23 Sampling.pdf
- 1. Sampling Theorem Dr. G.Aarthi, Associate Professor, School of Electronics Engineering
- 2. INTRODUCTION âĒ Modulation is the process of frequency translation in which any one parameter(Amplitude, frequency or phase) of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with instantaneous value of low frequency modulating signal. âĒ Modulation is either analog or digital. 2
- 3. Why Analog to Digital Transmission âĒAnalog transmission âĒ Transmission method of conveying voice, data, image, signal or video information using a continuous signal. âĒ It could be the transfer of an analog source signal using an analog modulation method such as FM or AM, or no modulation at all. âĒ Disadvantages âĒ High signal-to-noise ratio is required. âĒ In long distances, high output systems, analog is unattractive due to attenuation problems . âĒ The effects of random noise can make signal loss and distortion impossible to recover .
- 4. Digital Transmission âĒ Less Power needed to transmit over the same channel. âĒ Transmit longer distances. âĒ Compatibility with other digital systems âĒ A digital signal is superior to an analog signal because it is more robust to noise . âĒ Easily be recovered, corrected and amplified. âĒ For this reason, the tendency today is to change an analog signal to digital data
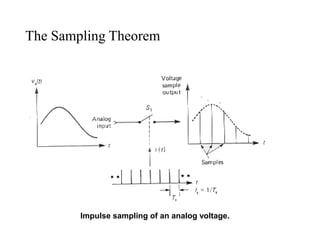
- 5. The Sampling Theorem Impulse sampling of an analog voltage.
- 6. The Sampling Theorem âĒ A sampler is a mixer with a train of very narrow pulses as the local oscillator input. âĒ If the analog input is sampled instantaneously at regular intervals at a rate that is at least twice the highest analog frequency fs > 2fa(max) âĒ then the samples contain all of the information of the original signal.
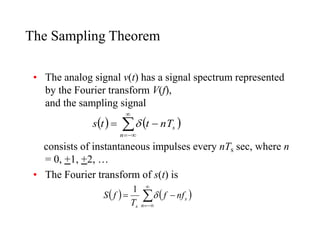
- 7. The Sampling Theorem âĒ The analog signal v(t) has a signal spectrum represented by the Fourier transform V(f), and the sampling signal consists of instantaneous impulses every nTs sec, where n = 0, +1, +2, âĶ âĒ The Fourier transform of s(t) is ïĻ ïĐ ïĻ ïĐ ïĨ ïĨ ïïĨ ï― ï ï― n s nT t t s ïĪ ïĻ ïĐ ïĻ ïĐ s n s nf f T f S ï ï― ïĨ ïĨ ïïĨ ï― ïĪ 1
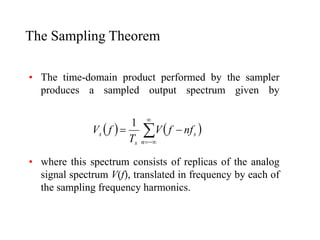
- 8. The Sampling Theorem âĒ The time-domain product performed by the sampler produces a sampled output spectrum given by âĒ where this spectrum consists of replicas of the analog signal spectrum V(f), translated in frequency by each of the sampling frequency harmonics. ïĻ ïĐ ïĻ ïĐ s n s s nf f V T f V ï ï― ïĨ ïĨ ïïĨ ï― 1
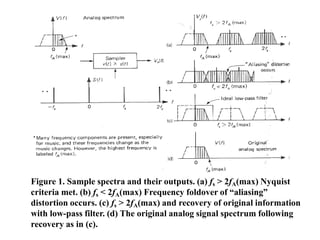
- 9. The Sampling Theorem âĒ The sampler is a wideband (harmonic) mixer producing upper and lower sidebands at each harmonic of the sampling frequency. âĒ Figure 1-a illustrates the correct way to sample: if sampling is done at fs > 2fA(max) the upper and lower sidebands do not overlap each other âĒ and the original information can be recovered by passing the signal through a low-pass filter (see Figure 1c and d).
- 10. Figure 1. Sample spectra and their outputs. (a) fs > 2fA(max) Nyquist criteria met. (b) fs < 2fA(max) Frequency foldover of âaliasingâ distortion occurs. (c) fs > 2fA(max) and recovery of original information with low-pass filter. (d) The original analog signal spectrum following recovery as in (c).
- 11. The Sampling Theorem âĒHowever, if the sampling rate is less than the Nyquist rate, fs < 2fA(max) the sidebands overlap, as shown in Figure 1b. âĒThe result is frequency-folding or aliasing distortion, which makes it impossible to recover the original signal without distortion.
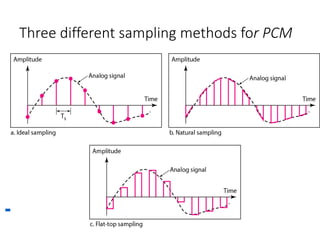
- 12. Sampling ï Analog signal is sampled every TS secs. ï Ts is referred to as the sampling interval. ï fs = 1/Ts is called the sampling rate or sampling frequency. ï There are 3 sampling methods: ï Ideal - an impulse at each sampling instant ï Natural - a pulse of short width with varying amplitude ï Flat top - sample and hold, like natural but with single amplitude value 12
- 13. Three different sampling methods for PCM 13