304127466-Whole-Numbers_for class 6-ppt.ppt
- 3. MATHEMATICS FORM 1 WHOLE NUMBERS COUNTING PLACE VALUE WRITING & READING
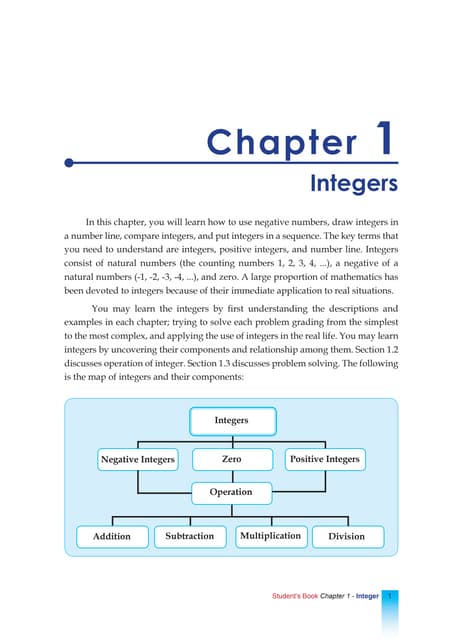
- 4. CONCEPT OF WHOLE NUMBER ’éŚ WRITING AND READING WHOLE NUMBERS ’éŚ COUNTING WHOLE NUMBERS ’éŚ IDENTIFY PLACE VALUE
- 5. Whole numbers are used in currency.
- 6. WHOLE NUMBERS ’éŚWhole numbers are a set of counting numbers that starts with 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ŌĆ”. ’éŚThe smallest whole number is zero (0)
- 7. WRITING AND READING WHOLE NUMBERS ONE SIXTY FOURTY- THREE ONE HUNDREDS TWENTY-ONE FOUR THOUSAND AND TEN
- 8. COUNTING WHOLE NUMBERS ’éŚCount on in tens from 30 to 100. ’éŚCount back in hundreds from 1500 to 700. 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100. 1500, 1400, 1300, 1200, 1100, 1000, 900, 800, 700.
- 9. PLACE VALUE ’éŚThe value of a digit depends on its place in the whole number. Each place has a different value which is known as the place value.
- 10. What is the number represented by the diagram? 100 HUNDREDS 30 TENS 6 UNITS
- 11. Activity 1: What is the place value of 9? The number of students in the school: 1 389 students
- 12. Answer: THOUSANDS HUNDREDS TENS UNITS 1 3 8 9
- 13. Activity 2: What is the place value of 3? The numbers of butterfly in the garden : 3 291 butterflies
- 14. Answer: THOUSANDS HUNDREDS TENS UNITS 3 2 9 1 Exercises
- 15. SYSTEM OF WRITING WHOLE NUMBERS Million Thousand Hundred Hundred Million Ten Million Unit Hundred Thousand Ten Thousand Unit Hundred Ten Unit
- 16. THANK TOU
- 18. Vocabulary standard form ŌĆō a number is written using digits and place value (the regular way to write numbers). expanded form ŌĆō a number is written as a sum using the place and value of each digit.
- 20. How To Read a Large Number ŌĆóNumbers are grouped in sets of three (each set is called a period). ŌĆóOnly read three numbers at a time. ŌĆóSay the name of the period that the numbers are in. ŌĆóSay ŌĆ£andŌĆØ for the decimal, but do not say ŌĆ£andŌĆØ if there isnŌĆÖt a decimal.
- 21. Example 4,658,089 Millions period Thousands period Ones period Four million, six hundred fifty-eight thousand, eighty-nine.
- 22. Comparing Numbers ŌĆó Line up the numbers vertically (up and down) by the ones place (or the decimal, if there is one). ŌĆó Start at the left and compare the digits. ŌĆó Move towards the right until you find a difference.
- 23. Just a ReminderŌĆ” < means ŌĆ£less than.ŌĆØ > means ŌĆ£greater than.ŌĆØ = means ŌĆ£equal to.ŌĆØ
- 24. Example 45,312 45,321 45,312 45,321 1 is less than 2 <
- 25. Example 2 ŌĆō Put the numbers in order from least to greatest. 321; 345; 354; 29; 1,013; 312; 332 321 345 354 29 1013 312 332 largest smallest 29 1,013 312 321 332 345 354 < < < < <
- 26. Rounding Whole Numbers Rounding to a specific place: ’éŚ Identify the place (ŌĆ£nearest hundredŌĆØ, for example) ’éŚ Look at the number immediately to th right. ’éŚ Is it 5 or higher? Round up. ’éŚ Is it 4 or lower? It stays the same. ’éŚ All digits to the right of the specified become zeros.
- 27. Try these examples Round to the nearest hundred: 4,856 10,527 234,567 8,648,078 And the answers areŌĆ” 4,900 10,500 234,600 8,648,100
- 28. Key Terms ’éŚ Addends: numbers being added ’éŚ Sum or total: The answer or result of addition. ’éŚ Commutative property of addition: two or more numbers can be added in either order without changing the sum ’éŚ Associative property of addition: When more than two numbers are being added, the addends can be grouped by two at a time in any way.
- 30. Addition ’éŚ Addition occurs when you join two numbers together. These numbers are called addends. 4 + 2 = ? Addends
- 31. You add the two addends together to get a sum. 4 + 2 = 6 Sum
- 32. LetŌĆÖs add large numbers. 12 and 34 Line up numbers 12 + 34 Line up the digits on top of each other starting with the number
- 33. LetŌĆÖs add large numbers. 12 and 34 Line up numbers 12 + 34 6 Line up the digits on top of each other starting with the number on the right (the rightmost digit, which is called the ŌĆ£onesŌĆØ place.) Then add the numbers that are on top of each other like you normally would add numbers.
- 34. LetŌĆÖs add large numbers. 12 and 34 Line up numbers 12 + 34 6 Line up the digits on top of each other starting with the number on the right (the rightmost digit, which is called the ŌĆ£onesŌĆØ place.) Then add the numbers that are on top of each other like you normally would add numbers.
- 35. LetŌĆÖs add large numbers. 12 and 34 Line up numbers 12 + 34 46 Line up the digits on top of each other starting with the number on the right (the rightmost digit, which is called the ŌĆ£onesŌĆØ place.) And do the same for the other column of numbers.
- 36. Adding larger numbers... You may have to ŌĆ£carryŌĆØ numbers to the next column of numbers being added if the first column is over 9. 2 3 1 + 4 5 9
- 37. Adding larger numbers... You may have to ŌĆ£carryŌĆØ numbers to the next column of numbers being added if the first column is over 9. 2 3 1 + 4 5 9 0 Since 9+1=10, we will write the last digit of 10
- 38. Adding larger numbers... You may have to ŌĆ£carryŌĆØ numbers to the next column of numbers being added if the first column is over 9. 2 3 1 + 4 5 9 0 Since 9+1=10, we will write the last digit of 10 1
- 39. Adding larger numbers... You may have to ŌĆ£carryŌĆØ numbers to the next column of numbers being added if the first column is over 9. 2 3 1 + 4 5 9 0 Now we will add the 3 and 5, and also the 1 since it was 1
- 40. Adding larger numbers... You may have to ŌĆ£carryŌĆØ numbers to the next column of numbers being added if the first column is over 9. 2 3 1 + 4 5 9 9 0 Now we will add the 3 and 5, and also the 1 since it was 1
- 41. Adding larger numbers... You may have to ŌĆ£carryŌĆØ numbers to the next column of numbers being added if the first column is over 9. 2 3 1 + 4 5 9 9 0 Now we will add the 2 and 4 that in the far left column. 1
- 42. Adding larger numbers... You may have to ŌĆ£carryŌĆØ numbers to the next column of numbers being added if the first column is over 9. 2 3 1 + 4 5 9 6 9 0 Now we will add the 2 and 4 that in the far left column. 1
- 43. With some practice, you will be able to successfully add positive whole numbers! This will be useful in all aspects of this class AND in your everyday life. LetŌĆÖs look at a real-world example...
- 44. You graduated from Islamic College!!!! As some of your graduation gifts, you receive gifts from family and friends with the values of $50, $129, $78, and $23.
- 45. You will simply need to ADD all of those numbers up to get the total. 5 0 1 2 9 7 8 + 2 3
- 46. 5 0 1 2 9 7 8 + 2 3 0 Keep in mind to line up the places, add each column, and carry if the number has more than one digit! 0+9+8+3=20 2
- 47. 5 0 1 2 9 7 8 + 2 3 8 0 Keep in mind to line up he places, add each column, and carry if the number has more than one digit! 2+5+2+7+2=18 2 1
- 48. 5 0 1 2 9 7 8 + 2 3 2 8 0 eep in mind to line up aces, add each column, d carry if the number s more than one digit! 1+1=2 2 1
- 49. 5 0 1 2 9 7 8 + 2 3 2 8 0 You got $280 in gifts! Congratulations!!! 2 1
- 50. ŌĆó Adding in columns - Uses no equal sign 5 + 5 10 897 + 368 1265 Simple Complex Answer is called ŌĆ£sum Table of Digits
- 51. What is Subtraction? Subtracting whole numbers is the inverse operation of adding whole numbers.
- 52. Subtraction ’éŚ Subtraction occurs when you take one number away from another number. 5 - 2 = ?
- 53. When you subtract the numbers, you end up with the difference. 5 - 2 = 3 Difference
- 54. Subtractions with one digit are usually fairly easy. Things start getting complicated when you have more than one digit and you cannot remove the number at the bottom from the number on top such as when doing 85 ŌłÆ 8
- 55. Example Since you could not remove 8 from 5, you
- 56. You can also write the problem without the tens and the ones to make it look simpler as illustrated below
- 57. Another example Always start with the ones. 5424 - 756
- 58. Step #1 Borrow a 10 from 2 tens The problem becomes
- 59. Step #2 Borrow 1 hundred from 4 hundreds. 1 hundred = 10 tens. Then add 10 tens to 1 ten to make it 11 tens
- 60. Step #3 Borrow 1 thousand from 5 thousands. 1 thousand = 10 hundreds. Then add 10 hundreds to 3 hundreds to make it 13 hundreds Then, just subtract now since all numbers at the bottom are smaller than the number on top
- 61. LetŌĆÖs Try Some! 4,987 - 2,158 3,230 - 320 17 7 212 9 2 8 2, 1,9 1 0
- 62. onclusion ’éŚ Now you should be able to add and subtract single digit numbers by using pictures to solve the problems given to you. You should also understand what an addend, sum, and difference is.
- 63. 63 Multiplication ŌĆó In Arithmetic - Indicated by ŌĆ£timesŌĆØ sign (x). Learn ŌĆ£TimesŌĆØ Table 6 x 8 = 48 In Arithmetic
- 64. ŌĆó Complex Multiplication - Carry result to next column. 64 Complex Multiplication Problem: 48 x 23 48 X 23 4 + 2 48 X 23 144 + 2 48 X 23 144 + 1 6 48 X 23 144 + 1 960 1104 Same process is used when multiplying three or four-digit problems.
- 65. 65 MULTIPLICATION PRACTICE EXERCISES 1. a. 21 x 4 b. 81 x 9 c. 64 x 5 d. 36 x 3 2. a. 87 x 7 b. 43 x 2 c. 56 x 0 d. 99 x 6 3. a. 24 x 13 b. 53 x 15 c. 49 x 26 d. 55 x 37 84 729 320 108 609 86 0 594 312 795 1274 2035
- 66. 66 MULTIPLICATION PRACTICE EXERCISES (conŌĆÖt) 4. a. 94 x 73 b. 99 x 27 c. 34 x 32 d. 83 x 69 5. a. 347 x 21 b. 843 x 34 c. 966 x 46 6. a. 360 x 37 b. 884 x 63 c. 111 x 19 6862 2673 1088 5727 7287 28,662 44,436 13,320 55,692 2109 7. a. 493 x 216 b. 568 x 432 c. 987 x 654 106,488 245,376 645,498
- 67. 67 Finding out how many times a divider ŌĆ£goes intoŌĆØ a whole number. ŌĆó Finding out how many times a divider ŌĆ£goes intoŌĆØ a whole number. Division 15 5 = 3 15 3 = 5
- 68. 68 Shown by using a straight bar ŌĆ£ ŌĆ£ or ŌĆ£ ŌĆ£ sign. ŌĆó Shown by using a straight bar ŌĆ£ ŌĆ£ or ŌĆ£ ŌĆ£ sign. 48 5040 1 48 ŌĆ£goes intoŌĆØ 50 one time. 48 1 times 48 = 48 2 50 minus 48 = 2 & bring down the 4 4 0 48 goes into 24 zero times. 0 Bring down other 0. 48 goes into 240, five times 5 240 0 5 times 48 = 240 240 minus 240 = 0 remainder So, 5040 divided by 48 = 105 w/no remainder. Or it can be stated: 48 ŌĆ£goes intoŌĆØ 5040, ŌĆ£105 timesŌĆØ
- 69. 69 DIVISION PRACTICE EXERCISES 1. a. b. c. 2. a. b. c. 3. a. b. 211 62 92 13 310 101 256 687 4. a. b. 98 67 48 5040 7 434 9 828 9 117 12 3720 10 1010 23 5888 56 38472 98 9604 13 871 5. a. b. 50 123 50 2500 789 97047
- 70. 70 DIVISION PRACTICE EXERCISES (conŌĆÖt) 6. a. b. 7. a. b. 8. a. b. 7 9000 61 101 67 r 19 858 r 13 9. a. b. 12 r 955 22 r 329 21 147 3 27000 32 1952 88 8888 87 5848 15 12883 994 12883 352 8073
- 72. Problem: Evaluate the following arithmetic expression: 3 + 4 x 2 Solution: Student 1 Student 2 3 + 4 x 2 3 + 4 x 2 = 7 x 2 = 3 + 8 = 14 = 11
- 73. To add and to subtract: we do the operations from left to right
- 74. To multiply and to divide: do the operation from left to right
- 75. To perform computation involving combined operations, a)first, multiply or divide from left to right b)then, add or subtract from left to right
- 76. To perform computations involving combined operations that include brackets ( ), work that brackets first then, multiply or divide from left to right lastly, add or subtract from left to right
- 77. SUMMARY COMBINED OPERATIONS To perform computations involving combined operations: 1.Work the brackets ( ) first. 2.Then, multiply or divide. 3.Finally add or subtract from left to right.