3 heat of diplacement
- 1. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT Thermochemistry Heat of Displacement The Heat of Diplacement is the heat change when one mole of metal is diplaced from its solution by a more electropositive metal. What is meant by âdisplacementâ reaction? Metal that more electropositive will displace metal that is less electropositive from its salt solution. Example 1; Zn + Cu2+ ï Zn2+ + Cu âH= â210 kJmol-1 Energy Zn + Cu2+ âH= â210 kJmol-1 Zn2+ + Cu When 1 mole Cu is displaced by Zn, 210 kJ heat energy is released/given out. 1
- 2. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT Example 2; Zn + Pb2+ ï Zn2+ + Pb âH= â112 kJmol-1 Energy Zn + Pb2+ âH= â112 kJmol-1 Zn2+ + Pb When 1 mole Pb is displaced by Zn, 112 kJ heat energy is released/given out. Example 3; Mg + Fe2+ ï Mg2+ + Fe âH= â80 kJmol-1 Energy Mg + Fe2+ âH= â80 kJmol-1 Mg2+ + Fe When 1 mole Fe is displaced by Mg, 80 kJ heat energy is released/given out. 2
- 3. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT Method to determine heat of displacement To determine the heat of diplacement of copper by zinc â Beaker that contain 1 g zinc powder Thermometer (excess) Polystyrene cup 50.0 cm3 copper(II) â sulphate solution 0.1 mol dm-3 Procedure; 50 cm3 copper(II) sulphate solution of 0.1 mol dm-3 is measured with measuring cylinder 50ml and poured into polystyrene cup, record the temperature with termometer (0-110)oC. 1.0 g metal powder is weighed by using electronic balance and quickly added into the polystyrene cup that contain copper(II) sulphate solution. The mixture is stirred using the thermometer. The highest/maximum temperature of heat is recorded. Repeat the step by using different substance. [if necessary] 3
- 4. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT Data tabulation Initial temperature of copper(II) sulphate , y CuSO4 /oC Highest/maximum temperature for the z solution /oC Temperature change /oC (z â y) = ÓĻ [Note : mass of zinc is used in excess] Chemical equation for the reaction Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) â Cu (s) + ZnSO4 (aq) Ionic Equation Zn + Cu2+ â Cu + Zn2+ Calculation the heat of displacement of copper by zinc; 1. Calculate the number of mole of Cu formed No of moles of Zn = . mass . = 1.0 = 0.015 mol molar mass 65 MV 0.1 X 50 No. of moles CuSO4 = = 1000 = 0.005 mol 1000 (No. of moles of CuSO4) 0.005 < 0.015 (No of moles of Zinc) [Important notes: calculation MUST based on CuSO4 solution because quantity of zinc used in excess] FBCE; 1 mole of CuSO4 produces 1 mole of Cu Therefore; 0.005 mole of CuSO4 produces 0.005 mole of Cu Thus; No. of mole of Cu formed = 0.005 mol 4
- 5. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT 2. Calculate the heat released/given out Heat release/given out = mcÓĻ (in exp.) = 50 x 4.2 x ÓĻ J Volume of solution = 50 x 4.2 x ÓĻ kJ 1000 3. Calculate the heat of diplacement for 1 mole copper by zinc 50 x 4.2 x ÓĻ 0.005 mole of copper diplaced produced kJ 1000 Therefore; When 1 mole of copper is diplaced by zinc, the heat released is 50 x 4.2 x ÓĻ 1000 . = kJ mol-1 0.005 = 50 x 4.2 x ÓĻ X 1 . kJ mol-1 1000 0.005 50 x 4.2 x ÓĻ = kJ mol-1 5 Thus; The heat of diplacement of copper by zinc âH = â 50 x 4.2 x ÓĻ kJ mol-1 5 5
- 6. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT Calculation heat of displacement Question 1 Excess iron powder is added into 50 cm3 copper(II) chloride solution, CuCl2 1.0 mol dm-3, brown solid is formed and blue solution change to green. Iron has displace copper from its salt solution. The following data is get from above experiment. Initial temperature for copper(II)chloride solution = 28.0 oC Highest temperature for mixture solution = 57.0 oC Calculate heat changes when 1 mol of copper is displace by iron. Solution chemical equation; Fe (s) + CuCl2 (aq) â FeCl2 (aq) + Cu (s) Ionic equation; Fe (s) + Cu2+ (aq) â Cu (s) + Fe+2 (aq) Step 1 : Calculate the number of mole of Cu formed MV 1 X 50 No. of mol CuCl2 = 1000 = 1000 = 0.05 mol No. of mol Fe = (no need to calculate because is in excess) FBCE; No. of mole of Cu formed = 0.05 mol Step 2 : Calculate the heat released/given out 6
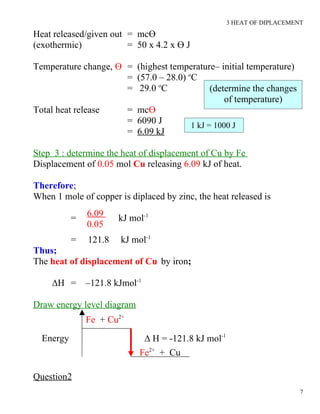
- 7. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT Heat released/given out = mcÓĻ (exothermic) = 50 x 4.2 x ÓĻ J Temperature change, ÓĻ = (highest temperatureâ initial temperature) = (57.0 â 28.0) oC = 29.0 oC (determine the changes of temperature) Total heat release = mcÓĻ = 6090 J 1 kJ = 1000 J = 6.09 kJ Step 3 : determine the heat of displacement of Cu by Fe Displacement of 0.05 mol Cu releasing 6.09 kJ of heat. Therefore; When 1 mole of copper is diplaced by zinc, the heat released is = 6.09 kJ mol-1 0.05 = 121.8 kJ mol-1 Thus; The heat of displacement of Cu by iron; âH = â121.8 kJmol-1 Draw energy level diagram Fe + Cu2+ Energy â H = -121.8 kJ mol-1 Fe2+ + Cu Question2 7
- 8. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT Study the following equation; Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) â Cu (s) + FeSO4 (aq) âH = -250 kJ mol-1 If excessive iron powder is add into 100 cm3 copper(II) sulphate solution 0.25 mol dm-3, calculate i. Heat released ii. Temperature rise iii. Mass of copper that is displace iv. Mass of salt that formed if it crystalize v. Draw energy level diagram If magnesium powder is use to replace iron powder, is it the energy that release is more higher, same or lower. [Ar = Cu, 64; Fe, 56; S, 32; O, 16] Solution Chemical equation; Fe (p) + CuSO4 (ak) â FeSO4 (ak) + Cu (p) Ionic equation; Fe (p) + Cu2+ (ak) â Fe+2 (ak) + Cu (p) i : calculate no. of mole of Cu formed MV 0.25 X 100 0.025 mol No. of mol CuSO4 = 1000 = 1000 = No. of mol Fe = (no need to calculate because excessive) 8
- 9. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT FBCE; 1 mol CuSO4 produced 1 mol Cu Therefore; 0.025 mol CuSO4 produce 0.025 mol Cu Thus; No. of mole of Cu formed = 0.025 mol calculate the heat released by 0.025 mol of Cu in the exp. [from question: âH = -250 kJ mol-1] Thatâs mean; When 1 mole Cu is displaced by Fe, 250 kJ heat energy is released/given out. Therefore; 0.025 mol Cu is diplaced by Fe, heat released is; = 0.025 Ã 250 kJ = 6.25 kJ = 6250 J Change to unit of kJ, because we want to find ÓĻ Thus; Heat released/given out = 6.25 kJ or 6250 J ii: determine the temperature changes during the reaction [Heat released/given out = 6250 J] Heat released/given out = mcÓĻ 6250 = 100 x 4.2 x ÓĻ ÓĻ = 14.9 oC Therefore; The increases in temperature = 14.9 oC iii: determine the mass of copper that is diplace 9
- 10. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT [from the previous information above] No. of mole of Cu formed = 0.025 mol No. of mol Cu = mass of Cu Ar Cu Mass of Cu = 0.025 Ã 64 = 1.6 g iv: determine the mass of salt formed FBCE; 1 mol CuSO4 produced 1 mol FeSO4 Therefore; 0.025 mol CuSO4 produce 0.025 mol FeSO4 Thus; No. of mole of FeSO4 formed = 0.025 mol No. of mol FeSO4 = mass of FeSO4 Mr FeSO4 Mass of FeSO4 = 0.025 Ã [56 + 32 + 4(16)] = 3.8 g v : draw energy level diagram Energy Fe + Cu2+ â H = -250 kJ mol-1 Fe2+ + Cu Question 3 10
- 11. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT 100 cm3 copper(II) nitrate solution 0.2 mol dm-3 is poured into plastic container. Temperature is recorded. Then excess magnesium powder is added to the solution. The mixture is stirred and the temperature rises is recorded. The temperature shows an increases of 5 oC. (a) What is the colour of the solution in the plastic container; i. before magnesium powder is place? ii. after magnesium powder is place? (b) Write the total ionic equation of the reaction. (c) How many mole of copper(II) nitrate reacts? (d) Calculate the heat releases in this experiment. (e) Calculate the heat energy release when one mol of copper is formed. (f) What is the heat of displacement of copper? (g) Draw energy level diagram for this experiment. (h) Why magnesium used is in form of fine powder not granulated? (i) i. if potassium hydroxide solution is mix with the solution in plastic beaker in the end of the experiment, what can you observe? ii. write the chemical equation for the reaction in (i)(i). iii. write the ionic equation for the reaction in (i)(i). SOLUTION 11
- 12. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT (a) i. blue ii. colourless (b) Mg (aq) + Cu2+ (aq) â Mg2+ (aq) + Cu (s) MV 0.2 x 100 (c) no. of mol Cu(NO3)2 = 1000 = 1000 = 0.02 mol (d) Heat release = mcÓĻ (during reaction) = 100 x 4.2 x 5.0 J = 2100 J = 2.1 kJ (e) FBCE; 1 mol CuSO4 produced 1 mol Cu Therefore; 0.02 mol CuSO4 produce 0.02 mol Cu Thus; No. of mole of Cu formed = 0.02 mol When 0.02 mol of Cu diplaced by Mg, 2.1 kJ of heat released. Therefore; 1 mol of Cu diplaced by Mg will releases heat; 2.1 kJ mol-1 = 0.02 = 105 kJ mol-1 (f) The heat of displacement of copper = -105 kJ mol-1 Heat change, âH = -105 kJ mol-1 (g) Energy level diagram 12
- 13. 3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT Mg (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Energy â H = - 105 kJ mol-1 Mg2+ (aq) + Cu (s) (h) To increase the total surface area per volume for magnesium, thus it will increase the rate of reaction. (i) i. white precipitate formed ii. Mg(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KOH (aq) â Mg(OH)2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq) iii. Mg2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) â Mg(OH)2 (s) Learning task: pg 158 no. 1 & 2 Effective Practise: pg. 158 no. 3 Kamal Ariffin B Saaim SMKDBL http://kemhawk.webs.com/ 13



![3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT
Method to determine heat of displacement
To determine the heat of diplacement of copper by zinc
â
Beaker that
contain
1 g zinc powder Thermometer
(excess)
Polystyrene
cup
50.0 cm3 copper(II)
â sulphate solution
0.1 mol dm-3
Procedure;
50 cm3 copper(II) sulphate solution of 0.1 mol dm-3 is
measured with measuring cylinder 50ml and poured into
polystyrene cup, record the temperature with
termometer (0-110)oC.
1.0 g metal powder is weighed by using electronic balance and
quickly added into the polystyrene cup that contain copper(II)
sulphate solution.
The mixture is stirred using the thermometer.
The highest/maximum temperature of heat is recorded.
Repeat the step by using different substance. [if necessary]
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3heatofdiplacement-100719091931-phpapp01/85/3-heat-of-diplacement-3-320.jpg)
![3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT
Data tabulation
Initial temperature of copper(II) sulphate ,
y
CuSO4 /oC
Highest/maximum temperature for the
z
solution /oC
Temperature change /oC (z â y) = ÓĻ
[Note : mass of zinc is used in excess]
Chemical equation for the reaction
Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) â Cu (s) + ZnSO4 (aq)
Ionic Equation
Zn + Cu2+ â Cu + Zn2+
Calculation the heat of displacement of copper by zinc;
1. Calculate the number of mole of Cu formed
No of moles of Zn = . mass . = 1.0 = 0.015 mol
molar mass 65
MV 0.1 X 50
No. of moles CuSO4 = = 1000 = 0.005 mol
1000
(No. of moles of CuSO4) 0.005 < 0.015 (No of moles of Zinc)
[Important notes: calculation MUST based on CuSO4 solution
because quantity of zinc used in excess]
FBCE;
1 mole of CuSO4 produces 1 mole of Cu
Therefore;
0.005 mole of CuSO4 produces 0.005 mole of Cu
Thus;
No. of mole of Cu formed = 0.005 mol
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3heatofdiplacement-100719091931-phpapp01/85/3-heat-of-diplacement-4-320.jpg)


![3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT
Study the following equation;
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) â Cu (s) + FeSO4 (aq)
âH = -250 kJ mol-1
If excessive iron powder is add into 100 cm3 copper(II) sulphate
solution 0.25 mol dm-3, calculate
i. Heat released
ii. Temperature rise
iii. Mass of copper that is displace
iv. Mass of salt that formed if it crystalize
v. Draw energy level diagram
If magnesium powder is use to replace iron powder, is it the energy
that release is more higher, same or lower.
[Ar = Cu, 64; Fe, 56; S, 32; O, 16]
Solution
Chemical equation;
Fe (p) + CuSO4 (ak) â FeSO4 (ak) + Cu (p)
Ionic equation;
Fe (p) + Cu2+ (ak) â Fe+2 (ak) + Cu (p)
i : calculate no. of mole of Cu formed
MV 0.25 X 100 0.025 mol
No. of mol CuSO4 = 1000 = 1000 =
No. of mol Fe = (no need to calculate because excessive)
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3heatofdiplacement-100719091931-phpapp01/85/3-heat-of-diplacement-8-320.jpg)
![3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT
FBCE;
1 mol CuSO4 produced 1 mol Cu
Therefore;
0.025 mol CuSO4 produce 0.025 mol Cu
Thus;
No. of mole of Cu formed = 0.025 mol
calculate the heat released by 0.025 mol of Cu in the exp.
[from question: âH = -250 kJ mol-1]
Thatâs mean;
When 1 mole Cu is displaced by Fe, 250 kJ heat energy is
released/given out.
Therefore;
0.025 mol Cu is diplaced by Fe, heat released is;
= 0.025 Ã 250 kJ
= 6.25 kJ
= 6250 J Change to unit of kJ, because we
want to find ÓĻ
Thus;
Heat released/given out = 6.25 kJ or 6250 J
ii: determine the temperature changes during the reaction
[Heat released/given out = 6250 J]
Heat released/given out = mcÓĻ
6250 = 100 x 4.2 x ÓĻ
ÓĻ = 14.9 oC
Therefore;
The increases in temperature = 14.9 oC
iii: determine the mass of copper that is diplace
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3heatofdiplacement-100719091931-phpapp01/85/3-heat-of-diplacement-9-320.jpg)
![3 HEAT OF DIPLACEMENT
[from the previous information above]
No. of mole of Cu formed = 0.025 mol
No. of mol Cu = mass of Cu
Ar Cu
Mass of Cu = 0.025 Ã 64
= 1.6 g
iv: determine the mass of salt formed
FBCE;
1 mol CuSO4 produced 1 mol FeSO4
Therefore;
0.025 mol CuSO4 produce 0.025 mol FeSO4
Thus;
No. of mole of FeSO4 formed = 0.025 mol
No. of mol FeSO4 = mass of FeSO4
Mr FeSO4
Mass of FeSO4 = 0.025 Ã [56 + 32 + 4(16)]
= 3.8 g
v : draw energy level diagram
Energy
Fe + Cu2+
â H = -250 kJ mol-1
Fe2+ + Cu
Question 3
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3heatofdiplacement-100719091931-phpapp01/85/3-heat-of-diplacement-10-320.jpg)


