Щ…ШӯШ§Ш¶ШұШ© Ш§Ш§Щ„ШӘШҜШұЩҠШЁ 2023-2022Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҠШҜШ§ЩҶЩҠ -3.ppt
Download as ppt, pdf0 likes10 views
ШӘШӘЩҶШ§ЩҲЩ„ Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮШ© ШЈШіШ§Щ„ЩҠШЁ Ш¬Щ…Ш№ Ш§Щ„ШЁЩҠШ§ЩҶШ§ШӘ ЩҲШӘШӯЩ„ЩҠЩ„ЩҮШ§ШҢ ШЁЩ…Ш§ ЩҒЩҠ Ш°Щ„Щғ ШЈШҜЩҲШ§ШӘ Ш§Щ„ШӘШӯЩ„ЩҠЩ„ Ш§Щ„ШҘШӯШөШ§ШҰЩҠ ЩҲШ§Щ„Щ…Ш¬ШӘЩ…Ш№ ЩҲШ§Щ„Ш№ЩҠЩҶШ©. ЩғЩ…Ш§ ШЈЩҶЩҮШ§ ШӘЩҶШ§ЩӮШҙ Ш§Щ„ЩҶШӘШ§ШҰШ¬ ЩҲШ№ШұШ¶ЩҮШ§ ЩҲШӘЩҒШіЩҠШұЩҮШ§ ЩҲШӘЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮ Ш§Щ„Щ…ШұШ§Ш¬Ш№ ЩҲШ§Щ„Щ…ЩӮШӘШұШӯШ§ШӘ. ШӘШӘШ¶Щ…ЩҶ Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮШ© ШЈЩҠШ¶ЩӢШ§ ЩҶЩ…Ш§Ш°Ш¬ ЩҲШ·ШұЩӮ Щ„ШӘЩӮЩҠЩҠЩ… ШЈШҜШ§ШЎ Ш§Щ„Ш·Щ„Ш§ШЁ ЩҲЩ…Щ„Ш§ШӯШёШ§ШӘ ШӯЩҲЩ„ ШӘЩҒШ§Ш№Щ„ Ш§Щ„ШӯШ§Ш¶ШұЩҠЩҶ.
1 of 11
Download to read offline








Ad
Recommended
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.ppt
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.pptM H
Мэ
The document outlines various parasitic infections caused by worms, including Ascaris, Enterobius, Ancylostoma, and Trichuris, detailing their life cycles, clinical features, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. Infections are primarily asymptomatic but can lead to significant health issues like respiratory problems, gastrointestinal symptoms, and anemia in heavy cases. Effective prevention strategies include improved sanitation, mass treatments, and proper health education.Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.ppt
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.pptM H
Мэ
The document provides a detailed overview of various intestinal parasites, their characteristics, modes of transmission, clinical features, laboratory diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. It discusses infections caused by Ascaris lumbricoides, Enterobius vermicularis, Ancylostoma duodenale, and Trichuris trichiura, highlighting symptoms associated with each, such as abdominal discomfort and respiratory issues. Treatment options generally include anthelmintic medications like mebendazole and albendazole, alongside recommendations for improved sanitation and hygiene.Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.ppt
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.pptM H
Мэ
The document provides a detailed overview of various intestinal nematodes, including ascariasis caused by Ascaris lumbricoides, enterobiasis from Enterobius vermicularis, hookworm disease from Ancylostoma duodenale, and trichuriasis from Trichuris trichiura. It covers the geographical distribution, life cycle, pathogenicity, clinical features, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment options for these infections. Key treatments include mebendazole, albendazole, and preventive measures focusing on sanitation and hygiene.fluid an dd.ppt
fluid an dd.pptM H
Мэ
The document covers fluid volume disturbances and electrolyte imbalances in the human body, highlighting causes, symptoms, diagnostic evaluations, and management strategies for conditions such as hypovolemia, hypervolemia, hyponatremia, hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and hyperkalemia. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining electrolyte homeostasis for cellular activities, offers detailed information on acid-base balance, and describes various intravenous solutions used for treatment. Additionally, it outlines the roles of body buffer systems in regulating pH levels.fluid a nd.ppt
fluid a nd.pptM H
Мэ
The document provides an overview of fluid compartments, daily fluid intake and output, and the importance of electrolyte balance in the body. It details conditions such as fluid volume disturbances, electrolyte imbalances, and their clinical implications, along with diagnostic assessments and management strategies. Additionally, it discusses various IV solutions and buffer systems that regulate acid-base balance in the body.Ш§Щ„Ш§ЩҮШҜ Ш§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШіЩ„ЩҲЩғЩҠЩҮ.pptx
Ш§Щ„Ш§ЩҮШҜ Ш§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШіЩ„ЩҲЩғЩҠЩҮ.pptxM H
Мэ
ЩҠШӘЩҶШ§ЩҲЩ„ Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮШ© ШЈЩҮЩ…ЩҠШ© ШӘШөЩҶЩҠЩҒ ШЁЩ„ЩҲЩ… ЩҒЩҠ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ®Ш·ЩҠШ· Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠ ЩҲШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒЩҮ Ш§Щ„ШӘШұШЁЩҲЩҠШ©ШҢ ШӯЩҠШ« ЩҠШЁШұШІ ШҜЩҲШұ ЩҮШ°Ш§ Ш§Щ„ШӘШөЩҶЩҠЩҒ ЩҒЩҠ ШӘШӯШҜЩҠШҜ Ш§Щ„ШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ© ЩҲШӘШ№ШІЩҠШІ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„Щ… Щ…ЩҶ Ш®Щ„Ш§Щ„ Щ…ШіШӘЩҲЩҠШ§ШӘ Щ…ШӘШҜШұШ¬Ш© Щ…ЩҶ Ш§Щ„ШөШ№ЩҲШЁШ©. ЩғЩ…Ш§ ЩҠЩҶШ§ЩӮШҙ ЩғЩҠЩҒЩҠШ© ШөЩҠШ§ШәШ© Ш§Щ„ШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ© Ш§Щ„ШіЩ„ЩҲЩғЩҠШ© ЩҲЩҒЩӮШ§ЩӢ Щ„Щ…Ш№Ш§ЩҠЩҠШұ Щ…ШӯШҜШҜШ© ШӘШ¶Щ…ЩҶ ШӘШӯЩӮЩҠЩӮ Ш§Щ„ЩҶШӘШ§ШҰШ¬ Ш§Щ„Щ…ШұШ¬ЩҲШ©. Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮШ© ШӘШіЩ„Ш· Ш§Щ„Ш¶ЩҲШЎ Ш№Щ„Щү Ш§Щ„ЩҒШұЩҲЩӮ Ш§Щ„ЩҒШұШҜЩҠШ© ШЁЩҠЩҶ Ш§Щ„Щ…ШӘШ№Щ„Щ…ЩҠЩҶ ЩҲШ¶ШұЩҲШұШ© ШӘШ№ШҜЩҠЩ„ Ш§Щ„Ш·ШұЩӮ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ© ШЁЩ…Ш§ ЩҠШӘЩҶШ§ШіШЁ Щ…Ш№ Ш§ШӯШӘЩҠШ§Ш¬Ш§ШӘЩҮЩ….Ш§Щ„Ш§ЩҮШҜШ§ ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШіЩ„ЩҲЩғЩҠЩҮ.pptx
Ш§Щ„Ш§ЩҮШҜШ§ ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШіЩ„ЩҲЩғЩҠЩҮ.pptxM H
Мэ
ШӘШӘЩҶШ§ЩҲЩ„ Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮШ© ШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„Ш№Щ…Щ„ЩҠШ© Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ© ЩҲЩғЩҠЩҒЩҠШ© ШӘЩҶШёЩҠЩ…ЩҮШ§ ЩҲШӘШӯЩӮЩҠЩӮЩҮШ§ ЩҲЩҒЩӮ Щ…Ш№Ш§ЩҠЩҠШұ Щ…ШӯШҜШҜШ©. ШӘШ№ШӘЩ…ШҜ ЩҮШ°ЩҮ Ш§Щ„ШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒ Ш№Щ„Щү ШӘШөЩҶЩҠЩҒ ШЁЩ„ЩҲЩ… Ш§Щ„Ш°ЩҠ ЩҠШұЩғШІ Ш№Щ„Щү Щ…ШіШӘЩҲЩҠШ§ШӘ Ш§Щ„ШӘЩҒЩғЩҠШұ Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш®ШӘЩ„ЩҒШ© ЩҲЩҠШұШҙШҜ Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш№Щ„Щ…ЩҠЩҶ ЩҒЩҠ ШӘШөЩ…ЩҠЩ… Ш§Щ„ШҜШұЩҲШі. ШӘШіШ№Щү Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮШ© Щ„ШӘШӯШҜЩҠШҜ ЩғЩҠЩҒЩҠШ© ШөЩҠШ§ШәШ© Ш§Щ„ШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ© ШЁЩҲШ¶ЩҲШӯ ЩҲШҜЩӮШ© Щ„Ш¶Щ…Ш§ЩҶ ЩҒШ§Ш№Щ„ЩҠШ© Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„Щ….Chain_of_Infe ction вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.ppt
Chain_of_Infe ction вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.pptM H
Мэ
The document explains the route of transmission for pathogens, detailing methods by which they move from reservoirs to new hosts. Transmission can occur through direct contact, air, or insects. These modes highlight the various ways pathogens can spread.Chain_of_Infecti on вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.ppt
Chain_of_Infecti on вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.pptM H
Мэ
The document outlines the stages of infectious disease transmission, starting with the infectious agent, which is a disease-causing microorganism. It details the reservoir host, where pathogens reside, and the portal of exit, which describes how pathogens leave the host. Finally, it explains the routes of transmission, including direct contact, air, and insects.Chain_of_In fection вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.ppt
Chain_of_In fection вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.pptM H
Мэ
The document outlines the six links in the chain of infection, which include the infectious agent, reservoir host, portal of exit, and route of transmission. It explains that the infectious agent is any disease-causing microorganism, while the reservoir host is the organism that houses these microbes. Additionally, it details how pathogens can exit the reservoir and the various methods through which transmission can occur, such as direct contact and airborne spread.Chain_of_Infe ction вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.ppt
Chain_of_Infe ction вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.pptM H
Мэ
The document outlines the six links in the chain of infection, which include the infectious agent, reservoir host, portal of exit, and route of transmission. It explains that an infectious agent is a disease-causing microorganism, while the reservoir host is where microbes reside. Additionally, the document discusses how pathogens exit and transmit to new hosts through various means such as contact or air.fractu re.pptx
fractu re.pptxM H
Мэ
A fracture is a disruption in bone continuity, classified as open or closed, with varying degrees of tissue damage. Common types include greenstick, transverse, oblique, and spiral fractures, each with distinct characteristics and causes. Treatment options range from conservative approaches like casts to surgical interventions such as internal and external fixation, with complications like infections and bone death being potential risks.fractur e.pptx
fractur e.pptxM H
Мэ
The document discusses the functions and types of bones, as well as fracture classifications and their causes, including the specifics of open and closed fractures. It outlines various treatment methods, including internal and external fixation options, and the complications associated with fractures. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of prevention through nutrition, physical activity, and awareness of bone health, particularly in aging populations.fractu re.pptx
fractu re.pptxM H
Мэ
The document provides an overview of the musculoskeletal system, including its functions such as protection of organs, support, and mobility. It details types of bone fractures, their classifications, and associated complications, as well as treatment methods like internal and external fixation. Additionally, it discusses prevention strategies for bone health, including nutrition, physical activity, and factors affecting bone density.Geriatric Anesth esia.pptx
Geriatric Anesth esia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document discusses anesthetic techniques for older patients, comparing neuraxial and general anesthesia while considering surgical requirements, patient conditions, and preferences. It highlights the importance of adjusted dosages for anesthetic agents due to age-related physiological changes, and emphasizes the need for careful pain management to mitigate postoperative complications such as delirium and respiratory issues. Additionally, it addresses potential outcomes and recovery challenges faced by older adults undergoing surgery.Geriatric Anesthe sia.pptx
Geriatric Anesthe sia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document outlines anesthetic considerations for older adult patients, emphasizing tailored approaches to anesthesia based on individual health status and surgical contexts. Key points include altered drug sensitivity and metabolism, management of intraoperative fluid and hemodynamics, and pain management strategies to mitigate the risks of postoperative complications. Additionally, the document addresses the increased risks of delirium, functional recovery, and hospital readmission following surgery in this demographic.Geriatric Anesth esia.pptx
Geriatric Anesth esia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document discusses anesthetic techniques and considerations for older patients undergoing surgery, highlighting the need for tailored approaches due to altered drug responses, potential for complications, and pre-existing health conditions. Among the key points are the importance of routine laboratory tests, the careful selection of anesthetic agents, and fluid management strategies to avoid dehydration and hemodynamic instability. It also emphasizes the challenges of postoperative pain management and the risk of complications such as delirium, pulmonary issues, and functional recovery variability in this patient demographic.Geriatric Anest hesia.pptx
Geriatric Anest hesia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document discusses preoperative considerations for older patients undergoing surgery, highlighting that routine chest radiographs and laboratory testing may not be necessary unless specific conditions warrant them. It emphasizes the importance of tailored anesthetic techniques and pain management strategies for older adults, particularly addressing the risks of respiratory and cardiac complications, and outlines recommendations for intraoperative and postoperative care. Additionally, the document notes that advanced age increases the risk of mortality, complications, and delayed recovery, necessitating careful management and monitoring during the perioperative period.Geriatric Anesthesi a.pptx
Geriatric Anesthesi a.pptxM H
Мэ
The document discusses preoperative assessment and anesthesia management for older patients, highlighting the limited value of ECGs and chest radiographs in routine evaluations while emphasizing the importance of carefully tailored anesthetic approaches and fluid management. It outlines risks such as postoperative complications, including cardiac, pulmonary, and renal issues, while noting the increased sensitivity of older adults to certain anesthetics and opioids, necessitating cautious dosing. The document also addresses recovery challenges, including functional recovery and hospital readmission rates in older adults post-surgery.Geriatric An esthesia.pptx
Geriatric An esthesia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document outlines guidelines for preoperative testing and anesthesia considerations for older adults undergoing surgery, emphasizing that routine preoperative testing is generally unnecessary for minor procedures. It highlights the importance of patient-specific factors, such as comorbidities, in determining the need for specific tests and anesthetic choices, as older patients may require tailored approaches to minimize complications. Additionally, it addresses postoperative challenges, including pain management, recovery, and potential complications like delirium and acute kidney injury.Geriatric A nesthesia.pptx
Geriatric A nesthesia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document outlines comprehensive guidelines for the preoperative assessment and management of older patients, emphasizing the importance of evaluating baseline cognitive function and medication history to mitigate the risk of postoperative complications. It highlights that routine preoperative testing is typically unnecessary for minor surgeries, while certain medications must be carefully managed due to age-related pharmacodynamic changes. Additionally, it addresses anesthetic techniques, intraoperative management, and postoperative care, stressing risk factors for mortality, pulmonary and cardiac complications, and the variability in functional recovery among older adults.More Related Content
More from M H (20)
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.ppt
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.pptM H
Мэ
The document provides a detailed overview of various intestinal parasites, their characteristics, modes of transmission, clinical features, laboratory diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. It discusses infections caused by Ascaris lumbricoides, Enterobius vermicularis, Ancylostoma duodenale, and Trichuris trichiura, highlighting symptoms associated with each, such as abdominal discomfort and respiratory issues. Treatment options generally include anthelmintic medications like mebendazole and albendazole, alongside recommendations for improved sanitation and hygiene.Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.ppt
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.pptM H
Мэ
The document provides a detailed overview of various intestinal nematodes, including ascariasis caused by Ascaris lumbricoides, enterobiasis from Enterobius vermicularis, hookworm disease from Ancylostoma duodenale, and trichuriasis from Trichuris trichiura. It covers the geographical distribution, life cycle, pathogenicity, clinical features, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment options for these infections. Key treatments include mebendazole, albendazole, and preventive measures focusing on sanitation and hygiene.fluid an dd.ppt
fluid an dd.pptM H
Мэ
The document covers fluid volume disturbances and electrolyte imbalances in the human body, highlighting causes, symptoms, diagnostic evaluations, and management strategies for conditions such as hypovolemia, hypervolemia, hyponatremia, hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and hyperkalemia. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining electrolyte homeostasis for cellular activities, offers detailed information on acid-base balance, and describes various intravenous solutions used for treatment. Additionally, it outlines the roles of body buffer systems in regulating pH levels.fluid a nd.ppt
fluid a nd.pptM H
Мэ
The document provides an overview of fluid compartments, daily fluid intake and output, and the importance of electrolyte balance in the body. It details conditions such as fluid volume disturbances, electrolyte imbalances, and their clinical implications, along with diagnostic assessments and management strategies. Additionally, it discusses various IV solutions and buffer systems that regulate acid-base balance in the body.Ш§Щ„Ш§ЩҮШҜ Ш§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШіЩ„ЩҲЩғЩҠЩҮ.pptx
Ш§Щ„Ш§ЩҮШҜ Ш§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШіЩ„ЩҲЩғЩҠЩҮ.pptxM H
Мэ
ЩҠШӘЩҶШ§ЩҲЩ„ Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮШ© ШЈЩҮЩ…ЩҠШ© ШӘШөЩҶЩҠЩҒ ШЁЩ„ЩҲЩ… ЩҒЩҠ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ®Ш·ЩҠШ· Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠ ЩҲШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒЩҮ Ш§Щ„ШӘШұШЁЩҲЩҠШ©ШҢ ШӯЩҠШ« ЩҠШЁШұШІ ШҜЩҲШұ ЩҮШ°Ш§ Ш§Щ„ШӘШөЩҶЩҠЩҒ ЩҒЩҠ ШӘШӯШҜЩҠШҜ Ш§Щ„ШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ© ЩҲШӘШ№ШІЩҠШІ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„Щ… Щ…ЩҶ Ш®Щ„Ш§Щ„ Щ…ШіШӘЩҲЩҠШ§ШӘ Щ…ШӘШҜШұШ¬Ш© Щ…ЩҶ Ш§Щ„ШөШ№ЩҲШЁШ©. ЩғЩ…Ш§ ЩҠЩҶШ§ЩӮШҙ ЩғЩҠЩҒЩҠШ© ШөЩҠШ§ШәШ© Ш§Щ„ШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ© Ш§Щ„ШіЩ„ЩҲЩғЩҠШ© ЩҲЩҒЩӮШ§ЩӢ Щ„Щ…Ш№Ш§ЩҠЩҠШұ Щ…ШӯШҜШҜШ© ШӘШ¶Щ…ЩҶ ШӘШӯЩӮЩҠЩӮ Ш§Щ„ЩҶШӘШ§ШҰШ¬ Ш§Щ„Щ…ШұШ¬ЩҲШ©. Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮШ© ШӘШіЩ„Ш· Ш§Щ„Ш¶ЩҲШЎ Ш№Щ„Щү Ш§Щ„ЩҒШұЩҲЩӮ Ш§Щ„ЩҒШұШҜЩҠШ© ШЁЩҠЩҶ Ш§Щ„Щ…ШӘШ№Щ„Щ…ЩҠЩҶ ЩҲШ¶ШұЩҲШұШ© ШӘШ№ШҜЩҠЩ„ Ш§Щ„Ш·ШұЩӮ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ© ШЁЩ…Ш§ ЩҠШӘЩҶШ§ШіШЁ Щ…Ш№ Ш§ШӯШӘЩҠШ§Ш¬Ш§ШӘЩҮЩ….Ш§Щ„Ш§ЩҮШҜШ§ ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШіЩ„ЩҲЩғЩҠЩҮ.pptx
Ш§Щ„Ш§ЩҮШҜШ§ ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШіЩ„ЩҲЩғЩҠЩҮ.pptxM H
Мэ
ШӘШӘЩҶШ§ЩҲЩ„ Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮШ© ШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„Ш№Щ…Щ„ЩҠШ© Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ© ЩҲЩғЩҠЩҒЩҠШ© ШӘЩҶШёЩҠЩ…ЩҮШ§ ЩҲШӘШӯЩӮЩҠЩӮЩҮШ§ ЩҲЩҒЩӮ Щ…Ш№Ш§ЩҠЩҠШұ Щ…ШӯШҜШҜШ©. ШӘШ№ШӘЩ…ШҜ ЩҮШ°ЩҮ Ш§Щ„ШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒ Ш№Щ„Щү ШӘШөЩҶЩҠЩҒ ШЁЩ„ЩҲЩ… Ш§Щ„Ш°ЩҠ ЩҠШұЩғШІ Ш№Щ„Щү Щ…ШіШӘЩҲЩҠШ§ШӘ Ш§Щ„ШӘЩҒЩғЩҠШұ Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш®ШӘЩ„ЩҒШ© ЩҲЩҠШұШҙШҜ Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш№Щ„Щ…ЩҠЩҶ ЩҒЩҠ ШӘШөЩ…ЩҠЩ… Ш§Щ„ШҜШұЩҲШі. ШӘШіШ№Щү Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮШ© Щ„ШӘШӯШҜЩҠШҜ ЩғЩҠЩҒЩҠШ© ШөЩҠШ§ШәШ© Ш§Щ„ШЈЩҮШҜШ§ЩҒ Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ© ШЁЩҲШ¶ЩҲШӯ ЩҲШҜЩӮШ© Щ„Ш¶Щ…Ш§ЩҶ ЩҒШ§Ш№Щ„ЩҠШ© Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„Щ….Chain_of_Infe ction вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.ppt
Chain_of_Infe ction вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.pptM H
Мэ
The document explains the route of transmission for pathogens, detailing methods by which they move from reservoirs to new hosts. Transmission can occur through direct contact, air, or insects. These modes highlight the various ways pathogens can spread.Chain_of_Infecti on вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.ppt
Chain_of_Infecti on вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.pptM H
Мэ
The document outlines the stages of infectious disease transmission, starting with the infectious agent, which is a disease-causing microorganism. It details the reservoir host, where pathogens reside, and the portal of exit, which describes how pathogens leave the host. Finally, it explains the routes of transmission, including direct contact, air, and insects.Chain_of_In fection вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.ppt
Chain_of_In fection вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.pptM H
Мэ
The document outlines the six links in the chain of infection, which include the infectious agent, reservoir host, portal of exit, and route of transmission. It explains that the infectious agent is any disease-causing microorganism, while the reservoir host is the organism that houses these microbes. Additionally, it details how pathogens can exit the reservoir and the various methods through which transmission can occur, such as direct contact and airborne spread.Chain_of_Infe ction вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.ppt
Chain_of_Infe ction вҖ«вҖ¬ вҖ«вҖ¬.pptM H
Мэ
The document outlines the six links in the chain of infection, which include the infectious agent, reservoir host, portal of exit, and route of transmission. It explains that an infectious agent is a disease-causing microorganism, while the reservoir host is where microbes reside. Additionally, the document discusses how pathogens exit and transmit to new hosts through various means such as contact or air.fractu re.pptx
fractu re.pptxM H
Мэ
A fracture is a disruption in bone continuity, classified as open or closed, with varying degrees of tissue damage. Common types include greenstick, transverse, oblique, and spiral fractures, each with distinct characteristics and causes. Treatment options range from conservative approaches like casts to surgical interventions such as internal and external fixation, with complications like infections and bone death being potential risks.fractur e.pptx
fractur e.pptxM H
Мэ
The document discusses the functions and types of bones, as well as fracture classifications and their causes, including the specifics of open and closed fractures. It outlines various treatment methods, including internal and external fixation options, and the complications associated with fractures. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of prevention through nutrition, physical activity, and awareness of bone health, particularly in aging populations.fractu re.pptx
fractu re.pptxM H
Мэ
The document provides an overview of the musculoskeletal system, including its functions such as protection of organs, support, and mobility. It details types of bone fractures, their classifications, and associated complications, as well as treatment methods like internal and external fixation. Additionally, it discusses prevention strategies for bone health, including nutrition, physical activity, and factors affecting bone density.Geriatric Anesth esia.pptx
Geriatric Anesth esia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document discusses anesthetic techniques for older patients, comparing neuraxial and general anesthesia while considering surgical requirements, patient conditions, and preferences. It highlights the importance of adjusted dosages for anesthetic agents due to age-related physiological changes, and emphasizes the need for careful pain management to mitigate postoperative complications such as delirium and respiratory issues. Additionally, it addresses potential outcomes and recovery challenges faced by older adults undergoing surgery.Geriatric Anesthe sia.pptx
Geriatric Anesthe sia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document outlines anesthetic considerations for older adult patients, emphasizing tailored approaches to anesthesia based on individual health status and surgical contexts. Key points include altered drug sensitivity and metabolism, management of intraoperative fluid and hemodynamics, and pain management strategies to mitigate the risks of postoperative complications. Additionally, the document addresses the increased risks of delirium, functional recovery, and hospital readmission following surgery in this demographic.Geriatric Anesth esia.pptx
Geriatric Anesth esia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document discusses anesthetic techniques and considerations for older patients undergoing surgery, highlighting the need for tailored approaches due to altered drug responses, potential for complications, and pre-existing health conditions. Among the key points are the importance of routine laboratory tests, the careful selection of anesthetic agents, and fluid management strategies to avoid dehydration and hemodynamic instability. It also emphasizes the challenges of postoperative pain management and the risk of complications such as delirium, pulmonary issues, and functional recovery variability in this patient demographic.Geriatric Anest hesia.pptx
Geriatric Anest hesia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document discusses preoperative considerations for older patients undergoing surgery, highlighting that routine chest radiographs and laboratory testing may not be necessary unless specific conditions warrant them. It emphasizes the importance of tailored anesthetic techniques and pain management strategies for older adults, particularly addressing the risks of respiratory and cardiac complications, and outlines recommendations for intraoperative and postoperative care. Additionally, the document notes that advanced age increases the risk of mortality, complications, and delayed recovery, necessitating careful management and monitoring during the perioperative period.Geriatric Anesthesi a.pptx
Geriatric Anesthesi a.pptxM H
Мэ
The document discusses preoperative assessment and anesthesia management for older patients, highlighting the limited value of ECGs and chest radiographs in routine evaluations while emphasizing the importance of carefully tailored anesthetic approaches and fluid management. It outlines risks such as postoperative complications, including cardiac, pulmonary, and renal issues, while noting the increased sensitivity of older adults to certain anesthetics and opioids, necessitating cautious dosing. The document also addresses recovery challenges, including functional recovery and hospital readmission rates in older adults post-surgery.Geriatric An esthesia.pptx
Geriatric An esthesia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document outlines guidelines for preoperative testing and anesthesia considerations for older adults undergoing surgery, emphasizing that routine preoperative testing is generally unnecessary for minor procedures. It highlights the importance of patient-specific factors, such as comorbidities, in determining the need for specific tests and anesthetic choices, as older patients may require tailored approaches to minimize complications. Additionally, it addresses postoperative challenges, including pain management, recovery, and potential complications like delirium and acute kidney injury.Geriatric A nesthesia.pptx
Geriatric A nesthesia.pptxM H
Мэ
The document outlines comprehensive guidelines for the preoperative assessment and management of older patients, emphasizing the importance of evaluating baseline cognitive function and medication history to mitigate the risk of postoperative complications. It highlights that routine preoperative testing is typically unnecessary for minor surgeries, while certain medications must be carefully managed due to age-related pharmacodynamic changes. Additionally, it addresses anesthetic techniques, intraoperative management, and postoperative care, stressing risk factors for mortality, pulmonary and cardiac complications, and the variability in functional recovery among older adults.Щ…ШӯШ§Ш¶ШұШ© Ш§Ш§Щ„ШӘШҜШұЩҠШЁ 2023-2022Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҠШҜШ§ЩҶЩҠ -3.ppt
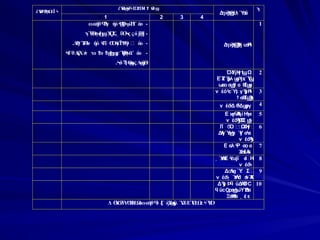
- 1. ПЎ О®О® Оҳ О®О» ОҺПӢ Пі ПҳПҹ ПЁ О®Ој ПӢ О“ О© О Оҳ Оҙ ПЁ ПһПң Пҹ П® Пҹ ПҜ П® ПЈ О” Оҹ ОӯОӘ Пҹ О®Ој ПҢ ПЁП Пҹ 4 3 2 1 1 ПҢ ПҘП®ПЁ Пҹ О” О®ПҲО” О§ Пі П§ Пҙ П” П О© ОӘОӨ Оҝ ОҚ Пӯ ПЈ ПӯПӯ - О— ОҺ ПҢО” ПӘ ПӨ П ПӣПӯПҘП®ПЁ Пҹ ПҗПҹ- О” О” Оі ПЈ П®П¬ П” ПЈ Пӯ ПӨ Пҙ П О• О®Оҳ О” Оё ПҗПӨ Пӯ П Пң ПӨ - О” ОӘО‘ О•О© ОӘОЈ П— ПҢО•ОҺ О© ОӘПӢ ПҘП®ПЁ Пҹ ПӨ П Пӣ - ПӢОӘ О°О— О” ПҢ ПҰ Пі П»Пӯ Пҹ П®ПҳПЈ 18 О”ПӨ П Пӣ О® О— П“ П® 3 О® ОҺ ПҢ Пҙ Пі ПЈ ПӮ Пҳ П“ О® О— П“ П® ОӯОҺПҢ ПҘ ПҙПЈ ПӮ Пҳ П“ Оҝ О®Пҙ ПҸ Пӯ Пҙ ПҸ - О— ОҺ ПҢО” О” О‘ ПҢО» ПӘ ПӨ П ПӣПӯПҘП®ПЁ Пҹ ПҗПҹ П® - О” Оё ОӘ ОӘОӨО— О” О© ПҢОҝ П Пң ПӨ Пҹ Пі П—П’ - О• О®Оҳ ПҙПҗ ПӨ Пҹ Пӯ О« ОҺ О· Оё Пғ О® Ој ПҰП« П® ПЈ ПһПіП® Пӯ Пҙ П—- Оү ОӯОҺ Пҳ Пҹ 2 О®О®Оҳ Оә ОЁ Пі ПҳПҹ П ПЈ 3 П• Пў Пӯ О•ОҺОҳ ОӨ ПіП® ПӨ Пҹ ОҺ О· ОӘО Пҹ ОҚ Пӯ ПңПӯ ПӯПӯ 4 О”ОӘ ПЈПҳ ПӨ Пҹ 5 О” Оё ОӘ ОӘОӨО— П Пң ПӨ Пҹ Пі Пү О®Оё О•ОҺОҝ О® Пӯ ПӨ Пҹ Пҙ П“ Пӯ Оҳ ОҢ Оі Пӯ Оғ ПӘП Пӯ 6 Пү О®Оё ОӘ Пӯ ПӨ Пҹ П‘ П« О©ОӘОЈ Оҳ П© Пӯ ПӯПӘ ПӨ П«Пӯ О®ПҢ Оҳ П’Пі Пӯ О— ОҺ ОӨП„Ој О‘ ПӘ П ПӨ 7 О®ПҲОӯОҺ ПғП№ ОҚ Пұ ПЁ ПүО®Оё Пӯ ПӨ П Пҹ
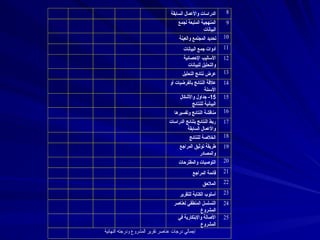
- 2. 8 вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШіШ§ШЁЩӮШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§ШЈЩ„Ш№Щ…Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШҜШұШ§ШіШ§ШӘвҖ¬ 9 вҖ«Щ„Ш¬Щ…Ш№вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШӘШЁШ№Ш©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҶЩҮШ¬ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШЁЩҠШ§ЩҶШ§ШӘвҖ¬ 10 вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„Ш№ЩҠЩҶШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш¬ШӘЩ…Ш№вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШӯШҜЩҠШҜвҖ¬ 11 вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШЁЩҠШ§ЩҶШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш¬Щ…Ш№вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈШҜЩҲШ§ШӘвҖ¬ 12 вҖ«Ш§ШҘЩ„ШӯШөШ§ШҰЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШЈЩ„ШіШ§Щ„ЩҠШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„Щ„ШЁЩҠШ§ЩҶШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШӘШӯЩ„ЩҠЩ„вҖ¬ 13 вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШӯЩ„ЩҠЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҶШӘШ§ШҰШ¬вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№ШұШ¶вҖ¬ 14 вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁШ§Щ„ЩҒШұШ¶ЩҠШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҶШӘШ§ШҰШ¬вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШЈЩ„ШіШҰЩ„Ш©вҖ¬ 15 15 вҖ«ЩҲШ§ШЈЩ„ШҙЩғШ§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш¬ШҜШ§ЩҲЩ„вҖ¬ - вҖ«Щ„Щ„ЩҶШӘШ§ШҰШ¬вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШЁЩҠШ§ЩҶЩҠШ©вҖ¬ 16 вҖ«ЩҲШӘЩҒШіЩҠШұЩҮШ§вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҶШӘШ§ШҰШ¬вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶШ§ЩӮШҙШ©вҖ¬ 17 вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШҜШұШ§ШіШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁШӘЩҶШ§ШҰШ¬вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҶШӘШ§ШҰШ¬вҖ¬ вҖ«ШұШЁШ·вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШіШ§ШЁЩӮШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§ШЈЩ„Ш№Щ…Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ 18 вҖ«Щ„Щ„ЩҶШӘШ§ШҰШ¬вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш®Ш§Щ„ШөШ©вҖ¬ 19 вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШұШ§Ш¬Ш№вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩҲШ«ЩҠЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш·ШұЩҠЩӮШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„Щ…ШөШ§ШҜШұвҖ¬ 20 вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„Щ…ЩӮШӘШұШӯШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘЩҲШөЩҠШ§ШӘвҖ¬ 21 вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШұШ§Ш¬Ш№вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…Ш©вҖ¬ 22 вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш§Щ„ШӯЩӮвҖ¬ 23 вҖ«Щ„Щ„ШӘЩӮШұЩҠШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩғШӘШ§ШЁШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈШіЩ„ЩҲШЁвҖ¬ 24 вҖ«Щ„Ш№ЩҶШ§ШөШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҶШ·ЩӮЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШіЩ„ШіЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШҙШұЩҲШ№вҖ¬ 25 вҖ«ЩҒЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§ШҘЩ„ШЁШӘЩғШ§ШұЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШЈЩ„ШөШ§Щ„Ш©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШҙШұЩҲШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҶЩҮШ§ШҰЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШҜШұШ¬ШӘЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШҙШұЩҲШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩӮШұЩҠШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№ЩҶШ§ШөШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҜШұШ¬Ш§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘШ¬Щ…Ш§Щ„ЩҠвҖ¬
- 3. ПЎ О” О· ОҺ ОӯО» ОҺПӢ П—П§ ПЈ Пҹ П§ ОӯОҺ ПҢ О“ О© О Оҳ Оҙ ПҙПЈ ПһПң Пҹ П® Пҹ ПҜ П® ПЈ ОӯОҺ ПҢ О” Оҹ ОӯОӘ ПҙПӨ П Пҹ Пҹ 4 3 2 1 1 О” О· ОҺ П… О— П—П§ ПЈ П Пҹ ПЎ Пі П§Пҹ Пү О®Оё ОҪ О®ПҢ ПҲО— ПҢОҝ Пӯ ПӨ П Пҹ Пҹ Пў Пҙ ПЁП’ - ОҺ Оҳ ОЈ О°Оҹ ПӮПҢ ПЎ ПӨП«П»ПҰ ПЈПӘ Пҳ ЛҜ ПһПӣ ПіПў Пҹ - .О” О’ ОіОҺ ОҪ О®ПҢ О“ О° Оҹ ОӘОЁ Оҳ ОіОҚ П’ ПҢОҝ ПЁ ПӨ Пҹ Пҹ П¬ ПЎ П’ - ОёО‘ О®О§ ОҮПү Оҝ ОҺ Оҳ ПҢОҝ ПһПң П° Пҹ П® П®ПЈ ПҰ ПЈПқ ПҳП§П»П’ - . Оҙ ОҙОҳ ПӮО‘О®Оҳ ПЈ Пһ П ПЈ Пӯ ПЈ 2 ОҸОҺ ПҢ О— Оі О© ПЈ Пі ПҜ ПЈ О•ОҺ ОЈ ПҒО» ОҺ П ПЈ ПӯПЎ ПіП« П” ПЈ ПүОҝ О— ОЈ Пӯ ПӯПЈ Пҹ ПҜ Пӯ ПЈ Пӯ 3 ОҪ ОӯПҢ Оі ОіО— Пҹ ПІП“ Пқ П Пҹ О— ОЈ ПҜ Пӯ ПЈ П Пҹ 4 ОҪ ОӯПҢО” О” Оі Пҹ Пҗ Пҹ ПЈ Пј 5 О• ОҺ О‘ ОҜ О— П— ПӯПҹ ПЎ Пҹ П» ОҪ ОӯПҢ О© О© ОЈ П Пҹ ПЈ Пҹ 6 О“ ОҜ Оҹ П· ОҚ ПЎ ОҚ О© О§О— ОіОҚ П¬ О” О‘ ОіОҺ ОҺ Оі П§ ПЈ Пҹ Пқ ПӯПҹ Пӯ ОҪ ОӯПҢ П Пҹ 7 О• О» ОЎ Оҝ Пӯ Пҹ Пӯ Пӯ О— ОӯО‘ ПӘП§ Пӯ 8 ОҺ ОӣО• ОӯП… ПҠ ОҜ Пӯ О— ЛҜ П§П§ Пҹ Пі Пӯ ОҪ ОӯПҢ Пҹ 9 О” ОӣОұ ОҺ ПЈ ОЈПҹ ОҚ ПӯПЈ ОҪ ОӯПҢ ОҺ ОӣОұ ОҺ О‘ Пҹ ЛҜ П§П” П§ Пҹ 10 О” Оі ПӢО” О‘ ОҺ Оҹ П П·ПҘ П№ ПӢ ПҒ Пү ОҺО© ПҘ ПІПҳ П§ ПЈ Пҹ П“ Пҹ Пӯ Оһ ОҺ О— Оӯ П§ Пҹ Пӯ ЛҜ Пө О¶ ОҺО®О» ОҺПӢО•ОҺ Оҹ ОӯО© ОҺ Оҹ ОҮ П—ПЁ ПЈ ПЁ ПІПҹ ПӨ О“ О” ОҺ ОҺ Оҳ Оҹ ОӯО©Пү О®Оё ПҙП¬ ПЁ Пҹ П¬ Пӯ Пӯ ПӨ Пҹ
- 4. вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҠШҜШ§ЩҶЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҶШІЩҲЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮШЁЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш·Ш§Щ„ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩӮЩҠЩҠЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШіШӘЩ…Ш§ШұШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҠШҜШ§ЩҶЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҶШІЩҲЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮШЁЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш·Ш§Щ„ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩӮЩҠЩҠЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШіШӘЩ…Ш§ШұШ©вҖ¬
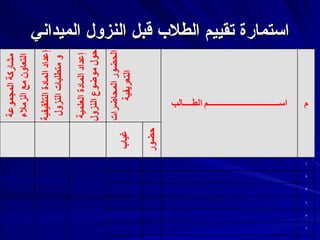
- 5. вҖ«ШҜШұШ¬Ш©вҖ¬...... вҖ«Ш§ЩӮШҙШ©вҖ¬uвҖ«ЩҶвҖ¬вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩӮЩҠЩҠЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШіШӘЩ…Ш§ШұШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШҜШұШ¬Ш©вҖ¬...... вҖ«Ш§ЩӮШҙШ©вҖ¬uвҖ«ЩҶвҖ¬вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩӮЩҠЩҠЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШіШӘЩ…Ш§ШұШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Ш§Щ„ШӯШёШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩҒШ§Ш№Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӯШ§Ш¶ШұЩҠЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШҘЩ„Щ„Щ…Ш§Щ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁШ§Щ„Щ…ЩҲШ¶ЩҲШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш·ШұЩҠЩӮШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш№ШұШ¶вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Ш§Щ„ШіЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШұЩӮЩ…вҖ¬