IOTA Update - NISO Update, ALA Annual Chicago 2013
- 1. NISO Annual Standards Update Interoperability and Its Role in Standardization IOTA OpenURL Quality Initiative American Library Association, Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, June 30, 2013 Rafal Kasprowski, Electronic Resources Librarian, Rice University, Houston, TX
- 2. What is IOTA? ŌĆó IOTA = Improving OpenURLs Through Analytics ŌĆó Objective: Improving the quality of OpenURL links ŌĆó Initiative that measures the relative importance of the elements that make up OpenURL links to help vendors improve their OpenURL strings so that the maximum number of OpenURL requests resolve to a correct record. Elements: ŌĆó journal title book title ISBN ŌĆó ISSN start page DOI ŌĆó volume author PMID ŌĆó issue date ŌĆ”
- 3. Topic: Deliverables published April 2013 Recommended Practice ŌĆó NISO RP-21-2013, Improving OpenURLs Through Analytics (IOTA): Recommendations for Link Resolver Providers Technical Report ŌĆó NISO TR-05-2013, IOTA Working Group Summary of Activities and Outcomes
- 4. OpenURL and Interoperability (1) ŌĆó Interoperability: capacity of different products to be compatible with each other. ŌĆó Standard exists for OpenURL syntax: how links should be constructed. ŌĆó Has the OpenURL syntax standard have bearing on the OpenURL links generated by different vendors? ŌĆó Is it possible to apply a quality metric to OpenURL links across all content providers and link resolvers? ŌĆó Global metric would be welcome as reliance on OpenURL linking continues to increase ŌĆó E.g. Use in new web-scale discovery products
- 5. OpenURL and Interoperability (2) ŌĆó Library product landscape is diversified ŌĆó Multiple vendors, many products, variety of components ŌĆó A-Z vendors operate independently of each other ŌĆó in selecting and organizing content providers in knowledge bases ŌĆó in developing link resolvers ŌĆó Content metadata keeps changing ŌĆó Publisher changes, title changes, increasingly greater holdings available online ŌĆó Content providersŌĆÖ work methods vary ŌĆó Apply their own content indexing schemes ŌĆó Provide updates to A-Z vendors at different times
- 6. A, Bernand, et al. "A versatile nanotechnology to connect individual nano-objects for the fabrication of hybrid single-electron devices." Nanotechnology 21, no. 44 (November 5, 2010): 445201. Academic Search Complete, EBSCOhost. OpenURL: syntax, resolver, linking nodes http://www.anytarget.com/?issn=0957-4484&volume=21&issue=44&date=20101105 &spage=445201&title=Nanotechnology&atitle=A+versatile+nanotechnology+to+ connect+individual+nano-objects+for+the+ fabrication+of+hybrid+single- electron+devices.&aulast=A++Bernand Source Citation (used to populate source OpenURL link) Target Link (uses OpenURL syntax or other consistent, proprietary URL structure)
- 7. Which OpenURL Link Works Better? http://link.resolver1.com/institution?issn=09277765&volume=110&spage=163 &epage=170&title=Colloids+and+Surfaces+B%3a+Biointerfaces&pages= 163-170&atitle=Anti-metastatic+activity+of+biologically+synthesized+gold +nanoparticles+on+human+fibrosarcoma+cell+line+HT&date=20131080 &aufirst=P.&aulast=Karuppaiya&id=doi:10.1016%2fj.colsurfb.2013.04.037 &sid=contentProviderA http://link.resolver2.com/institution?genre=article&atitle=Dirty%2c+White+ Candles%3a+Ernest+Hemingway%27s+Encounter+with+the+East.&title=Texas +Studies+in+Literature+%26+Language&volume=54&issue=4&date=20121201 &aulast=Kenne%2c+Mel&spage=494&sid=contentProviderB
- 8. IOTAŌĆÖs Objectives A. Produce qualitative reports that will help OpenURL providers quickly compare their OpenURL quality to that of their peers. B. Develop community-recognized index for measuring the quality of OpenURL links generated by content providers: ’üČ scalable across all OpenURLs and their providers
- 9. Usefulness of comparing OpenURLs ŌĆó Content providers that generate OpenURLs can: ŌĆó compare their OpenURLs with other providers; ŌĆó make improvements to their OpenURLs. ŌĆó Institutions can: ŌĆó compare links between OpenURL providers; ŌĆó make local adjustments to OpenURL setup. ŌĆó Resolver vendors can: ŌĆó compare links between OpenURL providers; ŌĆó change their link settings for OpenURL providers.
- 11. Report types ŌĆó Metric reports ŌĆó Viewing how often a particular element or element format ŌĆó A. is used across vendors ŌĆó B. is used across databases ŌĆó Source reports ŌĆó Viewing how often a particular (A) vendor or (B) database ŌĆó uses the metrics collected in the data logs
- 12. OpenURL Quality Metric: Components & Premises 1. Core Elements: ŌĆó Any element contained in IOTA's OpenURL reporting system; ŌĆó 25M OpenURLs obtained from libraries & content providers. 2. Scoring System: ŌĆó Assumption: Correlation exists between o # of core elements ("OpenURL completeness") & o ability of OpenURLs to link to specific content. 3. Element Weighting: ŌĆó Assigned based on their relative importance: o spage vs atitle o issn vs jtitle o doi/pmid vs date, etc.
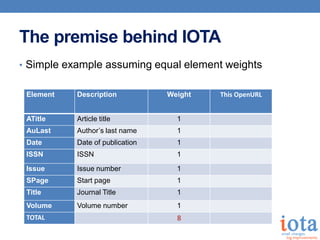
- 13. The premise behind IOTA ŌĆó Simple example assuming equal element weights Element Description Weight This OpenURL ATitle Article title 1 AuLast AuthorŌĆÖs last name 1 Date Date of publication 1 ISSN ISSN 1 Issue Issue number 1 SPage Start page 1 Title Journal Title 1 Volume Volume number 1 TOTAL 8
- 14. The premise behind IOTA ŌĆó Simple example assuming equal element weights Element Description Weight This OpenURL ATitle Article title 1 AuLast AuthorŌĆÖs last name 1 Date Date of publication 1 ISSN ISSN 1 Issue Issue number 1 SPage Start page 1 Title Journal Title 1 Volume Volume number 1 TOTAL 8 1 1 1 1 1 5 Completeness Score... (Total for This OpenURL) Total Weights 5 / 8 = .625
- 15. Initial Weights OpenURL data element Description Weight ATitle Article title 1 AuLast AuthorŌĆÖs last name 1 Date Date of publication 5 eISSN Online ISSN 3 ISSN Print ISSN 3 Issue Issue number 3 Jtitle Journal Title 1 Pmid PubMed ID 8 SPage Start page 3 Title Journal Title 1 Volume Volume number 3 DOI Digital Object Identifier 8
- 16. Initial Weights OpenURL data element Description Weight ATitle Article title 1 AuLast AuthorŌĆÖs last name 1 Date Date of publication 5 eISSN Online ISSN 3 ISSN Print ISSN 3 Issue Issue number 3 Jtitle Journal Title 1 Pmid PubMed ID 8 SPage Start page 3 Title Journal Title 1 Volume Volume number 3 DOI Digital Object Identifier 8 Initial weights were somewhat subjective.
- 17. Initial Weights OpenURL data element Description Weight ATitle Article title 1 AuLast AuthorŌĆÖs last name 1 Date Date of publication 5 eISSN Online ISSN 3 ISSN Print ISSN 3 Issue Issue number 3 Jtitle Journal Title 1 Pmid PubMed ID 8 SPage Start page 3 Title Journal Title 1 Volume Volume number 3 DOI Digital Object Identifier 8 Most link resolver knowledge bases can handle look-ups by either Print ISSN or Online ISSN (both are not needed)
- 18. Initial Weights OpenURL data element Description Weight ATitle Article title 1 AuLast AuthorŌĆÖs last name 1 Date Date of publication 5 eISSN Online ISSN 3 ISSN Print ISSN 3 Issue Issue number 3 Jtitle Journal Title 1 Pmid PubMed ID 8 SPage Start page 3 Title Journal Title 1 Volume Volume number 3 DOI Digital Object Identifier 8 Most link resolvers will enhance identifiers like PubMed ID and DOI; therefore, having an identifier is like having all metadata elements.
- 19. OpenURL Completeness Completeness Score ŌĆó measure of the ŌĆ£completenessŌĆØ of a single OpenURL ŌĆó sum of element weights found in an OpenURL divided by the maximum score possible Completeness Index ŌĆó attributed to the content provider as an overall measure of the completeness of their OpenURLs ŌĆó average of Completeness Scores of OpenURLs coming from that content provider
- 20. OpenURL linking ŌĆ£successŌĆØ ŌĆó Need to evaluate correlation between completeness score and ability of OpenURL to generate item-level link. ŌĆó The link generated should populate resolver menu. ŌĆó Success concept within bounds of OpenURL node (1st node) in link resolving process. Matthew Reidsma, ŌĆ£Rethinking Stock User Interfaces", http://matthew.reidsrow.com/articles/11 ŌĆó Initial OpenURL completeness / success correlation not high enough
- 21. A Statistical Approach to Determining Element Weights ŌĆó Select a set of ŌĆ£perfectŌĆØ OpenURLs ŌĆó include all key data elements and resolve to full text ŌĆó Perform step-wise regression ŌĆó Test failure rates for each element by removing that element ŌĆó Use failure rates as basis for weights ŌĆó Use new weights to test for correlation between weights and success for larger sample
- 22. Calculated Element Weights Core Element Failure Percentage* Element Weight** ATitle 0.74% 1.87 AuLast 0.07% 0.83 Date 0.40% 1.61 ISSN 22.02% 3.34 Issue 20.27% 3.31 SPage 33.27% 3.52 Title 0.61% 1.78 Volume 74.14% 3.87 *Failure Rates from 1,500 OpenURL test sample. **Element weight calculation: log10 (failure-rate-per-10,000 OpenURLs). Most important: Volume, Spage, ISSN, Issue
- 23. Validating the Completeness Score ŌĆó Use real OpenURLs and a commercial link resolver. (tested with LinkSource and 360 Link) ŌĆó Remove institutional holdings as a limit to resolution ŌĆó Process each OpenURL through the link resolver to determine ŌĆ£SuccessŌĆØ ŌĆó Score 1 point for finding at least one full text target; 0 for no success ŌĆó Calculate the completeness score for each OpenURL ŌĆó Look for a statistical correlation between the completeness score and the success score ŌĆó OpenURL completeness / success correlation close to 1 using statistical weights
- 24. Observations Testing the same OpenURLs on LinkSource and 360 Link results in different numbers but consistent trends. Differences may be attributed to: ŌĆó Variations in metadata enhancement techniques ŌĆó Strictness in target link rules (e.g. required elements before link shows ŌĆō tied to level of forgiveness of target) ŌĆó Link syntax used for target
- 25. Conclusions ŌĆó Step-wise regression approach to element weights works ŌĆó Completeness Index scores can be correlated to actual OpenURL ŌĆ£successŌĆØ ŌĆó KB and resolver technology influence results and prevent a universal set of element weights The Completeness Index is a mechanism individual link resolver vendors can use to provide metrics to help improve their service quality
- 26. Recommendations and Next Steps 1. Link Resolver Vendors to make use of IOTA Recommended Practice (NISO RP-21-2013) 2. Content providers to include volume, spage, and issn in article OpenURLs: critical for success 3. Content providers, link resolver vendors, librarians to use IOTA data repository to improve OpenURL linking 4. Stakeholders to continue contributing log data to IOTA repository 5. NISO to assemble working group to investigate standard for link syntaxes between link resolvers and full-text providers
- 27. IOTA Recommended Practice and Technical Reports ŌĆó NISO RP-21-2013, Improving OpenURLs Through Analytics (IOTA): Recommendations for Link Resolver Providers ŌĆó NISO TR-05-2013, IOTA Working Group Summary of Activities and Outcomes Websites ŌĆó http://www.niso.org/workrooms/openurlquality ŌĆó http://www.openurlquality.org/