4. loop
- 1. Loop: while, do-while, for
- 2. contents ï§ Loop statement: â While statement â For statement â do-while statement ï§ Statement for loop: â break, continue, ï§ Examples 2
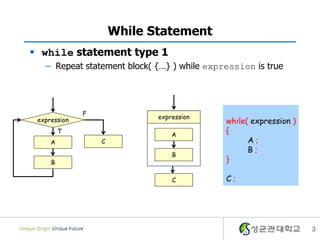
- 3. While Statement ï§ while statement type 1 â Repeat statement block( {âĶ} ) while expression is true F expression expression while( expression ) T A { A C A; B; B B } C C; 3
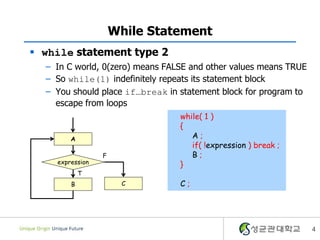
- 4. While Statement ï§ while statement type 2 â In C world, 0(zero) means FALSE and other values means TRUE â So while(1) indefinitely repeats its statement block â You should place ifâĶbreak in statement block for program to escape from loops while( 1 ) { A A; if( !expression ) break ; F B; expression } T B C C; 4
- 5. While Statement ï§ Note while (1) i++; /* infinite loop */ while(5/3) i++; while(-1) i++; while(0) i++; /*naver runs*/ 5
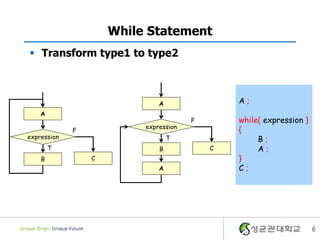
- 6. While Statement ï§ Transform type1 to type2 A A; A F while( expression ) expression F { expression T B; T B C A; B C } A C; 6
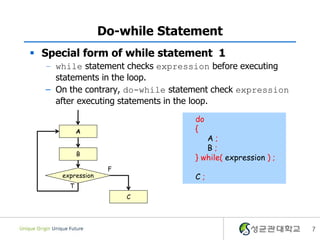
- 7. Do-while Statement ï§ Special form of while statement 1 â while statement checks expression before executing statements in the loop. â On the contrary, do-while statement check expression after executing statements in the loop. do A { A; B; B } while( expression ) ; F expression C; T C 7
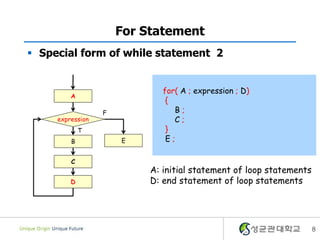
- 8. For Statement ï§ Special form of while statement 2 for( A ; expression ; D) A { F B; expression C; T } B E E; C A: initial statement of loop statements D D: end statement of loop statements 8
- 9. For Statement ï§ for statement vs. while statement for ( expr1; expr2; expr3 ) expr1; while (expr2) { { statement ; statement ; ... ... } expr3; next statement ; } next statement ; 9
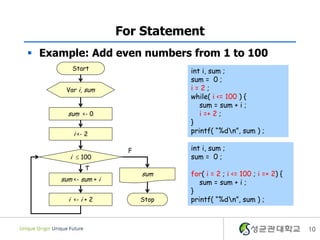
- 10. For Statement ï§ Example: Add even numbers from 1 to 100 Start int i, sum ; sum = 0 ; Var i, sum i=2; while( i <= 100 ) { sum = sum + i ; sum <- 0 i =+ 2 ; } i <- 2 printf( â%dnâ, sum ) ; F int i, sum ; i ïĢ 100 sum = 0 ; T sum for( i = 2 ; i <= 100 ; i =+ 2) { sum <- sum + i sum = sum + i ; } i <- i + 2 Stop printf( â%dnâ, sum ) ; 10
- 11. For Statement ï§ Example: Read 10 numbers and sum up those int i, n ; int i, n ; sum= 0 ; sum = 0 ; i= 0 ; for( i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++ ) while ( i < 10) { { scanf( â%dâ, &n ) ; scanf( â%dâ, &n ) ; sum += n ; sum += n ; i++ ; } } printf( â%dnâ, sum ) ; printf( â%dnâ, sum ) ; 11
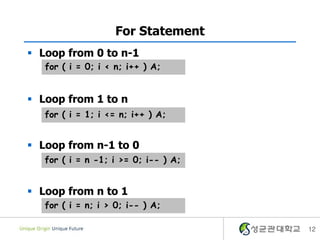
- 12. For Statement ï§ Loop from 0 to n-1 for ( i = 0; i < n; i++ ) A; ï§ Loop from 1 to n for ( i = 1; i <= n; i++ ) A; ï§ Loop from n-1 to 0 for ( i = n -1; i >= 0; i-- ) A; ï§ Loop from n to 1 for ( i = n; i > 0; i-- ) A; 12
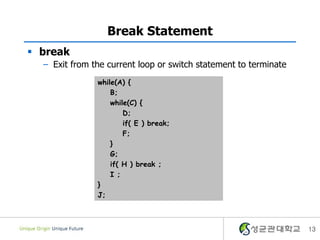
- 13. Break Statement ï§ break â Exit from the current loop or switch statement to terminate while(A) { B; while(C) { D; if( E ) break; F; } G; if( H ) break ; I ; } J; 13
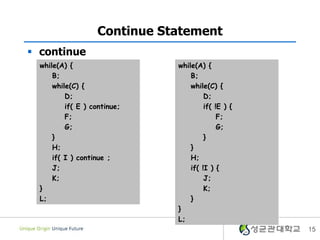
- 14. Continue Statement ï§ continue â Skip the rest of the statements in the loop while(A) { B; while(C) { D; if( E ) continue; F; } G; if( H ) continue ; I; } J; 14
- 15. Continue Statement ï§ continue while(A) { while(A) { B; B; while(C) { while(C) { D; D; if( E ) continue; if( !E ) { F; F; G; G; } } H; } if( I ) continue ; H; J; if( !I ) { K; J; } K; L; } } L; 15
- 16. Example ï§ Print all combinations of three numbers of which sum equals to seven 007 #include <stdio.h> 016 025 void main(void) 034 { âĶ int i, j, k ; 502 511 for ( i = 0; i <= 7; ++i ) { âĶ for( j = 0; j <= 7; ++j ) { 610 for ( k = 0; k <= 7; ++k ) { 700 if ( i + j + k == 7 ) printf( "%d %d %dn", i, j, k ); } } } return ; } 16
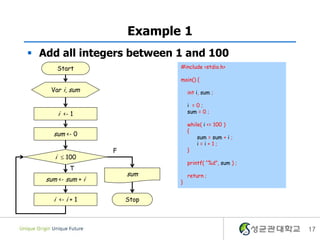
- 17. Example 1 ï§ Add all integers between 1 and 100 Start #include <stdio.h> main() { Var i, sum int i, sum ; i =0; i <- 1 sum = 0 ; while( i <= 100 ) { sum <- 0 sum = sum + i ; i=i+1; F } i ïĢ 100 printf( â%dâ, sum ) ; T sum return ; sum <- sum + i } i <- i + 1 Stop 17
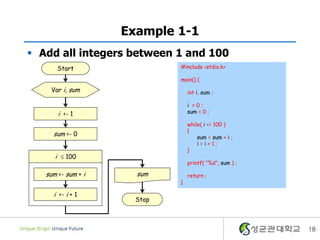
- 18. Example 1-1 ï§ Add all integers between 1 and 100 Start #include <stdio.h> main() { Var i, sum int i, sum ; i =0; i <- 1 sum = 0 ; while( i <= 100 ) { sum <- 0 sum = sum + i ; i=i+1; } i ïĢ 100 printf( â%dâ, sum ) ; sum <- sum + i sum return ; } i <- i + 1 Stop 18
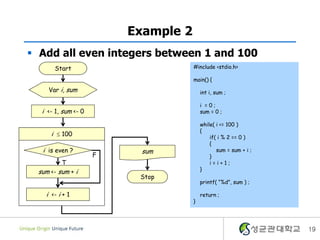
- 19. Example 2 ï§ Add all even integers between 1 and 100 Start #include <stdio.h> main() { Var i, sum int i, sum ; i =0; i <- 1, sum <- 0 sum = 0 ; while( i <= 100 ) { i ïĢ 100 if( i % 2 == 0 ) { i is even ? sum sum = sum + i ; F } T i=i+1; } sum <- sum + i Stop printf( â%dâ, sum ) ; i <- i + 1 return ; } 19
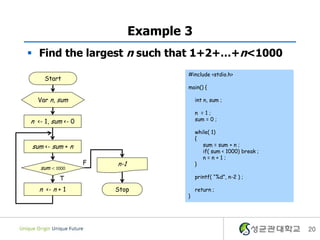
- 20. Example 3 ï§ Find the largest n such that 1+2+âĶ+n<1000 #include <stdio.h> Start main() { Var n, sum int n, sum ; n =1; n <- 1, sum <- 0 sum = 0 ; while( 1) { sum <- sum + n sum = sum + n ; if( sum < 1000) break ; n=n+1; F n-1 } sum < 1000 T printf( â%dâ, n-2 ) ; n <- n + 1 Stop return ; } 20
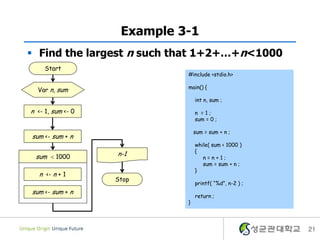
- 21. Example 3-1 ï§ Find the largest n such that 1+2+âĶ+n<1000 Start #include <stdio.h> main() { Var n, sum int n, sum ; n <- 1, sum <- 0 n =1; sum = 0 ; sum = sum + n ; sum <- sum + n while( sum < 1000 ) { sum < 1000 n-1 n=n+1; sum = sum + n ; } n <- n + 1 Stop printf( â%dâ, n-2 ) ; sum <- sum + n return ; } 21
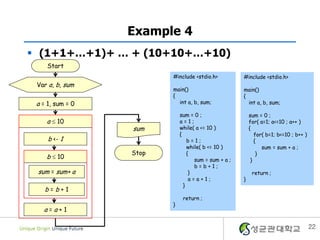
- 22. Example 4 ï§ (1+1+âĶ+1)+ âĶ + (10+10+âĶ+10) Start #include <stdio.h> #include <stdio.h> Var a, b, sum main() main() { { a = 1, sum = 0 int a, b, sum; int a, b, sum; sum = 0 ; sum = 0 ; a ïĢ 10 a=1; for( a=1; a<=10 ; a++ ) sum while( a <= 10 ) { { for( b=1; b<=10 ; b++ ) b <- 1 b=1; { while( b <= 10 ) sum = sum + a ; Stop { } b ïĢ 10 sum = sum + a ; } b=b+1; sum = sum+ a } return ; a=a+1; } } b=b+1 return ; } a=a+1 22
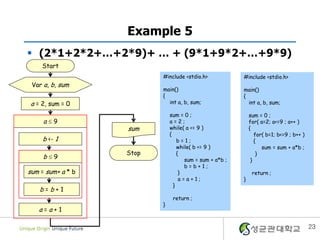
- 23. Example 5 ï§ (2*1+2*2+âĶ+2*9)+ âĶ + (9*1+9*2+âĶ+9*9) Start #include <stdio.h> #include <stdio.h> Var a, b, sum main() main() { { a = 2, sum = 0 int a, b, sum; int a, b, sum; sum = 0 ; sum = 0 ; aïĢ9 a=2; for( a=2; a<=9 ; a++ ) sum while( a <= 9 ) { { for( b=1; b<=9 ; b++ ) b <- 1 b=1; { while( b <= 9 ) sum = sum + a*b ; Stop { } bïĢ9 sum = sum + a*b ; } b=b+1; sum = sum+ a * b } return ; a=a+1; } } b=b+1 return ; } a=a+1 23
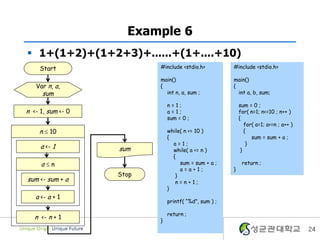
- 24. Example 6 ï§ 1+(1+2)+(1+2+3)+......+(1+....+10) Start #include <stdio.h> #include <stdio.h> main() main() Var n, a, { { sum int n, a, sum ; int a, b, sum; n=1; sum = 0 ; n <- 1, sum <- 0 a=1; for( n=1; n<=10 ; n++ ) sum = 0 ; { for( a=1; a<=n ; a++ ) n ïĢ 10 while( n <= 10 ) { { sum = sum + a ; a=1; } a <- 1 sum while( a <= n ) } { aïĢn sum = sum + a ; return ; a=a+1; } Stop } sum <- sum + a n=n+1; } a <- a + 1 printf( â%dâ, sum ) ; return ; n <- n + 1 } 24