3d printing...
Download as pptx, pdf1 like458 views
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process where a 3D model is sliced into layers and printed one layer at a time. The first 3D printer was developed in 1981 by Hideo Kodama, while Chuck Hull developed the first commercial 3D printer in 1984 and coined the term "stereolithography." 3D printing works by modeling a virtual object, printing it through layer-by-layer deposition of material, and then finishing the printed object. Applications of 3D printing include automotive parts, electronics, art, prototypes, education, healthcare, and fashion. Advantages are the ability to print complex geometries and movable parts, print in remote locations, and send digital designs over the internet to be printed.
1 of 18
Downloaded 11 times














Ad
Recommended
3D printers
3D printersSuDarshan Gj
Ã˝
The document summarizes information about 3D printing from an overview presented by Sudarshan GJ. It discusses the basics of 3D printing including how it works by building objects layer by layer, common printing methods like stereolithography and fused deposition modeling, materials that can be used, and applications in industries like manufacturing, clothing, medicine, and architecture. The future of 3D printing is also discussed including possibilities like 3D printed organs and food.3D printing PPT
3D printing PPTDandu Shaik Vaseem Akram
Ã˝
3D printing is an automated process that builds three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer rather than removing material. It was invented in the 1980s and first used commercially for rapid prototyping. There are several methods of 3D printing including selective laser sintering, stereolithography, and fused deposition modeling. 3D printing can use materials like plastic, metal, and food and has applications in manufacturing, medicine, fashion, and more. While it enables customization and rapid production, there are limitations on size and intellectual property issues need addressing.3D Printing PPT
3D Printing PPTOECLIB Odisha Electronics Control Library
Ã˝
The document discusses 3D printing and additive manufacturing. It defines 3D printing as a process that uses additive manufacturing to create 3D objects from a digital file by laying down successive layers of material. The document outlines several 3D printing methods like selective laser sintering, stereolithography, and fused deposition modeling. It also discusses applications of 3D printing like prototyping and challenges like intellectual property issues.Design & fabrication model of 3 d printing machine
Design & fabrication model of 3 d printing machineRavikumarBaraker
Ã˝
This document discusses the design and fabrication of a 3D printing machine. It provides details on the history of 3D printing, the basic process which involves layer-by-layer deposition of material, and the key components of a 3D printer including the print bed, hot end, extruder, and filament. The document outlines the progress made on building the 3D printer, describes Fused Deposition Modeling as the method used, and discusses advantages like reduced costs and limitations such as limited print size. Applications are mentioned in fields like architecture, medicine, aerospace, and optics.3D printing
3D printingGalgotias College of Engg. & Tech.
Ã˝
3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing that creates 3D objects by laying down successive layers of material using CAD software to guide the process. CAD software allows for accurate designs and documentation of parts, while 3D printing techniques like stereolithography, fused deposition modeling, selective laser melting, and laminated object manufacturing build objects layer by layer from digital models. While offering advantages like customization and reduced waste, 3D printing also faces limitations in materials used, maximum size, and potential safety issues.impact and non impact printers
impact and non impact printers ShouaQureshi
Ã˝
This document discusses different types of printers and their components and functions. It begins by distinguishing between impact printers, which use mechanical parts to print, and non-impact printers, which print without striking the paper. It then focuses on inkjet printers, describing their print heads, ink cartridges, stepper motors, and paper feeding systems. Specific components like nozzles and stepper motors are also defined. The printing processes for inkjet and laser printers are outlined in multiple stages. Applications of inkjet and laser printers in different fields are also mentioned.3D PRINTING
3D PRINTINGToshendra Rajwade
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of 3D printing, including its history, terminology, processes, methods, applications, challenges and advantages/disadvantages. 3D printing involves using additive manufacturing to create 3D objects by laying down successive layers of material based on a digital model. It was developed in the 1980s and now allows for rapid prototyping of custom parts using various techniques like selective laser sintering, stereolithography and fused deposition modeling. While 3D printing enables quick prototyping and modeling, it also faces challenges regarding intellectual property and potential illegal uses.3D -Printing
3D -PrintingAadesh Neupane
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of 3D printing, detailing its principles, processes, and applications across various fields including industrial manufacturing, medical uses, and hobbyist activities. It discusses different 3D printing techniques, such as extrusion deposition and stereolithography, and highlights the materials used, as well as challenges faced within the industry. Additionally, the document touches on the implications of 3D printing technology, including concerns regarding accessibility and illegal usage.3d printing
3d printingVikram raja
Ã˝
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that builds 3D objects layer by layer using digital files. It allows for rapid prototyping and production of customized parts. The document discusses various 3D printing technologies like stereolithography and multi-jet modeling that use lasers or inkjet printing to bind powder or liquid materials. Applications include healthcare, design prototyping, education, and more local manufacturing. Advantages are rapid production and customization while disadvantages include limitations of size and cost.3d Printing Technology by Sai Thangella
3d Printing Technology by Sai Thangellasadekha
Ã˝
The seminar presented by T. Sai Kumar Reddy at Jyothishmathi Institute of Technological Sciences focused on 3D printing technology, explaining its additive manufacturing process and potential applications. 3D printing allows for the creation of complex three-dimensional objects from digital models with minimal waste, offering benefits such as custom parts and prototyping. However, the technology also raises concerns about its use in illegal activities and the need for regulation of the products created.3 d – printing
3 d – printingSiddharth Panigrahi
Ã˝
3D printing, an emerging technology, allows for creating three-dimensional objects from digital models through an additive process that builds layers of material. This technique enables customized production with less waste and has applications in various industries, including manufacturing, food, and medicine. However, it also raises concerns about intellectual property rights and the potential misuse of the technology for illegal purposes.3D Priinters
3D Priinters ShouaQureshi
Ã˝
3D printers use additive manufacturing to build solid objects layer by layer using materials like powdered resin, metal, or paper. CAD software is used to design objects digitally and can then be 3D printed. There are different types of 3D printing including direct 3D printing which uses inkjet printing technology to deposit material layer by layer, and binder 3D printing which is similar but uses a binder to join dry powder layers. 3D printing enables the creation of complex geometries and customized parts for industries like aerospace, automotive, robotics, and more.3 d printing with flying robots
3 d printing with flying robotsAccenture in India
Ã˝
3D printing takes a digital 3D design file and prints a physical object by laying down successive layers of material. This document discusses using a quadcopter drone equipped with a printing module to deposit expanding polyurethane foam in mid-air, allowing 3D printing to be done in three dimensions. It describes the design of the printing module attached to the quadcopter to deliver and deposit the foam material according to the 3D design path. This takes 3D printing to the next level by enabling fully three-dimensional printing in space rather than layer by layer on a surface.3D Printing: All the facts
3D Printing: All the factsFuture Platforms
Ã˝
This document discusses personal 3D printing. It outlines different types of 3D printers like stereolithography, scintering, and fused filament fabrication units. It describes how the RepRap project founded by Dr. Adrian Bowyer drove the development of low-cost personal 3D printing. It lists many popular 3D printer models from companies like Makerbot, Printrbot, and Ultimaker. The document discusses what types of objects can be 3D printed from toys to functional items. It also outlines where to get 3D printing content from through CAD tools, scanning, downloading from sites like Thingiverse, or customizing existing models.3D printing
3D printingPrasad Narasimhan
Ã˝
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves building a three dimensional object by laying down successive layers of material until the object is complete. It requires a 3D model file that is sliced into thin layers and sent to the printer. There are several common 3D printing methods, including stereolithography (SLA) which uses a UV laser to harden liquid resin into layers, fused deposition modeling (FDM) which extrudes melted thermoplastics to build layers, and selective laser sintering (SLS) which fuses powdered materials like metal with a laser.3D PRINTING SEMINAR
3D PRINTING SEMINARBaqar Rizvi
Ã˝
3D printing is a new technology that builds up physical objects layer by layer based on a 3D digital model. It allows for the creation of complex objects from a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, food, and bio materials. Some key applications of 3D printing include rapid prototyping, mass customization, architectural designs, dental applications, clothing, rocket engine parts, and bio printing of living organs. The future scope of 3D printing includes using it to print houses and entire buildings, as well as for space exploration through technologies like bio printing.Presentation on 3D Printing & its Applications by Jahan International
Presentation on 3D Printing & its Applications by Jahan InternationalRavindu Jain
Ã˝
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves depositing successive thin layers of material in different shapes to build a 3D object from a digital file. The digital file is first processed into horizontal layers and then loaded into a 3D printer which reproduces the object layer by layer, blending each layer seamlessly. 3D printing allows rapid prototyping and has applications in education, automobiles, design, architecture, biology, and robotics by enabling students and professionals to physically create detailed models, customized parts, prototypes, and works of art.3 D printing new 2015
3 D printing new 2015Akhil Jose
Ã˝
3D printing involves converting a virtual 3D model into a physical object by laying down successive layers of material. It began in the 1980s and is now used for industrial prototyping, education, medicine, fashion, food and more. Various technologies are used including stereolithography (SLA), fused deposition modeling (FDM), selective laser sintering (SLS), and others. While it provides many benefits, 3D printing has limitations such as slow speeds and potential effects on certain jobs. The future may bring larger 3D printers that can build structures and even prepare meals.Addictive printing or 3d printing
Addictive printing or 3d printingSHUBHAM MORGAONKAR
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of additive printing (3D printing). It discusses the history of additive printing, which was first developed in 1984. It then defines additive printing as a process that creates 3D objects by laying down successive layers of material based on a digital model. The document outlines several common additive printing methods like stereolithography, selective laser sintering, and fused deposition modeling. It also discusses advantages like printing movable parts in remote locations with strong materials. Potential future applications are described while noting challenges like intellectual property and regulation of dangerous items.3D printing ppt
3D printing pptazhar_hussain_19
Ã˝
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process where a 3D model is sliced into layers and material is deposited layer by layer to build a physical object. There are three main methods - selective laser sintering uses a laser to sinter powdered material, stereolithography uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin layer by layer, and fused deposition modeling extrudes melted plastic through a nozzle to build layers. Common materials used include ABS, PLA, and nylon. 3D printing produces little waste and can be used to make replacement parts, though the machines can be expensive and materials may not be strong enough.3D Printing
3D PrintingMohanad Yehia
Ã˝
3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing that creates 3D objects by laying down successive layers of material. The main 3D printing techniques are stereolithography, fused deposition modeling, and selective laser sintering. 3D printing has applications in product prototyping, metal casting, geospatial designs, and art. It allows for increased part complexity, digital design and manufacturing, and relatively low cost and time of production. However, 3D printing has high costs for domestic use and may have implications for intellectual property rights.Fibrox - know about 3D printing technology world
Fibrox - know about 3D printing technology worldJessica Benson
Ã˝
Fibrox 3D Printing Solutions specializes in 3D printing technology and services, offering printing, training, and innovative solutions for various applications including architecture, dental implants, and custom products. The company, under Bluechip Infocorp, aims to globally expand its reach while providing high-quality 3D printers, scanners, and consumables. Additionally, Fibrox enhances traditional manufacturing methods like investment casting with modern 3D printing techniques.3D Printing: Endless Opportunities
3D Printing: Endless OpportunitiesInstitute of Customer Experience
Ã˝
This document discusses 3D printing technology. It begins with a brief overview of how 3D printing works by building objects layer by layer from a digital file. It then provides a history of 3D printing, highlighting key developments. Examples are given of different uses for 3D printing, such as concept modeling, functional prototyping, manufacturing tools, end use parts, and more. Projections for significant growth in the 3D printing industry are mentioned. Notable 3D printer manufacturers and specific printer models are listed, along with potential future applications and scenarios involving 3D printing technology.3D printing
3D printingAnsari Danish
Ã˝
3D printing is the process of making 3D objects from a digital file by laying down successive layers of material. A typical 3D printer uses a digital blueprint to print objects layer by layer using plastic, metal or other materials. 3D printing has evolved from initially making models to now printing complex parts for aerospace and medical industries. The future of 3D printing is promising with possibilities like printing human organs, rapidly constructing buildings, and personalized manufacturing of parts. However, 3D printing technology also faces challenges like high costs, limited materials, and potential misuse for unauthorized arms production.Recent trends in manufacturing technology
Recent trends in manufacturing technologyAkashPatil283
Ã˝
The document discusses recent trends in 3D printing technology, highlighting its definition, advantages, and applications compared to traditional manufacturing methods. It includes a literature survey detailing key contributions to the field and outlines the working process of 3D printing. Additionally, it lists companies involved in the 3D printing industry.Introduction to 3D printing and its applications within Art and Design
Introduction to 3D printing and its applications within Art and DesignAnn Marie Shillito, FRSA
Ã˝
The document outlines a presentation by Ann Marie Shillito about 3D printing and its applications in applied arts and design, highlighting various types of 3D printers and materials used. It emphasizes the transformative potential of 3D printing technology in crafting, art, and practical applications such as jewelry, prosthetics, and fashion. The presentation also discusses the importance of acquiring good digital models for successful 3D printing.3D Printing
3D PrintingDeepak Anguran Sidharthan
Ã˝
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that creates 3D objects by laying down materials layer by layer based on a digital model. It allows for the creation of complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to make with traditional manufacturing methods. The technology was first developed in the 1980s and has since been used for rapid prototyping, production of consumer goods, medical devices, and more. 3D printers use materials like plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites to build up a digital design into a physical object through various methods like stereolithography, fused deposition modeling, and selective laser sintering. 3D printing offers advantages like reduced material waste, lower costs, and the ability to produce customized designs.3D PRINTING
3D PRINTINGrakesh kumar
Ã˝
This document discusses the history and types of 3D printing. It begins by defining 3D printing as a process that creates physical objects from 3D digital models by laying down successive thin layers of material. The technology was developed by Charles Hull in 1984 and is called stereolithography. Common types of 3D printing include stereolithography, fused deposition modeling, selective laser sintering, and multi-jet modeling. The document also discusses applications of 3D printing in medicine and art, as well as benefits like time and cost savings, and risks like misuse by terrorists.3 d printing
3 d printingRahul Stoy
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of 3D printing including its history from 1984, terminology, the printing process involving STL files and layering, applications in fields like rapid prototyping and manufacturing, and future prospects and challenges. It discusses how 3D printing may revolutionize industries through mass customization and personalized manufacturing while intellectual property and safety issues require addressing.3 D Printers
3 D PrintersMehvish Mushtaq
Ã˝
Printing involves reproducing text and images. There are various printer types like dot matrix, inkjet, and laser. 3D printing creates physical objects by laying down successive layers of material from a 3D digital file. The first 3D printer was developed in 1984 and since then 3D printing technology has advanced, allowing for rapid prototyping in fields like industrial design, automotive, aviation, architecture, medicine, and more. 3D printing provides advantages like low waste and ability to produce complex shapes, though the process can be slow.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
3d printing
3d printingVikram raja
Ã˝
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that builds 3D objects layer by layer using digital files. It allows for rapid prototyping and production of customized parts. The document discusses various 3D printing technologies like stereolithography and multi-jet modeling that use lasers or inkjet printing to bind powder or liquid materials. Applications include healthcare, design prototyping, education, and more local manufacturing. Advantages are rapid production and customization while disadvantages include limitations of size and cost.3d Printing Technology by Sai Thangella
3d Printing Technology by Sai Thangellasadekha
Ã˝
The seminar presented by T. Sai Kumar Reddy at Jyothishmathi Institute of Technological Sciences focused on 3D printing technology, explaining its additive manufacturing process and potential applications. 3D printing allows for the creation of complex three-dimensional objects from digital models with minimal waste, offering benefits such as custom parts and prototyping. However, the technology also raises concerns about its use in illegal activities and the need for regulation of the products created.3 d – printing
3 d – printingSiddharth Panigrahi
Ã˝
3D printing, an emerging technology, allows for creating three-dimensional objects from digital models through an additive process that builds layers of material. This technique enables customized production with less waste and has applications in various industries, including manufacturing, food, and medicine. However, it also raises concerns about intellectual property rights and the potential misuse of the technology for illegal purposes.3D Priinters
3D Priinters ShouaQureshi
Ã˝
3D printers use additive manufacturing to build solid objects layer by layer using materials like powdered resin, metal, or paper. CAD software is used to design objects digitally and can then be 3D printed. There are different types of 3D printing including direct 3D printing which uses inkjet printing technology to deposit material layer by layer, and binder 3D printing which is similar but uses a binder to join dry powder layers. 3D printing enables the creation of complex geometries and customized parts for industries like aerospace, automotive, robotics, and more.3 d printing with flying robots
3 d printing with flying robotsAccenture in India
Ã˝
3D printing takes a digital 3D design file and prints a physical object by laying down successive layers of material. This document discusses using a quadcopter drone equipped with a printing module to deposit expanding polyurethane foam in mid-air, allowing 3D printing to be done in three dimensions. It describes the design of the printing module attached to the quadcopter to deliver and deposit the foam material according to the 3D design path. This takes 3D printing to the next level by enabling fully three-dimensional printing in space rather than layer by layer on a surface.3D Printing: All the facts
3D Printing: All the factsFuture Platforms
Ã˝
This document discusses personal 3D printing. It outlines different types of 3D printers like stereolithography, scintering, and fused filament fabrication units. It describes how the RepRap project founded by Dr. Adrian Bowyer drove the development of low-cost personal 3D printing. It lists many popular 3D printer models from companies like Makerbot, Printrbot, and Ultimaker. The document discusses what types of objects can be 3D printed from toys to functional items. It also outlines where to get 3D printing content from through CAD tools, scanning, downloading from sites like Thingiverse, or customizing existing models.3D printing
3D printingPrasad Narasimhan
Ã˝
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves building a three dimensional object by laying down successive layers of material until the object is complete. It requires a 3D model file that is sliced into thin layers and sent to the printer. There are several common 3D printing methods, including stereolithography (SLA) which uses a UV laser to harden liquid resin into layers, fused deposition modeling (FDM) which extrudes melted thermoplastics to build layers, and selective laser sintering (SLS) which fuses powdered materials like metal with a laser.3D PRINTING SEMINAR
3D PRINTING SEMINARBaqar Rizvi
Ã˝
3D printing is a new technology that builds up physical objects layer by layer based on a 3D digital model. It allows for the creation of complex objects from a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, food, and bio materials. Some key applications of 3D printing include rapid prototyping, mass customization, architectural designs, dental applications, clothing, rocket engine parts, and bio printing of living organs. The future scope of 3D printing includes using it to print houses and entire buildings, as well as for space exploration through technologies like bio printing.Presentation on 3D Printing & its Applications by Jahan International
Presentation on 3D Printing & its Applications by Jahan InternationalRavindu Jain
Ã˝
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves depositing successive thin layers of material in different shapes to build a 3D object from a digital file. The digital file is first processed into horizontal layers and then loaded into a 3D printer which reproduces the object layer by layer, blending each layer seamlessly. 3D printing allows rapid prototyping and has applications in education, automobiles, design, architecture, biology, and robotics by enabling students and professionals to physically create detailed models, customized parts, prototypes, and works of art.3 D printing new 2015
3 D printing new 2015Akhil Jose
Ã˝
3D printing involves converting a virtual 3D model into a physical object by laying down successive layers of material. It began in the 1980s and is now used for industrial prototyping, education, medicine, fashion, food and more. Various technologies are used including stereolithography (SLA), fused deposition modeling (FDM), selective laser sintering (SLS), and others. While it provides many benefits, 3D printing has limitations such as slow speeds and potential effects on certain jobs. The future may bring larger 3D printers that can build structures and even prepare meals.Addictive printing or 3d printing
Addictive printing or 3d printingSHUBHAM MORGAONKAR
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of additive printing (3D printing). It discusses the history of additive printing, which was first developed in 1984. It then defines additive printing as a process that creates 3D objects by laying down successive layers of material based on a digital model. The document outlines several common additive printing methods like stereolithography, selective laser sintering, and fused deposition modeling. It also discusses advantages like printing movable parts in remote locations with strong materials. Potential future applications are described while noting challenges like intellectual property and regulation of dangerous items.3D printing ppt
3D printing pptazhar_hussain_19
Ã˝
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process where a 3D model is sliced into layers and material is deposited layer by layer to build a physical object. There are three main methods - selective laser sintering uses a laser to sinter powdered material, stereolithography uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin layer by layer, and fused deposition modeling extrudes melted plastic through a nozzle to build layers. Common materials used include ABS, PLA, and nylon. 3D printing produces little waste and can be used to make replacement parts, though the machines can be expensive and materials may not be strong enough.3D Printing
3D PrintingMohanad Yehia
Ã˝
3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing that creates 3D objects by laying down successive layers of material. The main 3D printing techniques are stereolithography, fused deposition modeling, and selective laser sintering. 3D printing has applications in product prototyping, metal casting, geospatial designs, and art. It allows for increased part complexity, digital design and manufacturing, and relatively low cost and time of production. However, 3D printing has high costs for domestic use and may have implications for intellectual property rights.Fibrox - know about 3D printing technology world
Fibrox - know about 3D printing technology worldJessica Benson
Ã˝
Fibrox 3D Printing Solutions specializes in 3D printing technology and services, offering printing, training, and innovative solutions for various applications including architecture, dental implants, and custom products. The company, under Bluechip Infocorp, aims to globally expand its reach while providing high-quality 3D printers, scanners, and consumables. Additionally, Fibrox enhances traditional manufacturing methods like investment casting with modern 3D printing techniques.3D Printing: Endless Opportunities
3D Printing: Endless OpportunitiesInstitute of Customer Experience
Ã˝
This document discusses 3D printing technology. It begins with a brief overview of how 3D printing works by building objects layer by layer from a digital file. It then provides a history of 3D printing, highlighting key developments. Examples are given of different uses for 3D printing, such as concept modeling, functional prototyping, manufacturing tools, end use parts, and more. Projections for significant growth in the 3D printing industry are mentioned. Notable 3D printer manufacturers and specific printer models are listed, along with potential future applications and scenarios involving 3D printing technology.3D printing
3D printingAnsari Danish
Ã˝
3D printing is the process of making 3D objects from a digital file by laying down successive layers of material. A typical 3D printer uses a digital blueprint to print objects layer by layer using plastic, metal or other materials. 3D printing has evolved from initially making models to now printing complex parts for aerospace and medical industries. The future of 3D printing is promising with possibilities like printing human organs, rapidly constructing buildings, and personalized manufacturing of parts. However, 3D printing technology also faces challenges like high costs, limited materials, and potential misuse for unauthorized arms production.Recent trends in manufacturing technology
Recent trends in manufacturing technologyAkashPatil283
Ã˝
The document discusses recent trends in 3D printing technology, highlighting its definition, advantages, and applications compared to traditional manufacturing methods. It includes a literature survey detailing key contributions to the field and outlines the working process of 3D printing. Additionally, it lists companies involved in the 3D printing industry.Introduction to 3D printing and its applications within Art and Design
Introduction to 3D printing and its applications within Art and DesignAnn Marie Shillito, FRSA
Ã˝
The document outlines a presentation by Ann Marie Shillito about 3D printing and its applications in applied arts and design, highlighting various types of 3D printers and materials used. It emphasizes the transformative potential of 3D printing technology in crafting, art, and practical applications such as jewelry, prosthetics, and fashion. The presentation also discusses the importance of acquiring good digital models for successful 3D printing.3D Printing
3D PrintingDeepak Anguran Sidharthan
Ã˝
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that creates 3D objects by laying down materials layer by layer based on a digital model. It allows for the creation of complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to make with traditional manufacturing methods. The technology was first developed in the 1980s and has since been used for rapid prototyping, production of consumer goods, medical devices, and more. 3D printers use materials like plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites to build up a digital design into a physical object through various methods like stereolithography, fused deposition modeling, and selective laser sintering. 3D printing offers advantages like reduced material waste, lower costs, and the ability to produce customized designs.3D PRINTING
3D PRINTINGrakesh kumar
Ã˝
This document discusses the history and types of 3D printing. It begins by defining 3D printing as a process that creates physical objects from 3D digital models by laying down successive thin layers of material. The technology was developed by Charles Hull in 1984 and is called stereolithography. Common types of 3D printing include stereolithography, fused deposition modeling, selective laser sintering, and multi-jet modeling. The document also discusses applications of 3D printing in medicine and art, as well as benefits like time and cost savings, and risks like misuse by terrorists.Similar to 3d printing... (20)
3 d printing
3 d printingRahul Stoy
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of 3D printing including its history from 1984, terminology, the printing process involving STL files and layering, applications in fields like rapid prototyping and manufacturing, and future prospects and challenges. It discusses how 3D printing may revolutionize industries through mass customization and personalized manufacturing while intellectual property and safety issues require addressing.3 D Printers
3 D PrintersMehvish Mushtaq
Ã˝
Printing involves reproducing text and images. There are various printer types like dot matrix, inkjet, and laser. 3D printing creates physical objects by laying down successive layers of material from a 3D digital file. The first 3D printer was developed in 1984 and since then 3D printing technology has advanced, allowing for rapid prototyping in fields like industrial design, automotive, aviation, architecture, medicine, and more. 3D printing provides advantages like low waste and ability to produce complex shapes, though the process can be slow.3 D printing
3 D printingiqranoreen10
Ã˝
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process where objects are created by laying down successive layers of material. The document discusses the history and development of 3D printing. It describes how 3D printers work by using CAD software to slice 3D models into layers and depositing materials to build the layers up into a final object. The document outlines different 3D printing methods and discusses pros, cons, applications, advantages, disadvantages and challenges of the technology. It envisions future possibilities for 3D printing including printing replacement parts and eventually whole appliances at home.3d printing
3d printingKartikMeena5
Ã˝
This document provides information about 3D printing from the National Institute of Technology in Hamirpur, India. It defines 3D printing as a process that creates physical objects by depositing material layer by layer based on a digital model. The document then discusses the history and development of 3D printing, including the first commercial 3D printer in 1987, and covers various 3D printing technologies, materials, applications and benefits and limitations.3D printing
3D printing Vinny Chweety
Ã˝
This document summarizes a technical seminar on 3D printing presented by B.Vineetha. It discusses the history and development of 3D printing, how 3D printers work by building objects layer by layer from a digital design. It describes common 3D printing methods like stereolithography, selective laser sintering, and fused deposition modeling. The document also covers applications of 3D printing in fields like industrial design, medicine, fashion, and more. It concludes that 3D printing offers advantages like time and cost savings compared to traditional manufacturing.DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF 3D PRINTING MACHINE IHP.pptx
DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF 3D PRINTING MACHINE IHP.pptxPiyanshPiyansh
Ã˝
The document outlines the design and functioning of 3D printing technology, detailing processes like modeling, printing, and finishing. It highlights the components of a 3D printer, such as the extruder and print bed, and discusses future applications in various fields along with challenges like intellectual property rights. Additionally, it emphasizes the advantages of 3D printing in creating complex shapes and prototypes efficiently.3D Printing - from mass production to Customized on demand production
3D Printing - from mass production to Customized on demand productionRaphael Moisa
Ã˝
3D printing has evolved from an early technique developed in 1984 to a process that is transforming manufacturing. It allows for customized production through additive methods that build objects layer by layer rather than traditional subtractive techniques. Emerging applications include food printing, medical implants, wearable devices, and construction materials. While intellectual property and misuse pose challenges, 3D printing may enable open source scientific tools and on-demand manufacturing in space.3D Printer
3D PrinterZunair Bhatti
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of 3D printing technology. It describes 3D printing as a process where a three dimensional object is created by laying down successive layers of material using an additive process. The document outlines the history of 3D printing, from its development in the 1980s to its increasing applications today. Both the opportunities and challenges of the technology are discussed, with the conclusion that 3D printing could revolutionize manufacturing through mass personalization.3D PRINTER technology by sultana.pptx
3D PRINTER technology by sultana.pptxriyasathalikhan03
Ã˝
The document provides a comprehensive overview of 3D printing technology, including its definition, history, comparisons with 2D printing, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, enables the creation of physical objects layer by layer from digital models and is being increasingly utilized across various industries such as healthcare, automotive, and aerospace. Additionally, it discusses the future potential of 3D printing in design flexibility and sustainability.Seminar Presentation on 3D Printing
Seminar Presentation on 3D PrintingAnshul Joshi
Ã˝
The document discusses the history and development of 3D printing technology. It began in 1984 with Charles Hull inventing stereolithography. Since then, other technologies like fused deposition modeling and selective laser sintering were introduced. The document defines 3D printing terminology and describes common printing mechanisms like stereolithography, selective laser sintering, and fused deposition modeling. It also covers applications in fields like medicine, jewelry, forensics, and more. Challenges discussed include intellectual property issues and the ability to print dangerous objects.3D PRINTING - AN EMERGING ERA OF FUTURE PRINTING
3D PRINTING - AN EMERGING ERA OF FUTURE PRINTINGPravin Ahirwar
Ã˝
The document discusses 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, detailing its history, working principles, technologies, advantages, and disadvantages. It explains how 3D printing involves creating objects layer by layer from digital models and highlights various printing methods like stereolithography, selective laser sintering, and fused deposition modeling. The document also addresses potential applications, including rapid prototyping and future possibilities such as printing organs and large building elements.3D printing complete
3D printing completeICEEM
Ã˝
The document discusses the history and process of 3D printing. 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process where a 3D object is created by laying down successive layers of material under computer control. The first 3D printer was created in 1984 by Charles Hull and worked by a technique called stereolithography. Today, there are several methods for 3D printing including selective laser sintering (SLS), stereolithography (SL), and fused deposition modeling (FDM). 3D printing has applications in industries such as medicine, architecture, industrial design, food, games and more.3d printing technology
3d printing technologyMuhammad Faraz
Ã˝
This document discusses 3D printing and provides an overview of the technology. It describes the different types of 3D printers including SLS, FDM, and SLA printers. The document outlines the 3D printing process from CAD preparation to cleaning printed objects. Applications of 3D printing discussed include designing prototypes, education, and healthcare. Both advantages such as rapid prototyping and manufacturing speed, and disadvantages including fewer manufacturing jobs and limited materials are presented. The document concludes that 3D printing allows quick communication of ideas through physical models printed from CAD files.3D Printer University-assignment
3D Printer University-assignmentAnowar Hossain
Ã˝
This document provides an outline and overview of 3D printing. It discusses the history of 3D printing, which was first developed in 1984. It then defines 3D printing as a process that creates 3D objects by laying down successive layers of material based on a digital file. The document outlines the general principles of 3D printing, including modeling an object digitally, printing it by adding layers, and sometimes finishing the printed object. It also discusses some common 3D printing methods and potential advantages and disadvantages.3d technology rahul
3d technology rahulrahul katiyar
Ã˝
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of making 3D objects from a digital file by successively adding material layer by layer under computer control. It works by slicing a virtual 3D model into thin horizontal layers and then producing the object by depositing one layer at a time. Applications of 3D printing include producing design prototypes, models for education, and customized medical implants and prosthetics. While the technology offers advantages like customization, there remain challenges to address such as cost, speed, and intellectual property issues.3d printing
3d printingRavindra Jondhale
Ã˝
3D printing allows for the creation of physical objects from 3D model data. It works by laying down successive layers of material under computer control. There are several types of 3D printing technologies that differ in the materials and processes used. 3D printing brings advantages like rapid prototyping, reduced design complexity, and ability to produce complex shapes. However, it also faces disadvantages such as slow speeds, limited strength of printed parts, and high costs of materials and equipment. 3D printing has applications in fields such as industrial design, medical, automotive, aerospace, architecture, entertainment and more. The future of 3D printing is promising as technologies advance and costs reduce.3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY.pptx
3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY.pptxMallaAbhinaya
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of 3D printing, including its history, technologies, applications, effects, and challenges. It describes how 3D printing works by using computer-aided design to create a 3D model that is built up in layers, with different methods using materials like plastic, powder, or resin. Applications discussed include fashion, entertainment, medicine, and space exploration. Challenges addressed are intellectual property issues and potential misuse, though advantages are noted as flexibility, rapid prototyping, and cost effectiveness. The conclusion discusses the technology's promising future in areas like medicine, arts, and manufacturing.3D Printing-The next industrial revolution
3D Printing-The next industrial revolutionneelam kanojiya
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of 3D printing, including its history, how it works, current applications, advantages, disadvantages, and areas for future development. It notes that 3D printing involves building an object layer by layer using a printer that deposits material. Key developments included Charles Hull coining the term "stereolithography" and early commercial 3D printers entering the market in the 1990s. Current applications span industries like medical, automotive, aviation, and more. Advantages include affordable customization and efficient designs, while disadvantages include potential for counterfeiting or unemployment.3 d printing
3 d printingDhruvilkumar patel
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of 3D printing. It discusses the history of 3D printing, which began in 1984 with the development of stereolithography. It then defines 3D printing as a form of additive manufacturing that creates three-dimensional objects by laying down successive layers of material. The document outlines several common 3D printing methods like stereolithography, selective laser sintering, and fused deposition modeling. It also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing, as well as applications in industries like healthcare, engineering, and consumer products.seminar report on 3d printing Shubham srivastava
seminar report on 3d printing Shubham srivastavaofficiallyshubh
Ã˝
This document is a seminar report on 3D printing submitted by Shubham Srivastava to his professor Anuj Gupta. It includes an introduction to 3D printing, its history, sustainable aspects, materials used, general printing principles and applications. The report acknowledges those who helped with the seminar and provides an abstract, table of contents, and sections on the various topics relating to 3D printing.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Cadastral Maps
Cadastral MapsGoogle
Ã˝
Preparation of cadastral maps based by Engineer Dungo Tizazu from Dire Dawa University VARICELLA VACCINATION: A POTENTIAL STRATEGY FOR PREVENTING MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
VARICELLA VACCINATION: A POTENTIAL STRATEGY FOR PREVENTING MULTIPLE SCLEROSISijab2
Ã˝
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a debilitating neurological condition affecting approximately 2.9 million people worldwide. Its cause remains unclear but environmental factors, such as post-childhood Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, are thought to contribute to MS incidence. Abraham Silberschatz-Operating System Concepts (9th,2012.12).pdf
Abraham Silberschatz-Operating System Concepts (9th,2012.12).pdfShabista Imam
Ã˝
Complete book of operating system edition 9David Boutry - Mentors Junior Developers
David Boutry - Mentors Junior DevelopersDavid Boutry
Ã˝
David Boutry is a Senior Software Engineer in New York with expertise in high-performance data processing and cloud technologies like AWS and Kubernetes. With over eight years in the field, he has led projects that improved system scalability and reduced processing times by 40%. He actively mentors aspiring developers and holds certifications in AWS, Scrum, and Azure.Learning – Types of Machine Learning – Supervised Learning – Unsupervised UNI...
Learning – Types of Machine Learning – Supervised Learning – Unsupervised UNI...23Q95A6706
Ã˝
Learning – Types of Machine Learning – Supervised Learning – Unsupervised Learning- semi supervised learning - The Brain and the Neuron – Design a Learning System – Perspectives and Issues in Machine Learning – Concept Learning Task – Concept Learning as Search – Finding a Maximally Specific Hypothesis – Version Spaces and the Candidate Elimination Algorithm
Deep Learning for Natural Language Processing_FDP on 16 June 2025 MITS.pptx
Deep Learning for Natural Language Processing_FDP on 16 June 2025 MITS.pptxresming1
Ã˝
This gives an introduction to how NLP has evolved from the time of World War II till this date through the advances in approaches, architectures and word representations. From rule based approaches, it advanced to statistical approaches. from traditional machine learning algorithms it advanced to deep neural network architectures. Deep neural architectures include recurrent neural networks, long short term memory, gated recurrent units, seq2seq models, encoder decoder models, transformer architecture, upto large language models and vision language models which are multimodal in nature.Machine Learning - Classification Algorithms
Machine Learning - Classification Algorithmsresming1
Ã˝
This covers traditional machine learning algorithms for classification. It includes Support vector machines, decision trees, Naive Bayes classifier , neural networks, etc.
It also discusses about model evaluation and selection. It discusses ID3 and C4.5 algorithms. It also describes k-nearest neighbor classifer.Tally.ERP 9 at a Glance.book - Tally Solutions .pdf
Tally.ERP 9 at a Glance.book - Tally Solutions .pdfShabista Imam
Ã˝
Tally.ERP 9 at a Glance.book, a fully completed guidance to learn tally erp 9.0FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE
FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTUREShabista Imam
Ã˝
FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE
By : Mostafa Abd-El-Barr & Hesham El-Rewini:: wiley
A complete guidance bookIntroduction to Python Programming Language
Introduction to Python Programming Languagemerlinjohnsy
Ã˝
This PPT covers features, applications, variable, data types and statements in PythonStructured Programming with C++ :: Kjell Backman
Structured Programming with C++ :: Kjell BackmanShabista Imam
Ã˝
Step into the world of high-performance programming with the Complete Guidance Book of C++ Programming—a definitive resource for mastering one of the most powerful and versatile languages in computer science.
Whether you're a beginner looking to learn the fundamentals or an intermediate developer aiming to sharpen your skills, this book walks you through C++ from the ground up. You'll start with basics like variables, control structures, and functions, then progress to object-oriented programming (OOP), memory management, file handling, templates, and the Standard Template Library (STL).Complete guidance book of Asp.Net Web API
Complete guidance book of Asp.Net Web APIShabista Imam
Ã˝
Unlock the full potential of modern web development with the Complete Guidance Book of ASP.NET Web API—your all-in-one resource for mastering RESTful services using Microsoft’s powerful ASP.NET Core framework. This book takes you on a step-by-step journey from beginner to expert, covering everything from routing and controllers to security, performance optimization, and real-world architecture.Ad
3d printing...
- 1. 3D PRINTING A Technology towards revolution
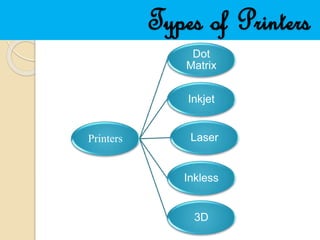
- 2. Contents  Printers  Types of printers  Dot matrix  Inkjet  Laser  Inkless  3D printers  General principles  Applications  Advantages  Conclusion  References
- 3. Printers  Output Device  First Printer in 19th Century by Charles Babbage  In 1980 Daisy wheel system like typewriter  Low cost Laser printers invented in 1984  By 2000 high quality printers are available  In 2010 3D printing has become an area of intense interest
- 5. Dot matrix  Each dot is produced by a tiny metal rod called wire or pin.  Up to 48 pins can be used to form the characters.  It is also called line dot matrix printers.  Capable of printing up to 1000 cps.  Capable of printing 800 pages/hour
- 6. Inkjet  First developed in early 1950s.  Prints by propelling droplets of ink on print materials.  Produces 64,000 to 165,000 droplets per seconds.  They can print finer and smoother.  Commonly used.
- 7. Laser  In 1969 Gary Stark developed laser printer.  First commercial implementation of laser printer was IBM3800.  A laser beam projects an image of the page to be printed. Then powdered ink particle are charged which is attracted onto paper.
- 8. Inkless  Thermal printers work by selectively heating regions of special heat-sensitive paper.  Monochrome thermal printers are used in cash registers, ATMs, gasoline dispensers and some older inexpensive fax machines.
- 9. 3D Printers  In 1981 Hideo Kodama of Nagoya municipal industrial research institute developed first 3D printed model.  Followed by Chuck Hull in 1984 named it stereo lithography.  3D printable models can be created with computer aided design.  The printers were originally large expensive and highly limited.
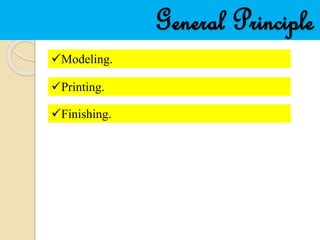
- 11. Modeling Additive manufacturing takes virtual blueprints from computer aided design (CAD) or animation modeling software and "slices" them into digital cross-sections for the machine to successively use as a guideline for printing.
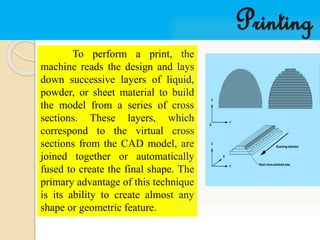
- 12. Printing To perform a print, the machine reads the design and lays down successive layers of liquid, powder, or sheet material to build the model from a series of cross sections. These layers, which correspond to the virtual cross sections from the CAD model, are joined together or automatically fused to create the final shape. The primary advantage of this technique is its ability to create almost any shape or geometric feature.
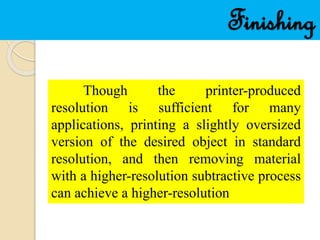
- 13. Finishing Though the printer-produced resolution is sufficient for many applications, printing a slightly oversized version of the desired object in standard resolution, and then removing material with a higher-resolution subtractive process can achieve a higher-resolution
- 14. Applications  Automobiles.  Electric motors and generators.  Art.  Prototypes.  Education.  Healthcare.  Faison clothing.
- 15. Advantage  Print movable parts.  Print items in remote location.  Ability to send items over internet and print out at home.  Plastic used is strong.
- 16. Conclusion 3D printing is an expanding technology which may soon start an industry in which everyone has the possibility of being a manufacturer. 3D printing has a lot of possible benefits to society, although the products created must be regulated.
- 17. Reference  3D Printer Technology – Animation of layering. Create It Real. Retrieved 2012-01-31.  Hideo Kodama, “Automatic method for fabricating a three- dimensional plastic model with photo-hardening polymer,” Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 52, No. 11, pp 1770-1773, November 1981  “3D Printing: What You Need to Know”. PCMag.com. Retrieved 2013-10-30.  “3D printing: Ultimaker 2 Review”. David Hana t. 2014- 11-07. Retrieved 2014-12-01.  http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3D_computer_graphics