwitterionic detergent) – 2-20 mM Tris base (for buffering) – 5-20 mM DTT (to reduce disulfides) – Carrier ampholytes or IPG buffer (up to 2% v/v) to enhance protein solubility and reduce charge-charge interactions - 0.002% bromophenol blue
- 10. 1ST DIMENSION : ISOELECTRIC FOCUSSING
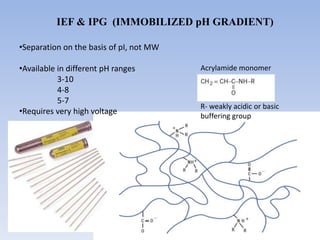
- 11. IEF & IPG (IMMOBILIZED pH GRADIENT) •Separation on the basis of pI, not MW •Available in different pH ranges 3-10 4-8 5-7 •Requires very high voltage Acrylamide monomer R- weakly acidic or basic buffering group
- 12. Amersham Biosciences Bio-Rad 1-D ±ő˛Ô˛őłŮ°ůłÜłľ±đ˛ÔłŮ˛ő…â¶Ä¦
- 16. Or…. Place the IPG strip on the IEF apparatus and apply current
- 17. 2nd Dimension – SDS PAGE equilibration
- 18. Casting IPG on 2nd Dimension
- 19. Visualization…… Desired features…….. • High sensitivity • Wide linear range for quantification • Compatibility with mass spectrometry • Low toxicity and environmentally safe • Environmentally friendly
- 20. Autoradiography and fluorography are the most sensitive detection methods. To employ these techniques, the sample must consist of protein radiolabelled in vivo using either 35S, 14C, 3H or, in the case of phosphoproteins, 32P. For autoradiographic detection, the gel is simply dried and exposed to X-ray film or—for quicker results and superior dynamic range of quantification—to a storage phosphor screen. Fluorography is a technique that provides extra sensitivity by impregnating the gel in a scintillant such as PPO (2,4- diphenyloxazole) prior to drying.
- 24. Further Analysis of Protein Spots • Picking the spots Ettan Spot picker is a robotic system that automatically picks selected protein spots from stained or destained gels using a pick list from the image analysis, and transfers them into microplates. • Digestion of the proteins supernatant peptides are mixed with MALDI matrix material and spotted onto MALDI slides using Ettan Spotter. • MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry In the Ettan MALDI-ToF mass spectrometer, a laser beam is fired into the dried peptide-matrix spots for ionization of the peptides. De novo sequencing of proteins.