3 work charting_methods
- 2. Objective • Objectively document the work task or process for analysis • Many methods are available • New ones are invented regularly • Break down the job into sub-components or tasks • Describe the tasks in a meaningful way 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 2
- 3. Pareto Chart • Items of interest are identified and measured on a common scale • Then ordered in ascending order, creating a cumulative distribution 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 3
- 4. Pareto Chart • Pareto principle: 80% of the total activity can be found in the first 20% of the items. • Goal is to identify the appropriate 20% for analysis. – 80% of inventory is associated with 20% of the parts. – 80% of the injuries are associated with 20% of the jobs. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 4
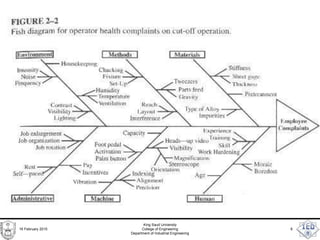
- 5. Fishbone Diagram (Cause-Effect) • Identifies components lead to undesirable (desirable) event in a process • Principle event is identified at the fish head • Associated contributing factors are identified using a tree type structure. • Closely related to many different charts used in safety analysis (Fault-Tree method) 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 5
- 6. Example 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 6
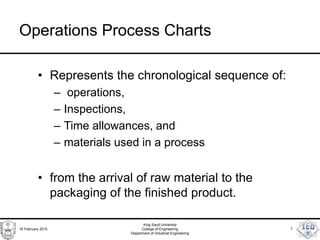
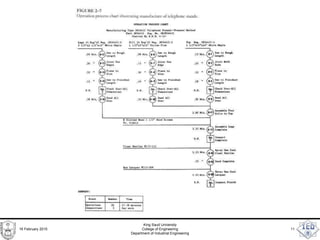
- 7. Operations Process Charts • Represents the chronological sequence of: – operations, – Inspections, – Time allowances, and – materials used in a process • from the arrival of raw material to the packaging of the finished product. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 7
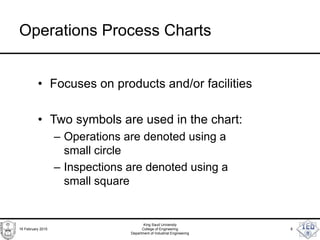
- 8. Operations Process Charts • Focuses on products and/or facilities • Two symbols are used in the chart: – Operations are denoted using a small circle – Inspections are denoted using a small square 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 8
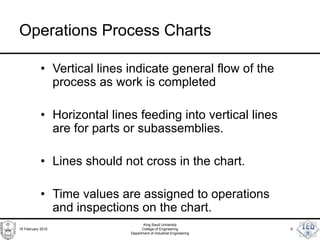
- 9. Operations Process Charts • Vertical lines indicate general flow of the process as work is completed • Horizontal lines feeding into vertical lines are for parts or subassemblies. • Lines should not cross in the chart. • Time values are assigned to operations and inspections on the chart. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 9
- 10. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 10
- 11. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 11
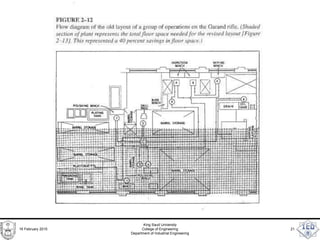
- 12. Flow Process Charts • Identify operations, inspections, materials, moves, storages, and delays involved in making a part or completing a process. • Show all events in the correct sequence. • Show the relationship between parts and fabrication complexity. • used for workers, components, or sub- assemblies. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 12
- 13. Flow Process Charts • Distinguish between produced and purchased parts. • Provide information on the number of employees utilized and the time required to perform each operation and inspection. • More details than operations process charts 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 13
- 14. Flow Process Charts • Two types are commonly used: – Product or material – Operative or person • Help identify nonproduction hidden costs such as distances traveled, delays, and temporary storage. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 14
- 15. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 15
- 16. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 16
- 17. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 17
- 18. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 18
- 19. Flow Diagrams • Supplement to Flow process charts to indicate process flow • Overhead pictorial plan of the facility. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 19
- 20. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 20
- 21. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 21
- 22. Worker and Machine Process Charts • Show time relationship between the working cycle of a person and the operating cycle of a machine(s) at a single workstation. • Machine times and operator times must be known for each element • Chart drawn vertically to scale. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 22
- 23. Worker and Machine Process Charts • Solid lines represent productive time, • Breaks indicate idle time, • Dotted lines represent non-productive time. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 23
- 24. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 24
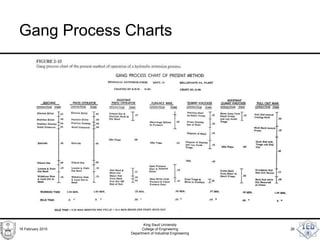
- 25. Gang Process Charts • Worker and Machine Process charts showing many workers are called Gang Process Charts. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 25
- 26. Gang Process Charts 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 26
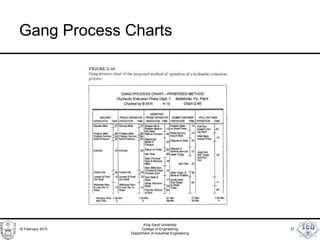
- 27. Gang Process Charts 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 27
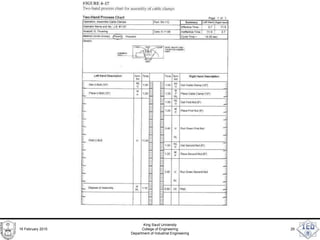
- 28. Two-Handed Process Chart • Left-hand / right-hand chart • Operator process chart. • Is a flow process chart directed at an operator • Each hand is documented separately. • Useful when doing work methods analysis. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 28
- 29. 16 February 2015 King Saud University College of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering 29