2Âş eso unit 9
- 2. VOCABULARY • Is there much TRAFFIC in the streets ? • Solutions or positive things : PUBLIC TRANSPORT • Advantages and Disadvantages
- 3. VOCABULARY • Is there much NOISE in the streets ? • Solutions or positive things : PUBLIC TRANSPORT • Advantages and Disadvantages
- 4. VOCABULARY • Is there much POLLUTION in the streets ? • Solutions or positive things : PUBLIC TRANSPORT, OPEN SPACES • Advantages and Disadvantages
- 5. VOCABULARY • Is there much GRAFFITI in the streets ? • Solutions or positive things : PARK , YOUTH CLUB , OPEN SPACES • Advantages and Disadvantages
- 6. VOCABULARY • Is there much CRIME in the streets ? • Solutions or positive things : SECURITY CAMERA • Advantages and Disadvantages
- 7. VOCABULARY • Is there much LITTER in the streets ? • Solutions or positive things : BIN • Advantages and Disadvantages
- 8. VOCABULARY • Is there much VANDALISM in the streets ? • Solutions or positive things : SECURITY CAMERAS • Advantages and Disadvantages
- 9. COUNTABLE WORDS UNCOUNTABLE WORDS MANY MUCH Security cam Traffic Open space Pollution Graffiti ( there are two graffities in this wall) Graffiti Bin Litter Park Noise Sign Crime Street light Public transport Youth club Vandalism Teenager Food Sign Money Problem Burguer People
- 10. Countable nouns are things that can be counted. A countable noun can be singular or plural: one apple, two apples... When we want to count them we use ….. • A/An (singular / just one) A/An … or any cardinal number ten houses An apple A doctor A class three colleges A meal • SOME Some cups Some books Some libraries Some flights • ANY (As SOME but in negative and interrogative) I don’t have any cups at home (I have some glasses at home) They bought some CDs but they didn’t buy any books • A LOT OF (It means MUCHOS) A lot of questions A lot of problems A lot of issues • MANY (As A LOT OF but in negative and interrogative) They didn’t asked many questions. (They asked a lot of questions) Do they have many problems with the baby? Yes, they have a lot of problems with him • You cannot use singular countable nouns alone (without a/my/the car...) but you can use plural countable nouns alone REMEMBER A/ANARE USED FOR SINGULAR WORDS, NOT WITH PURAL AND NOT WHENEVER YOU WANT!! A/ANARE USED FOR SINGULAR WORDS, NOT WITH PURAL ONE!! A/ANARE USED FOR ________WORDS So….is it correct saying? I like playing A football, A tennis.. No?????Really ???Well, don’t use it please!!!
- 11. Countable nouns A/An (singular / just one) A/An … or any cardinal number ten houses An apple A doctor A class three colleges A meal SOME Some cups Some books Some libraries Some flights ANY (As SOME but in negative and interrogative) I don’t have any cups at home (I have some glasses at home) They bought some CDs but they didn’t buy any books A LOT OF (It means MUCHOS) A lot of questions A lot of problems A lot of issues MANY (As A LOT OF but in negative and interrogative) They didn’t asked many questions. (They asked a lot of questions) Do they have many problems with the baby? Yes, they have a lot of problems with him
- 12. Uncountable nouns are things that cannot be counted so they only have singular form: some rice, some tea... They usually refer to abstractions (such as confidence or advice) or collectives (such as equipment or luggage). Information, happiness, equipment… • Some and Any are used with both countable and uncountable nouns.
- 13. • COUNTING THE UNCOUNTABLES. • SOME Some sugar Some money Some water Some time • ANY (As SOME but in negative and interrogative) Have you got any salt? Yes I have some salt but I • A LOT OF A lot of traffic A lot of time A lot of sleep A lot of confidence • MUCH(As A LOT OF but in negative and interrogative) There isn’t much traffic today because it is Sunday (There was a lot of traffic yesterday) They didn’t have much time to finish the project (they have a lot of time to finish it) Expressions to count uncountable nouns. a tube of a litre of a kilo of one carton/two cartons of a slice of a bottle of a packet of a tin of an item of a piece of a spoonful of a glass of a bowl of a loaf of a can of Some uncountable nouns in English can be countable in other languages. Here you have a list of the most common uncountable English words: haven’t got any sugar advice bread news luggage baggage furniture spaghetti pasta weather research work money grass scenery health progress º
- 14. • UNCOUNTABLES. • SOME Some sugar Some money Some water Some time • ANY (As SOME but in negative and interrogative) Have you got any salt? Yes I have some salt but I • A LOT OF A lot of traffic A lot of time A lot of sleep A lot of confidence • MUCH(As A LOT OF but in negative and interrogative) There isn’t much traffic today because it is Sunday (There was a lot of traffic yesterday) They didn’t have much time to finish the project (they have a lot of time to finish it)
- 15. A / AN / SOME / ANY Type of sentence Countable Uncountable + We need an apple some apples some butter some milk - We don’t need a tomato any tomatoes any rice any sugar ? Do we need a tomato? any tomatoes? any rice? any sugar? • Use a / an with singular countable nouns. • SOME.- with plural countable nouns and uncountable nouns in + sentences. • ANY.- with plural countable nouns and uncountable nouns in – or ? sentences. • We can also use some in ? to ask for and offerings: – Can I have some coffee? – Do you want some biscuits? AFFIRMATIVE INTERROGATIVE NEGATIVE SUMMING UP
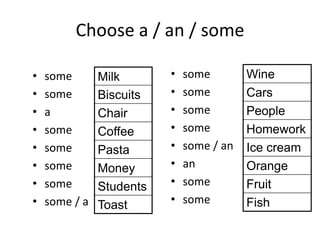
- 16. Choose a / an / some • some • some • a • some • some • some • some • some / a • some • some • some • some • some / an • an • some • some Milk Biscuits Chair Coffee Pasta Money Students Toast Wine Cars People Homework Ice cream Orange Fruit Fish
- 17. How much / how many…? • Use How much…? with uncountable nouns. • How much water do you drink? • Use How many…? with plural countable nouns. • How many students do you have? • Possible answers: • I drink a lot of water. • I drink quite a lot. • I don’t drink much water. (not much) • I don’t drink any water. • None. • Not many (students).
- 19. The words expressing quantity or quantifiers used with countable and uncountable words are:
- 21. Some nouns are countable with one meaning and uncountable with another meaning: A fish/Some fish A paper (a newspaper)/Some paper An iron/Some iron A wood/Some wood A hair/Some hair A coffee (a cup)/Some coffee A glass/Some glass A time/Some time
- 22. Exercises • http://www.mdelu.com/useex/coun1.htm You have to choose the correct quantifier depending on the following word • http://www.mdelu.com/useex/counta/count2.htm you have to quantify the uncountable words according to the pictures • http://www.mdelu.com/useex/counta_mis/count3.ht m you will see some typical mistakes of misuse of quantifiers.
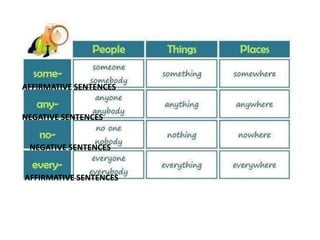
- 23. Indefinite pronouns • We use indefinite pronouns to refer to people or things without saying exactly who,what or where they are. • We use pronouns ending in -body or -one for people, and pronouns ending in -thing for things: • -where PLACES • -one PEOPLE • - thing OBJETCS We use SOME or ANY in affirmative and interrogative and negative sentences •SOME AFFIRMATIVE •ANY NEGATIVE AND INTERROGATIVE
- 24. INDEFINITE PRONOUNS -ONE (people) -THING(objects) -WHERE(places) AFFIRMATIVE SOMEONE SOMEBODY SOMETHING SOMEWHERE NEGATIVE ANYONE ANYBODY NOONE* ANYTHING NOTHING* ANYWHERE ANYPLACE NOWHERE* INTERROGATIVE Alguien Algo AlgĂşn lugar
- 25. Indefinite pronouns are singular, so the verb must wear “s” in the present simple and you must use “is” and “was” with “to be”. E.g: • Somebody is at the door. (Alguien está en la puerta.) • Everybody loves chocolate. (A todo el mundo le encanta el chocolate.) • Nothing was ever the same. (Nada fue lo mismo.) • Is there anywhere you want to go? (¿Hay un sitio dónde quieras ir?)
- 26. • Would you like something to drink? • I need nothing • I went nowhere • Nobody came to the meeting
- 27. Someone / Something/ Somewhere Anyone/ Anything / Anywhere • She bought ____________ in the supermarket • I saw _______________there.(people) • I did not see _______________ there. • Did you see _______________ there? (people) • Would you like _______________ better? • I want _______________to eat. • Have you seen my car keys _______________? • ________________ phoned while we were out, but they did not leave a message. • They are looking for ____________ to settle down and have children. They want to find a quiet place to lead a quiet life. • "Is there ____________ at home?“ something someone anything anyone something something anywhere Somebody Somewhere anybody
- 28. • I spent the night ______________________ near the beach. • There is ____________ to park here. Let's go ____________ else to park. • Would you like _______________________ to wash your hands?. • They took him ________________ in London, and he never returned. • Please don't leave __________________ behind at home. We'll be away for a fortnight. • She needs _______________ to love. She's very lonely. • There isn't _______________ you can do to help them. • We do not need _____________ else to run this department. We can do it ourselves. • __________________ is ringing the bell. Go and see who it is somewhere nowhere somewhere something somewhere anything Somebody anything anyone Someone
- 29. AFFIRMATIVE SENTENCES NEGATIVE SENTENCES NEGATIVE SENTENCES AFFIRMATIVE SENTENCES
- 30. Activities • Make the following sentences negative: x There is some milk on the floor. x There is some water in the refrigerator. x. Someone is at the door. x. Everyone is tired after the trip. • Make the following sentences positive: x. There isn't anything good on TV tonight. x. No-one is at home. x. There aren't any books on the shelf. • Answer the following questions positively and negatively: x. Are there any boys in your math class? x. Is anyone ready for the test? x. Are any of you Chinese? x. Are there any good book stores in your town? x Is anything better than chocolate ice cream? • Ask questions for the following answers: x. Nobody is at the school today; it's Sunday. x. Yes, someone is in the kitchen with Dinah.
- 31. ONLINE ACTIVITIES • http://www.shertonenglish.com/resources/es/pr onouns/pronouns-indefinite.php • http://www.blueblocnotes.com/activities/gramm ar/quantity-expressions/some-and-any- compounds-activities • http://www.grammarbank.com/indefinite- pronouns-exercise.html • http://www.english-4u.de/some_any_ex4.htm • http://www.agendaweb.org/grammar/anyth ing-someone-exercises.html
- 32. SHOULD / MUST
- 33. Modal verbs • Rules – They are followed by a verb in the base form • I should study more – They are the same for all the pronouns • She/they/I/ you should make it better – They do not need auxiliars. They take direct negative and qestion forms • You mustn’t smoke here – They never combine with another modal verbs • You can’t must read**
- 34. SHOULD AND MUST Should is used for advices and recommendations •You should read books in English if you want to improve your vocabulary •She shouldn’t smoke because she is always coughing •Where should we go next summer? Must is used to talk about strong obligations and prohibitions. They are usually related with laws and rules. •I must go now , I start working in five minutes •You must wear a helmet to drive a motorbike •He mustn’t drink alcohol, he is underage STRUCTURE SUBJECT + SHOULD/MUST+ BASE FORM OF THE VERB (without to) SUBJECT + SHOULDN’T/MUSTN’T + BASE FORM OF THE VERB SHOULD/MUST + SUBJECT + BASE FORM?
- 36. YOU MUSTN’T SMOKE HEREYOU MUSTN’T EAT IN THE CLASSROOM YOU MUSTN’T SWIM IN THIS LAKE YOU MUSTN’T BRING A GUN, SMOKE, USE THE MOBILE AND BRING YOUR DOG AT THE SCHOOL
- 37. YOU MUST BRING A PHOTO IDYOU MUST THROUGH THE LITTER INTO A BIN
- 38. YOU SHOULD
- 39. YOU SHOULD…..
- 41. THIS IS THE ONE I LIKE THE MOST…
- 42. VOCABULARY • WATCH OUT FOR • PUT ON • SLOW DOWN • GET ON • PUT DOWN • GO INTO • RUN OVER • TAKE OF • SPEED UP • GET OFF • PICK UP • STAY OUT