4. treatment
- 1. TREATMENT OF LEPROSY Susana V. Caseria, MD
- 2. What is MDT? âĒ Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT) is the accepted standard treatment for leprosy. âĒ It is a combination of two (2) or more anti-leprosy drugs: âĒ Dapsone âĒ Ofloxacin âĒ Rifampicin âĒ Minocycline âĒ Clofazimine
- 3. PB Blister Pack PB Blister Pack (Adult) (Child)
- 4. MB Blister Pack MB Blister Pack (Adult) (Child)
- 5. SIDE EFFECTS: Rifampicin: âĒ May cause slightly reddish discoloration of urine within a few hours after intake. âĒ Patient may experience body malaise, joint and muscle pains.
- 6. SIDE EFFECTS: Clofazimine: âĒ Gastric irritation. âĒ Skin discoloration (disappears a few months after stopping treatment).
- 7. SIDE EFFECTS: Clofazimine: âĒ Gastric irritation. âĒ Skin discoloration (disappears a few months after stopping treatment). âĒ Dryness of skin.
- 8. SIDE EFFECTS: Dapsone: âĒ Side effects are rare. âĒ Some patients may develop allergic reactions causing itchy skin rashes and exfoliative dermatitis. âĒ Patients who are allergic to any of the sulfa drugs should not be given Dapsone.
- 9. SIDE EFFECTS DAPSONE ïŪ Hemolytic anemia â most common G6PD deficiency ïŪ Psychosis ïŪ DDS Syndrome - 1st 6 weeks ïŪ Fever ïŪ Exfoliative dermatitis ïŪ Hepatitis ïŪ Cholestatic jaundice ïŪ splenomegaly ïŪ lymphadenopathy
- 10. FLUOROQUINOLONES ïŪ Inhibit DNA gyrase ïŪ Basically vs. gram (-) bacteria ïŪ In vivo & in vitro activity of Ofloxacin against M.leprae (Saito,et al, 1986) ïŪ 3 commercial derivatives tested in mouse footpad system (Grosset, et al) -Ciprofloxacin was inactive -Pefloxacin had bactericidal activity at 150mg/KBNW/day -Ofloxacin at 50 mg/KBW/day had the same effect -Ofloxacin at 1500 mg/KBW/day had profound killing activity
- 11. SIDE EFFECTS: Ofloxacin: âĒ Well absorbed, reaches peak serum concentration after 2 hours. âĒ May cause nausea, diarrhea, headache, dizziness and insomnia.
- 12. MINOCYCLINE ïŪ Activity of minocycline in M. leprae infected mice ( Dr. Gelber, 1987) ïŪ Clinical trial of minocycline in lepromatous leprosy (Dr. Gelber et al) - 8 untreated lepromatous pts - 100 OD X 3 mos. - all were negative after 3 months - clearance :faster than dapsone &, clofazimine, slower than rifampicin & similar to pefloxacin, ofloxacin
- 13. SIDE EFFECTS: Minocycline: âĒ Has significant bactericidal activity against M. leprae. âĒ May cause discoloration of teeth in children, occasional pigmentation of the skin, gastro-intestinal disturbance and dizziness.
- 14. CONTRA-INDICATIONS TO MDT: âĒ Cases with severe liver and kidney disease. âĒ Severe hypersensitivity to any of the MDT drugs. âĒ Severe anemia. âĒ Ofloxacin & Minocycline are not recommended for use in pregnant women and children below five (5) years old.
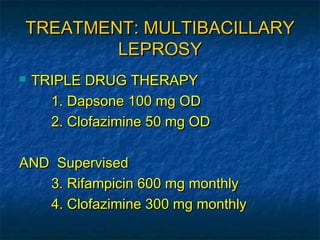
- 15. TREATMENT: MULTIBACILLARY LEPROSY ïŪ TRIPLE DRUG THERAPY 1. Dapsone 100 mg OD 2. Clofazimine 50 mg OD AND Supervised 3. Rifampicin 600 mg monthly 4. Clofazimine 300 mg monthly
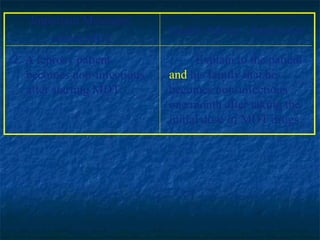
- 16. TREATMENT: PAUCIBACILLARY LEPROSY ïŪ DUAL DRUG THERAPY 1. Dapsone 100 mg OD AND Supervised 2. Rifampicin 600 mg monthly
- 17. DURATION OF TREATMENT ïŪ MULTIBACILLARY: 12 months ïŪ PAUCIBACILLARY: 6 months
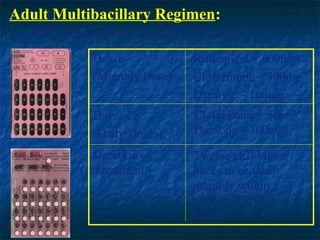
- 18. Adult Multibacillary Regimen: (For MB leprosy patients above 15 years old) Day 1 Rifampicin â 600mg (Monthly Dose) Clofazimine â 300mg Dapsone â 100mg Day 2-28 Clofazimine â 50mg (Daily Doses) Dapsone â 100mg Duration of Twelve (12) blister Treatment packs to be taken monthly within a maximum of 18 months
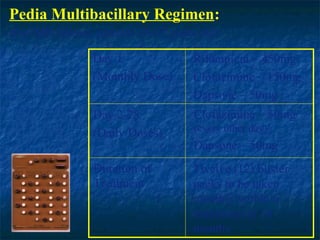
- 19. Pedia Multibacillary Regimen: (For MB leprosy patients 10-15 years old) Day 1 Rifampicin â 450mg (Monthly Dose) Clofazimine â 150mg Dapsone â 50mg Day 2-28 Clofazimine â 50mg (Daily Doses) (every other day) Dapsone â 50mg Duration of Twelve (12) blister Treatment packs to be taken monthly within a maximum of 18 months
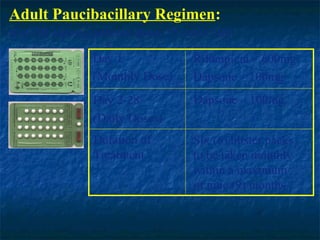
- 20. Adult Paucibacillary Regimen: (For PB leprosy patients above 15 years old) Day 1 Rifampicin â 600mg (Monthly Dose) Dapsone â 100mg Day 2-28 Dapsone â 100mg (Daily Doses) Duration of Six (6) blister packs Treatment to be taken monthly within a maximum of nine (9) months
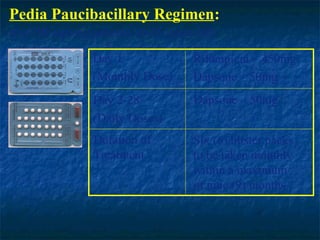
- 21. Pedia Paucibacillary Regimen: (For PB leprosy patients 10-15 years old) Day 1 Rifampicin â 450mg (Monthly Dose) Dapsone â 50mg Day 2-28 Dapsone â 50mg (Daily Doses) Duration of Six (6) blister packs Treatment to be taken monthly within a maximum of nine (9) months
- 22. For children below ten (10) years old, the dose may be adjusted. i
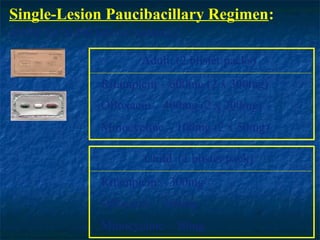
- 23. Single-Lesion Paucibacillary Regimen: (ROM for SLPB leprosy patients) Adult (2 blister packs) Rifampicin â 600mg (2 x 300mg) Ofloxacin â 400mg (2 x 200mg) Minocycline â 100mg (2 x 50mg) Child (1 blister pack) Rifampicin â 300mg Ofloxacin â 200mg Minocycline â 50mg
- 24. TREATMENT ïŪ Leprosy can now be treated at home ïŪ Health Education is an integral part of treatment ïŪ To be effective, treatment should be adequate, regular and continuous
- 25. TREAT CORRECTLY THEN STOP TREATMENT ïŪ Always treat with full doses ïŪ Never reduce the dose ïŪ If complications arise, may use a different drug
- 26. THE MAJOR PROBLEM IN LEPROSY CONTROL IS PATIENT COMPLIANCE Use every means to gain patientâs cooperation, so that they will take treatment as long as necessary
- 29. PATIENT EDUCATION: The success of MDT treatment is the joint responsibility of the doctor and the leprosy patient. Please educate your patient about the importance of treatment compliance and give corresponding instructions or advice.
- 31. Important Messages Health Advice / Instruction About MDT 1. Leprosy is curable with Advise the patient to MDT if taken regularly take his monthly and daily and continuously, and if doses of MDT drugs the prescribed number regularly, continuously of blister packs are and adequately to make consumed within the sure that he gets cured of prescribed period of 12- the disease. 18 months for MB and 6-9 months for PB.
- 32. Important Messages Health Advice / Instruction About MDT 2. A leprosy patient Explain to the patient becomes non-infectious and his family that he after starting MDT. becomes non-infectious one month after taking the initial dose of MDT drugs.
- 33. Important Messages Health Advice / Instruction About MDT 3. During the course of Teach the patient to treatment, leprosy recognize the early signs reactions may occur. of reaction and advise him to report immediately for appropriate intervention in case it occurs. Advise him to continue MDT intake even during reactions.
- 34. Important Messages Health Advice / Instruction About MDT 4. Impairments of the eyes, Advise the patient to hands and feet are take care of his anesthetic preventable. eyes, hands and feet by using protective devices such as sunglasses, hats, gloves and shoes.
- 35. Important Messages Health Advice / Instruction About MDT 5. MDT is available FREE Advise the patient to of charge in Rural collect his MDT blister Health Units. packs at the RHU until all the prescribed number of blister packs are taken.
- 36. TREATMENT COMPLETION: Treatment is completed when: âĒ A PB patient has taken 6 MDT blister packs within 6-9 months. âĒ An MB patient has taken 12 MDT blister packs within 12-18 months. âĒ An SLPB patient has taken the single dose of ROM.
- 37. Remember: A leprosy case who has completed a full course of treatment i should no longer be regarded as a leprosy patient.
- 38. TREATMENT COMPLETION: Upon completion of treatment: âĒ Remind the patient about the early signs of a leprosy reaction. âĒ Teach him the early signs of a relapse. âĒ Encourage him to continue self-care of the eyes, hands and feet to prevent injuries that may lead to deformities.
- 39. DEFAULTERS: A defaulter is a patient who has started treatment but who has not collected his MDT drugs for six (6) consecutive months. It is, however, important that adequate efforts are made to trace these patients and persuade them to return for assessment and re-treatment.
- 40. A defaulter who returns for re-treatment should be given a new course of i MDT.
- 41. PATIENTS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS: Accompanied MDT: Sometimes, patients have to interrupt their treatment for one reason or another: âĒ Poor access to the health service; âĒ No one is at the Health Center when they come to collect their blister packs; âĒ Nature of work (e.g. fisherman); âĒ Insurgency.
- 42. PATIENTS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS: Accompanied MDT: With Accompanied MDT, they are given the first dose at the Health Center, and allowed to bring home the remaining blister packs to complete the treatment at home.
- 43. PATIENTS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS: Accompanied MDT: The treatment procedure is taught to the patient and, if possible, a home companion. They are then instructed to report to the Health Center if problems occur or when treatment is completed.
- 44. PATIENTS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS: Pregnancy: The standard regimens are considered safe for both the mother and child. If a woman becomes pregnant during the course of treatment, continue MDT. However, if a woman is 1-3 months pregnant, wait until the 2nd trimester before starting MDT.
- 45. PATIENTS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS: Tuberculosis: Patients suffering from both leprosy and tuberculosis require appropriate anti-TB therapy in addition to MDT.
- 46. PATIENTS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS: Tuberculosis: Since Rifampicin doses for TB are larger than those in MDT, remove the Rifampicin capsules from the MDT blister packs for the duration of the TB therapy. Give the Clofazimine and Dapsone together with the TB regimen. When the TB treatment is completed, resume the prescribed MDT regimen.
- 47. PATIENTS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS: HIV Infection: The management of a leprosy patient infected with HIV is the same as with any other leprosy patient. Information available so far indicate that their response to MDT is the same. The management, including treatment of reactions, does not require modifications.
- 48. PATIENTS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS: Relapse: Relapse is the recurrence of leprosy after the successful completion of treatment. It is characterized by the occurrence of new lesions.
- 49. PATIENTS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS: Relapse: The probability of relapse after MDT is very rare. It is often confused with reactions which can also occur after cure. A Morphological Index is highly recommended when there is suspicion of a relapse.
- 50. OTHER POSSIBLE DRUGS ïŪ CLARITHROMYCIN ïŪ BETA LACTAM ANTIBIOTIC ïŪ RIFAMYCIN DERIVATIVES ïŪ STREPTOMYCIN ïŪ FUSIDIC ACID
- 51. CLARITHROMYCIN ïŪ Completely prevented the growth of M. leprae resistant & susceptible to dapsone & rifampicin (Walker,et al) ïŪ No antagonistic drug interaction with rifampicin ïŪ Less active than minocycline (Ji, et al) ïŪ Minocycline and clarithromycin have additive effects
- 52. OTHER DRUGS ïŪ Beta Lactam antibiotic -interfere with cell wall synthwesis -must be administered by injection ïŪ Rifamycin derivatives -Rifabutin, Rifapertine, and R-76-1 -No difference in activity with Rifampicin -No report to support activity vs. rifampicin-resistant strains
- 53. OTHER DRUGS STREPTOMYCIN -Bacteriostatic -Given by injection FUSIDIC ACID -Highly active against intra/extracellular M. leprae (Franzblau, et al)
- 54. Thank You!