3.grain size analysis of soil
- 1. WELCOME TO OUR PRESENTATION Submitted To Dr. Md. Abu Taiyab Prof. Dept. Of CE. Mr. Md . Ariful Islam Lecturer, Dept. of CE. Prepared By MD. Parvej ID: 131046 CE- 3/2 SEC A DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING. DHAKA UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ,GAZIPUR.
- 2. Grain size analysis of soil COURSE NO. CE -3302 GEOTECHNINICAL ENGINEERING -I SESSIONAL
- 3. Objectives ïŪ To determine the grain size distribution Test Standard ASTM D 421 Applicable for most granular soil analysis (Sieve analysis) ASTM D 422 Applicable for soils with small grain size< .075mm
- 7. Hydrometer Analysis The hydrometer analysis is based on Stokesâ Law, which gives the relationship among the velocity of fall of spheres in a fluid, the diameter of the sphere, the specific weights of the sphere and of the fluid, and the fluid viscosity. In equation form this relationship is where, v = velocity of fall of the spheres (cm/s) Gs = specific gravity of the sphere Gf = specific gravity of fluid (varies with temperature) ïĻ = absolute, or dynamic, viscosity of the fluid (g /(cm * s)) D = diameter of the sphere (cm) 2 (Gs â Gf ) v = ---- * ------------ * (D / 2)2 9 ïĻ
- 8. Solving the equation for D and using the specific gravity ofwater Gw, we obtain ________________ D = ï 18 ïĻ v/ ( Gs â Gw) v = L / t _______________ A = ï 18 ïĻ / (Gs â Gw) ________________ D = Aï L (cm) / t (min) where 0.002 mm < D < 0.2 mm Fig.12 Hydrometer and its Activities K K CONTâD:
- 10. 1. CALIBRATION OF THE HYDROMETER
- 11. Fig: Hydrometer Calibration Chart Hydrometer Calibration Chart
- 12. Corrections to hydrometer readings
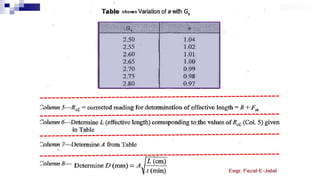
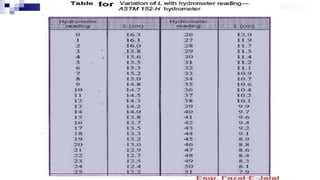
- 13. Some Tables for Calculation
- 14. Some Tables for Calculation
- 15. Some Tables for Calculation
- 17. Grain size distribution curve
- 18. & DO YOU HAVE ANY QUESTION???? THANK YOU
- 25. Sl. No. OBSERVATIONS CALCULATIONS Elaspsed time Hydrometer reading Temperature Composite correction Corrected reading Rh=Rhâ+Cm Height (cm) He Reading R= Rhâ+C Factor M Particle size D % Finer 1 15 sec 25 27 2 1/2min 24.5 3 1 â 24 4 2 â 21.5 5 4 â 20.1 6 8 â 17.5 7 15 â 16.1 8 30 â 15.1 9 1 hr 14.5 12 24 hr 11.2
- 30. Solving the equation for D and using the specific gravity of w ________________ D = ï 18 ïĻ v / ( Gs â Gw) v = L / t _______________ K = ï 18 ïĻ / ( Gs â Gw) where 0.002 mm < D < 0.2 mm