4.1 trig ratios
- 2. ïTrigonometric ratios are used with right triangles to solve for missing angles and/or sides. ïThe 3 main trig ratios are: ïSine (sin) ïCosine (cos) ïTangent (tan)
- 3. ïSides are labeled in reference to a certain angle, often Îļ (âthetaâ) or x. ïHypotenuse: the longest side. Always across from the right angle. ïAdjacent: side that is touching the angle Îļ. ïOpposite: side across from the angle Îļ.
- 5. ïSet up ratio using the correct side lengths. ïReduce if possible. - OR - ïDivide and round your decimal answer. *Depends on the directions given.*
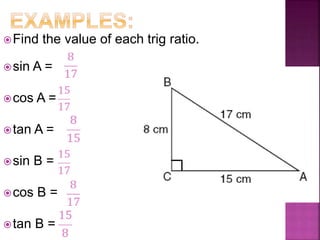
- 6. ïFind the value of each trig ratio. ïsin A = ïcos A = ïtan A = ïsin B = ïcos B = ïtan B =
- 7. ïFind the value of each trig ratio to the nearest ten-thousandth. ïsin R = ïcos R = ïtan S =