24 Dna Mitosis
- 1. Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division âĶ 2006-2007
- 2. Making New Cells Making New DNA 2006-2007
- 3. Where it all beganâĶ You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentenceâĶ
- 4. And now look at youâĶ How did you get from there to here?
- 5. Going from egg to babyâĶ. the original fertilized egg has to divideâĶ and divideâĶ and divideâĶ and divideâĶ Getting from there to hereâĶ
- 6. Why do cells divideâĶ for reproduction one celled organisms (clones) for growth & development from fertilized egg to multi-celled organism for repair replace cells that die from normal wear & tear or from injury amoeba starfish
- 7. Dividing cellsâĶ What has to be copied DNA organelles cell membrane lots of other molecules enzymes animal cell plant cell
- 8. Copying DNA A dividing cell duplicates its DNA creates 2 copies of all DNA separates the 2 copies to opposite ends of the cell splits into 2 daughter cells But the DNA starts loosely wound in the nucleus If you tried to divide it like that, it could tangle & break nucleus cell DNA
- 9. Organizing & packaging DNA nucleus cell DNA nucleus cell 4 chromosomes in this organism DNA in chromosomes in everyday âworkingâ cell DNA in chromosomes in cell getting ready to divide DNA has been âwound upâ
- 10. Chromosomes of Human Female 46 chromosomes 23 pairs
- 11. Chromosomes of Human Male 46 chromosomes 23 pairs
- 12. Paired bases DNA structure double helix 2 sides like a ladder Bases match together A pairs with T A : T C pairs with G C : G
- 13. Watson and Crick
- 14. Copying DNA Matching bases allows DNA to be easily copied
- 15. Making new DNA Copying DNA replication DNA starts as a double-stranded molecule matching bases (A:T, C:G) then it unzipsâĶ
- 16. DNA replication Strands âunzipâ at the weak bonds between bases
- 17. DNA replication Enzyme DNA polymerase adds new bases DNA polymerase DNA bases in nucleus
- 18. Copying DNA DNA Polymerase Build daughter DNA strand use original parent strand as âtemplateâ add new matching bases synthesis enzyme = DNA polymerase
- 19. New copies of DNA Get 2 exact copies of DNA to split between new cells DNA polymerase DNA polymerase
- 20. Copied & Paired Up Chromosomes
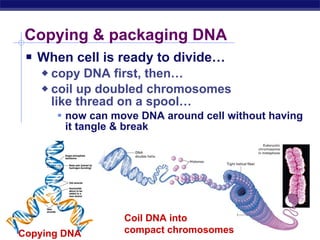
- 21. Copying & packaging DNA When cell is ready to divideâĶ copy DNA first, thenâĶ coil up doubled chromosomes like thread on a spoolâĶ now can move DNA around cell without having it tangle & break Copying DNA Coil DNA into compact chromosomes
- 22. double-stranded human chromosomes ready for mitosis
- 23. DNA must be duplicatedâĶ nucleus cell DNA in chromosomes nucleus cell duplicated chromosomes chromosomes in cell 4 single-stranded chromosomes duplicated chromosomes 4 double-stranded chromosomes
- 24. Mitosis: Interphase Dividing DNA & cells Stage 1: cell copies DNA nucleus cell DNA Copy DNA!
- 25. Mitosis: Prophase Stage 2: DNA winds into chromosomes DNA is wound up into chromosomes to keep it organized nucleus cell duplicated chromosomes Wind up!
- 26. Mitosis: Metaphase Stage 3: Chromosomes line up chromosomes line up in middle attached to protein âcablesâ that will help them move duplicated chromosomes lined up in middle of cell Meet In Middle!
- 27. Mitosis: Anaphase Stage 4: Chromosomes separate chromosomes split, separating pairs start moving to opposite ends chromosomes split & move to opposite ends Apart!
- 28. Mitosis: Telophase Stage 5: Cell starts to divide cells start to divide nucleus forms again Divide!
- 29. Mitosis: Cytokinesis Stage 6: DNA unwinds again cells separate now they can do their every day jobs
- 30. New âdaughterâ cells Get 2 exact copies of original cells same DNA â clonesâ
- 31. Cell division in Animals
- 32. Mitosis in whitefish embryo
- 33. Mitosis in plant cell
- 34. onion root tip
- 35. Overview of mitosis Copy DNA Wind Up Meet in Middle Apart Divide
- 36. 2006-2007 Any Questions?? Any Questions??
Editor's Notes
- #7: Unicellular organisms Cell division = reproduction Reproduces entire organism& increase population Multicellular organisms Cell division provides for growth & development in a multicellular organism that begins as a fertilized egg Also use cell division to repair & renew cells that die from normal wear & tear or accidents