3 Types of Argument.pdf for effective comunication
- 1. 3 Types of Argument: Classical, Rogerian, Toulmin Get ready to take notes
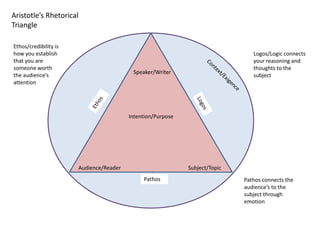
- 2. Aristotleâs Rhetorical Triangle Speaker/Writer Audience/Reader Subject/Topic Intention/Purpose Pathos Logos/Logic connects your reasoning and thoughts to the subject Pathos connects the audienceâs to the subject through emotion Ethos/credibility is how you establish that you are someone worth the audienceâs attention
- 4. Classical 1. Introduction(Exordium):Capture the audienceâs attention. Introduce the issue and create exigence for your claim. Why is this an issue? Why do we need to pay attention? 2. Statement of Background (Narratio) Supply the context needed to understand the case you present. What circumstances, occurrences, or conditions do we need to be made aware of? 3. Proposition (Partitio) State your position (claim/thesis), based on the information you have presented, and outline the major points that will follow. The partitio divides the background information from the reasoning. 4. Proof (Confirmatio)Present your reasons, subclaims, and evidence. Establish inferences between claim and support. Provide additional evidence for subclaims and evidence, where necessary. Explain and justify assumptions. 5. Refutation (Refutatio) Anticipate and refute opposing arguments. In this section you demonstrate that you have already considered the issue thoroughly and have reached the only reasonable conclusion. 6. Conclusion (Peroratio) Summarize the most important points. Make a final appeal to values, motivations, and feelings that are likely to encourage the audience to identify with your argument
- 5. Classical âĒ Example: I have a dream speech. âĒ When to use: â More direct â More aggressive â To establish power â When the audience already respects you or â When the audience needs to get something from you.
- 7. 1. Zeke! (yelling) (Introductionâcapture attention) 2. Stop antagonizing your brother. He had a tough day at school. (Background âcontext) 3. The next time you gloat about beating Luigiâs Mansion you are going to be sitting in time out. Proposition (claim/thesis) 4. This is the third time that you have brought this up in the past 15 minutes. He is crying on the floor. He knows that you have beat the game; you are just being mean. Proof 5. I know that he is a little pipsqueak sometimes, and he gets on your nerves by talking about âWee-geeâs Mansionâ, but you have to set a good example for him. Refutation (concession and counterargument) 6. If you say one more thing about beating Luigiâs mansion you will be in time out. I donât care if we are in a grocery store and your friends are watching. Conclusion (Peroratio) Classical Example
- 8. Rogerian 1. Introduction of Problem: State the problem you hope to resolve. By presenting your issue as a problem you raise the possibility of positive change. Often opponents will want to solve the same problem. 2. Summary of Opposing Views: As accurately and neutrally as possible, state the views of the people with whom you disagree. By doing this you show that you are capable of listening without judging and have given a fair hearing to people who think differently from you. 3. Statement of Understanding: Also called the statement of validity. Show that you understand that there are situations in which these views are valid. Which parts of the opposing argument s do you concede? Under which conditions might you share these views? 4. Statement of Your Position: Now that readers have seen that youâve given full consideration to views other than your own, they should be prepared to listen fairly to your views. State your position. 5. Statement of Contexts: Describe situations in which you hope your views will be honored. By showing that your position has merit in specific contexts, you recognize that people wonât agree with you all of the time. However, opponents are allowed to agree in part and share common ground. 6. Statement of Benefits: Appeal to the self-interest of your opponents by showing how they would benefit from accepting your position; this concludes your essay on a hopeful, positive note.
- 9. Rogerian âĒ Example: Queen Elizabethâs speech at Tilbury âĒ When to use: â With an audience who you donât relate to â With an audience who doesnât share your views â With an audience who has authority over you â With an audience who is overly sensitive
- 11. Rogerian Example 1. Peanut, you have all of this homework that has to get done. (Problem) 2. I know that you really want to beat Luigiâs Mansion, and that you are hungry. (Summary of Opposing Views) 3. If you had all of your home work done, you could play as much Luigiâs Mansion as you want. (Statement of Understanding) 4. Right now, I need for you to finish your homework. When your homework is finished, you can have a snack. (Statement of Your Position) 5. I am going to put the package of fruit snacks over your place at the table so that you can eat it as soon as you finish. (Statement of Contexts) 6. When you finish your homework, you can play Luigiâs Mansion until bedtime, and you will have good grades in school. (Statement of Benefits)
- 12. Toulmin The twentieth-century British philosopher Stephen Toulmin noticed that good, realistic arguments typically will consist of six parts. He used these terms to describe the items. 1. Data: The facts or evidence used to prove the argument 2. Claim: The statement being argued (a thesis) 3. Warrants: The general, hypothetical (and often implicit) logical statements that serve as bridges between the claim and the data. 4. Qualifiers: Statements that limit the strength of the argument or statements that propose the conditions under which the argument is true. 5. Rebuttals: Counter-arguments or statements indicating circumstances when the general argument does not hold true. 6. Backing: Statements that serve to support the warrants (i.e., arguments that don't necessarily prove the main point being argued, but which do prove the warrants are true.)
- 13. Toulmin âĒ Example John Gageâs The Shape of Reason âĒ When to use: â When speaking to the scientific community â When you are trying to put the facts at the forefront of your argument â When your audience is very logical and rational
- 14. from John Gage's The Shape of Reason âĒ Congress should ban animal research (Claim #1) because animals are tortured in experiments that have no necessary benefit for humans such as the testing of cosmetics (Data). The well being of animals is more important than the profits of the cosmetics industry (Warrant). Only congress has the authority to make such a law (Warrant)because the corporations can simply move from state to state to avoid legal penalties (Backing). Of course, this ban should not apply to medical research (Qualifier). A law to ban all research would go too far (Rebuttal).So, the law would probably (qualifier) have to be carefully written to define the kinds of research intended (claim #2). âĒ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yZJFDSEBORw
- 16. 1. Reagan, when was the last time you took a shower? â Reagan: I donât remember. â Me: So it has been a while then. (Data) 2. You need to take a shower. (Claim) 3. You are starting to get stinky. Your hair is looking a little crazy. (Warrants) 4. Birds will build a nest in your hair if it isnât clean and brushed. You donât want to be the stinky girl at school. (Qualifiers) 5. My Husband yelling from the other room: âShe always smells like cinnamon and sugar.â â Me: Usually she does, but she is getting a little ripe. (Rebuttals) 6. You are a precious girl, but you still have to take a shower. (Backing) Toulmin Example