2019 intrinsic barriers intellectual impairments
- 1. Intrinsic Barriers to Learning & Development in the Foundation Phase Classroom -Intellectual Impairments - Presented by Dr Soraya Motsabi
- 2. CONTENT OVERVIEW ŌĆó Learning Units 2: ŌĆō Intellectual Impairments Understand and Identify Signs Assess the LearnerŌĆÖs Needs Practically Support the Learner You need to be able toŌĆ”.
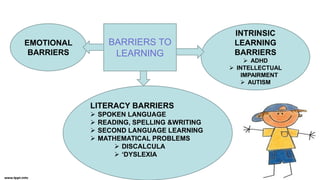
- 3. BARRIERS TO LEARNING EMOTIONAL BARRIERS LITERACY BARRIERS ’āś SPOKEN LANGUAGE ’āś READING, SPELLING &WRITING ’āś SECOND LANGUAGE LEARNING ’āś MATHEMATICAL PROBLEMS ’āś DISCALCULA ’āś ŌĆśDYSLEXIA INTRINSIC LEARNING BARRIERS ’āś ADHD ’āś INTELLECTUAL IMPAIRMENT ’āś AUTISM
- 5. INTELLECTUAL IMPAIRMENT ŌĆ£Disability is a matter of perception. If you can do just one thing well, you're needed by someone.ŌĆØ - Martina Navratilova Intellectual impairment Mental handicap Mental retardation Mental disability Cognitive development Cybernetic model for teaching practice Teaching learners with intellectual impairment
- 6. Intellectual Impairments Identifying, Assessing and Supporting Study Chapter 23: Learning Impairment from your prescribed book: Addressing Barriers to Learning by Landsberg , Kruger & Swart (2011:399) ADDESSING BARRIERS TO LEARNING: A SOUTH AFRICAN PERSPECTIVE 2008 CHAPTER 17
- 7. Defining Intellectual Impairments ŌĆó Significant limitations both in: ŌĆō intellectual functioning (learning, reasoning, problem solving, memory, thinking) ŌĆōadaptive behavior (includes many everyday social and practical skills) ŌĆó Origin before age 18
- 8. WHAT IS INTELLECTUAL IMPAIRMENT ŌĆó Use of different terms over the years (idiot; retarded etc unacceptable ŌĆó SA White Paper 6: disability and intellectual impairment adopted ŌĆó Important for teachers to equip themselves to be able to deal with these learners HISTORICAL DEFINITION ŌĆó Widespread impairment ŌĆó 3.3% of overall population ŌĆó More males 3:2 than females ŌĆó More have mild intellectual impairment than severe PREVALENCE Sub average general intellectual functioning that originates in the developmental period and is associated with impaired maturation and learning, and social maladjustment. Retardation is commonly defined in terms of intelligence quotient:
- 10. ’ā╝Intellectual impairment is a particular state of functioning. It is not a medical disease or a mental disorder. ’ā╝There is an internationally accepted definition for intellectual impairment, developed by the American Association on intellectual impairment (AAMR). According to this definition intellectual impairment refers to substantial limitations in present functioning. ’ā╝It is characterized by: ’ā╝significantly below average intellectual functioning, existing concurrently with related limitations in two or more of the following applicable adaptive skill areas: ’ā╝ communication ŌĆó self-care ’ā╝ home living ŌĆó social skills, ’ā╝ community use ŌĆó self-direction ’ā╝ health and safety ŌĆó functional academics ’ā╝ leisure ŌĆó work.
- 11. Limitations in scholastic abilityŌĆ” Mental retardation Level IQ Range Educational Category 1. Mild 50-70 IQ ŌĆ£EducableŌĆØ; 85% of population of MR; Acquire Communication and Academic Skills up to Grade 6; Vocational Training; Supervision; Considered educable; Can get jobs later in life 2. Moderate 35-50 IQ ŌĆ£TrainableŌĆØ; 10% of population of MR; Acquire communication and Academic Skills up to Grade 2; Vocational Training; Supervised personal care, work and living settings; Need structured classrooms 3.Severe 20-35 IQ 3-4% of MR population; little or no communicative speech; familiar with alphabet, counting, sight reading survival words; trained in elementary self care skills; simple tasks in closely supervised work settings 4. Profound 20 and below 1-2% of MR population; cannot measure performance on IQ test ŌĆō too impaired / uncooperative to perform on it.
- 12. Limitations in these areasŌĆ” Intellectual Impairments Conceptual Skills Social Skills Practical Skills Language Literacy Money Time Number concepts Self-direction
- 13. Causes of intellectual impairment External causes/ Extrinsic factors ŌĆó Poverty ŌĆó Linguistic deprivation ŌĆó Low literacy levels of parents ŌĆó Poor nutrition ŌĆó Unsuccessful child rearing practices ŌĆó Lack of motivation ŌĆó Lack of schooling ŌĆó Environmental toxins ŌĆó Medical conditions eg HIV/AIDS ŌĆó Labelling Internal Causes/Intrinsic factors ŌĆó PRENATAL CAUSES ŌĆó Chromosomal abnormalities leading to Down syndrome (WATCH VIDEO) ŌĆó Phenylketonoria (Watch Video) ŌĆó Fragile X syndrome ŌĆó Fetal alcohol syndrome ŌĆó OTHER FACTORS ŌĆó Smoking ŌĆó Drug abuse POST NATAL CAUSES PRENATAL AND PERINATAL CAUSES
- 16. Consequences of intellectual impairment for learners. - Physical aspects -Moral aspects -Self-concept -Social aspects -Personality aspects -Independence
- 17. Role of the Teacher The 4 Levels of Intensities and Supports (from least TO most intensive and supportive) 1. Intermittent 2. Limited 3. Extensive 4. Pervasive
- 18. STRATEGIES OF CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT Allow for many break throughout the school day. Children with MR may require time to relax and unwind. Always speak directly to the child so he can see you. Never speak with your back to him Build a foundation of success by providing a series of short and simple assignments. Encourage interaction with children without disabilities. Assign jobs to the child in the classroom so that he/she can feel success and accomplishment. Monitor the childŌĆÖs diet. Some children with MR are on very strict diets.. Encourage interaction with children without disabilities
- 19. Teacher Skills required to work with Intellectual Impairments ŌĆó Know and understand side effects of medications on learning ŌĆó Know personal characteristics of learners ŌĆó Work as a member of a support team: ŌĆō class support team or ŌĆō institutional level support team ŌĆō district based support team ŌĆō informal support ŌĆó Know and use Learner in Context Assessment and Support Profile ŌĆó Know support strategies for developing cognitive and metacognitive (monitoring and control) abilities
- 20. Learner in Context Assessment and Support Profile (LCASP) ŌĆó A model to visually organize information. ŌĆó Helps teachers: screen, identify and assess difficulties and plan for individual support. ŌĆó Helps assess change and functioning over time. ŌĆó Tool for the teacherŌĆÖs critical self reflection. ŌĆó Factors to consider when compiling a support plan: ŌĆō Predisposing/precipitating/intensifying intrinsic factors as barriers to learning ŌĆō LearnerŌĆÖs strengths ŌĆō Contextual risk factors ŌĆō Contextual assets ŌĆō classroom, family, school, education system ŌĆó Consideration to developmental history, physiological and physical functioning; emotive (affective) functioning; cognitive functioning; communication and behavioral functioning.
- 21. Case Study: ŌĆ£Skippy NkosiŌĆØ Skippy Nkosi is 10 Years Old and in Grade 2 at Funda and you are his class teacher. You have just started teaching his class having taken over from the previous teacher who resigned because of ŌĆśwork stressŌĆÖ. After observing him for a month, you are concerned about his progress at school and decide to read his Learner Profile to get some background information. In the Profile you find a completed Informal Adaptive Behaviour Inventory, done by his previous teacher. You can see that he needs support, so you need to now fill out a Support Needs Assessment (SNA 1 & 2) ŌĆō School Level Intervention document.
- 22. SkippyŌĆÖs Learner Profile ŌĆó What kinds of information would you look out for in SkippyŌĆÖs Learner Profile, specifically in these sections: ŌĆōmedical information section; ŌĆōearly interventions services rendered, ŌĆōschools attended; ŌĆōareas needing ongoing support
- 23. SkippyŌĆÖs Support Need Assessment (SNA 1 &2) ŌĆó You suspect that Skippy is moderately intellectually impaired, what things are you likely to state as areas of concern? ŌĆó Describe how moderate intellectual impairment can affect SkippyŌĆÖs: ŌĆō Ability to communicate ŌĆō Ability to learn ŌĆō Behaviour and social competence ŌĆō Health, wellness and personal care ŌĆó What would you do differently to support Skippy with
- 24. 24 Recommend suitable play and stimulation to parents Maternal Depression Caring for a child with developmental delay is very demanding. Assess for depression: ŌĆó Are you ok? ŌĆó How are you coping? ŌĆó Do you feel that this is too difficult for you? ŌĆó Do you have time to rest or visit relatives and friends? Poorly Simulating Environment How do you play with your child? How do you communicate with your child?
- 25. 25 Recommend suitable play and stimulation to parents Maternal Depression Caring for a child with developmental delay is very demanding. Assess for depression: ŌĆó Are you ok? ŌĆó How are you coping? ŌĆó Do you feel that this is too difficult for you? ŌĆó Do you have time to rest or visit relatives and friends? Poorly Simulating Environment How do you play with your child? How do you communicate with your child?
- 26. ŌĆó Identify and treat reversible causes of ID ŌĆó Alleviate suffering for child and family ŌĆó Promote healthy development towards greatest possible independence. 26
- 27. Evidence-Based Treatments: ŌĆó Etiological treatment if cause is known and treatable ŌĆó Parent skills training ŌĆó Behaviour intervention for challenging behaviour ŌĆó Psychoeducation ŌĆó Physio/speech/occupational therapy (when available) 27
- 28. ŌĆó Family psychoeducation ’é¦ explain problem to carers ’é¦ give parents skills to support child development ’é¦ promote participation in family, school and community life ’é¦ address psychosocial needs of carers ŌĆó Advice for teachers ŌĆó Manage risk/contributing factors ’é¦ hearing and vision problems ’é¦ nutrition ’é¦ maternal depression ’é¦ lack of stimulation ŌĆó Manage co-occurring epilepsy, depression and behaviour problems 28
- 29. ŌĆó Many effective parent training programs available to reduce behavior problems and increasing adaptive functioning ŌĆó In the absence of formal training teach parents about promoting learning and managing challenging behavior etc.)
- 30. 30
- 31. ŌĆó Not much evidence for effectiveness ŌĆó Only use after comprehensive assessment and in combination with psycho-social treatment ŌĆó Antipsychotics sometimes useful in crisis situations, short-term use safer ŌĆó Doses: start low ŌĆō go slow! ŌĆō Sensitivity to medication common in ID ŌĆó Co-morbidity (e.g. depression, ADHD) can be treated in the same way as in non-ID children
- 32. ŌĆó Which children with ID should be seen in pediatrics? ŌĆó Who should be seen in psychiatry? ŌĆó Who should receive community care? ŌĆó What training do workers in the community need to care for children with ID? ŌĆó Who should deliver the training?
- 33. ŌĆó Primary (preventing occurrence of ID): ŌĆō Prenatal: (toxins, infections incl. HIV) ŌĆō Peri-natal: (delivery, neo-natal screening) ŌĆō Post-natal: (immunization, treatment for infections, safe and enriching environment) ŌĆó Secondary (halting disease progression): ŌĆō Discover ID early, provide stimulation for optimal development ŌĆó Tertiary (maximizing functioning) ŌĆō Support for families
- 34. ŌĆó American Association on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities ŌĆó Australian Institute of Health and Welfare ŌĆó Australasian Society for Intellectual Disability ŌĆó Center for Effective Collaboration and Practice ŌĆó Council for Exceptional Children (CEC) ŌĆó DownŌĆÖs Syndrome Association (UK) ŌĆó European Association of Intellectual Disability Medicine ŌĆó Independent Living Canada ŌĆó National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities (US) ŌĆó National Dissemination Center for Children with Disabilities (US)