2015-08-19_Benseler_Imaging.ppt
- 1. Introduction to Medical Imaging Jeff Benseler, D.O.
- 2. Objectives ´ü« Medical Imaging: What to expect in your first 2 years at OUHCOM ´ü« Overview: How do x-rays create an image of internal body structures? ´ü« What are the advantages of CT, MRI and Ultrasound?
- 3. Medical Imaging (Radiology) ´ü« Nearly all medical disciplines utilize medical imaging ´ü« As you move from block to block we will learn: ´ü« How each modality works to create an image of internal body structures ´ü« Selecting the best imaging tests for a given clinical presentation ´ü« Develop a stepwise repeatable pattern of evaluating medical images
- 4. Method for learning medical image interpretation ´ü« Most blocks will contain recorded presentations ´ü« These recordings last approximately 10 to 30 minutes each ´ü« Most blocks will have 2 to 4 recordings to view before the live class ´ü« The recordings can be viewed and reviewed as needed anytime 24/7 ´ü« In class, we will learn by interpreting unknown cases
- 5. Questions about medical imaging ´ü« Please feel free to contact me with questions ´ü« My preferred contact method is email ´ü« benseler@ohio.edu
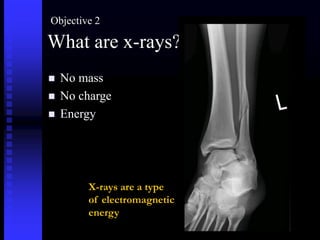
- 6. What are x-rays? ´ü« No mass ´ü« No charge ´ü« Energy X-rays are a type of electromagnetic energy Objective 2
- 7. How do x-rays passing through the body create an image? ´ü« X-rays that pass through the body render the image dark (black) ´ü« X-rays that are totally blocked render the image light (white) ´ü« Air = low atomic # = x-rays get through = image is dark (black) ´ü« Metal = high atomic # = x-rays blocked = image is light (white)
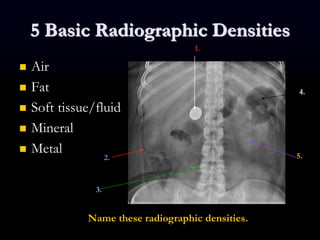
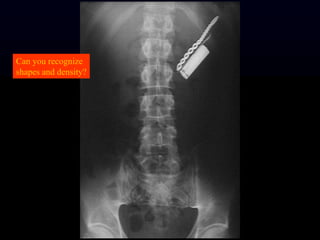
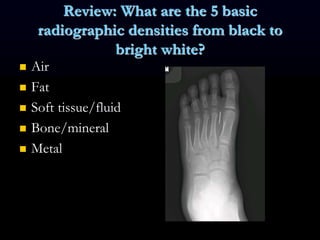
- 8. 5 Basic Radiographic Densities ´ü« Air ´ü« Fat ´ü« Soft tissue/fluid ´ü« Mineral ´ü« Metal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Name these radiographic densities.
- 9. Optimal environment for visual perception ´ü« Dedicated source of light (5 to 9 mega pixel monitors) ´ü« Darkened environment (like a movie theater) ´ü« Limit distraction
- 11. Can you recognize shapes and density?
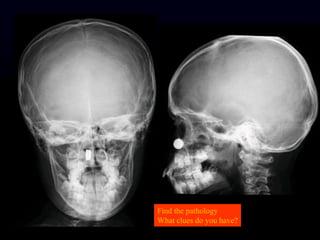
- 12. Find the pathology What clues do you have?
- 13. Medical Imaging Interpretation 3 basic steps ´ü« First learn how each modality creates an image of internal body structures ´ü« Next, be able to accurately label normal anatomy (body structures) ´ü« Then, search for structures that donÔÇÖt belong and for body structures that are abnormal in size, shape, position and/or density
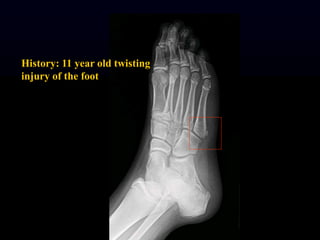
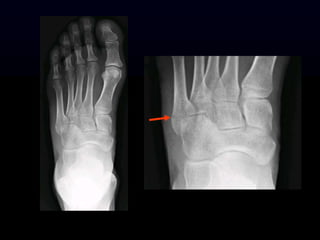
- 14. History: 11 year old twisting injury of the foot
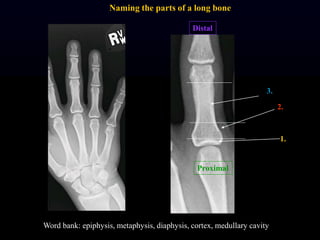
- 16. Proximal Distal 1. 2. 3. Word bank: epiphysis, metaphysis, diaphysis, cortex, medullary cavity Naming the parts of a long bone
- 17. Review: What are the 5 basic radiographic densities from black to bright white? ´ü« Air ´ü« Fat ´ü« Soft tissue/fluid ´ü« Bone/mineral ´ü« Metal
- 18. Summary for objective 2: How do x-rays create an image of internal body structures? ´ü« X-rays pass through the body to varying degrees ´ü« Higher atomic number structures block x-rays better, example bone ´ü« Lower atomic number structures allow x-rays to pass through, example: air in the lungs
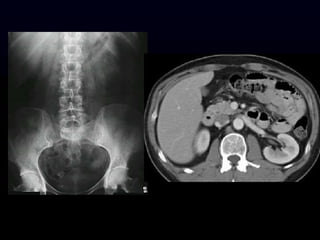
- 19. Objective 3 Advantages of CT, MRI and Ultrasound These modalities are cross sectional imaging Cross sections are like slices X-ray studies are a 2 dimensional representation of 3 dimensional structures can result in undesirable overlapping densities and artifacts
- 20. CT ´ü« Advantages ´ü« Eliminates overlapping densities ´ü« Excellent resolution ´ü« Excellent for detecting intracranial bleeding ´ü« Excellent in the neck, chest and abdomen ´ü« Excellent for evaluating fractures ´ü« Disadvantages ´ü« More expensive than x- ray and ultrasound ´ü« Much more radiation ´ü« Dense bone (petrous ridge for example) and metal cause severe artifacts
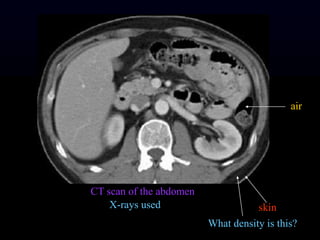
- 21. CT scan of the abdomen X-rays used skin What density is this? air
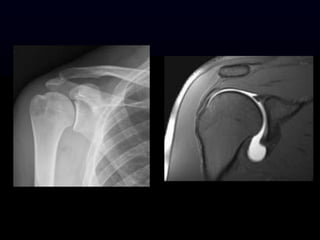
- 23. MRI ´ü« Advantages ´ü« No overlapping artifact ´ü« Excellent resolution ´ü« Very good at detecting fluid ´ü« Excellent for imaging the brain, spine and joints ´ü« No radiation ´ü« Multiple imaging tests within the same study (T1, T2, IR, GE) ´ü« Disadvantages ´ü« Very expensive ´ü« Patients cannot have a pacemaker or ferromagnetic material ´ü« Slower to acquire images (approximately 45 minutes)
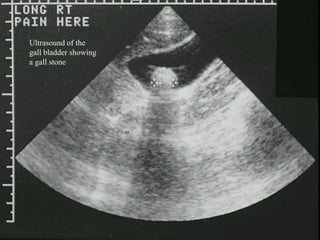
- 25. Ultrasound ´ü« Advantages ´ü« No radiation ´ü« Portable ´ü« Instantaneous (real time) ´ü« Excellent for cysts and fluid ´ü« Doppler ultrasound is excellent to assess blood flow ´ü« Excellent for newborn brain, thyroid, gall bladder, female pelvis, scrotum, pregnancy ´ü« Disadvantages ´ü« Does not work well in large or obese patients ´ü« Resolution less than CT and MRI ´ü« Air or bowel gas prevents visualization of structures
- 26. Ultrasound of the gall bladder showing a gall stone
- 27. X-rays, CT, MRI and ultrasound help us see into the body ´ü« Internal body structures are composed of varied material (fat, muscle, bone, gland) or contain air, water or minerals that ÔÇ£show upÔÇØ differently on each type of imaging test. ´ü« Each modality has its own advantages allowing us the choose the best one for each medical circumstance.
- 28. What an excellent medical student at your level can do: ´ü« Be able to describe how x-rays can create an image of internal body structures ´ü« Recognize and label the 5 basic densities on an x-ray ´ü« Be familiar with the advantages for CT, for MRI and for ultrasound
- 29. List of Potentially Helpful Radiology Websites ´ü« http://www.med-ed.virginia.edu/courses/rad/ ´ü« Online tutorial series. ´ü« http://radiopaedia.org/ ´ü« A free educational radiology resource with one of the web's largest collections of radiology cases and reference articles. ´ü« http://www.radiologyassistant.nl/en/p42023a885587e /welcome-to-the-radiology-assistant.html
- 30. Websites Continued ´ü« http://learningradiology.com/index.htm ´ü« Seems to have some good stuff but difficult to navigate the site. ´ü« http://www.swansea-radiology.co.uk/index.html ´ü« http://bubbasoft.org/ ´ü« Strange name but the website is useful. Breaks it into radiologic anatomy (identification of structures) and clinical radiology (identification of pathology).
- 31. Websites continued ´ü« http://eradiology.bidmc.harvard.edu/index.html ´ü« This source seems really valuable. Includes sections on primary care radiology, representative images of classic cases, interactive tutorials, and living anatomy ´ü« http://www.radiologyeducation.com/ ´ü« List of radiology resources ´ü« http://www.med.wayne.edu/diagRadiology/TeachingF ile.html ´ü« Collection of interesting cases
- 32. Websites continued ´ü« http://headneckbrainspine.com/ ´ü« Neuroradiology anatomy and cases. ´ü« https://3s.acr.org/CIP/Default.aspx ´ü« Case in point. American College of RadiologyÔÇÖs case of the day.