4g mobile technology and itŌĆÖs comparisons
- 1. GURU TEGH BAHADUR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Prepared By Sunmeet Singh CSE ŌĆō 1 02713202711 4G Mobile Technology and ItŌĆÖs Comparison
- 2. ŌĆó Introduction ŌĆó Technology Behind 4G ŌĆó Comaprison between 3G & 4G ŌĆó Comparison between 4G & 5G ŌĆó Advantages of 4G ŌĆó Limitations of 4G ŌĆó Applications of 4G ŌĆó Scope of 4G Contents
- 3. 4G (also known as Beyond 3G), is a term used to describe the next complete evolution in wireless communication. A 4G system will be able to provide a comprehensive IP solution where voice, data and streamed multimedia can be given to users on an ŌĆ£Anytime, AnywhereŌĆØ basis and on higher data rates than previous generations. INTRODUCTION
- 4. 1. OFDM stands for Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing. It is a technique for squeezing more data onto the same amount of radio frequency. Data is split up and sent via small chunks of frequency in parallel, therefore increasing the capacity of the network. 2. MIMO stands for Multiple-input and multiple-output. It is another reason 4G is able to provide faster speeds. It is simply the use of multiple antenna arrays at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. 3. Ultra Wide Band Networks Ultra Wideband technology is an advanced transmission technology that can be used in the implementation of a 4G network. Technology Behind 4G
- 6. 4G Enabled Handsets Availability Handset Availability Apple iPhone 5 Out now HTC One XL Out now Huawei Ascend P1 LTE Out now Nokia Lumia 820 LTE Out Now Nokia Lumia 920 LTE Out Now Samsung Galaxy Note 2 LTE Out now Samsung Galaxy S3 LTE Out now
- 7. 3G Vs 4G
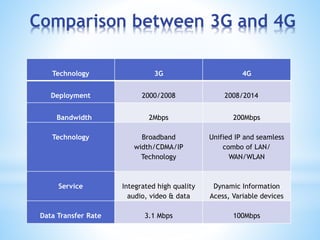
- 8. Comparison between 3G and 4G Technology 3G 4G Deployment 2000/2008 2008/2014 Bandwidth 2Mbps 200Mbps Technology Broadband width/CDMA/IP Technology Unified IP and seamless combo of LAN/ WAN/WLAN Service Integrated high quality audio, video & data Dynamic Information Acess, Variable devices Data Transfer Rate 3.1 Mbps 100Mbps
- 9. 4G vs 5G
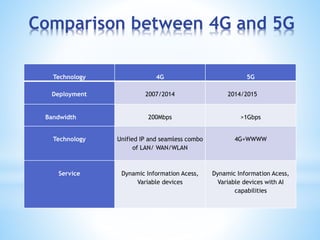
- 10. Comparison between 4G and 5G Technology 4G 5G Deployment 2007/2014 2014/2015 Bandwidth 200Mbps >1Gbps Technology Unified IP and seamless combo of LAN/ WAN/WLAN 4G+WWWW Service Dynamic Information Acess, Variable devices Dynamic Information Acess, Variable devices with AI capabilities
- 11. 1. Government Organization - With the use of 4G technology the performance of the organization will improve by: Reducing cost of travel. 2. Educational Institutions Wider spectrum of use, quickly tracking student and teacher performance. 3. Electronics Industry An escalation in demand for new products. 4. Telecommunication Sector New markets emerge with new demand for technology. Applications of 4G
- 12. 1. Data Transfer rate of upto 100Mbps. 2. High browsing speed, download and upload speed. 3. Moblie ŌĆō TV resolution is very high. 4. High Quality of Service (QOS) and high security. 5. Low cost per bit. Advantages of 4G
- 13. 1. Battery Usage is more. 2. Hard to implement. 3. Need complicated hardware. 4. Expensive equipments are required to implement 4G network. i.e. 4G enabled mobiles are very costly in INDIA(it cost above Rs.30000). 5. Recharge for 4G services like Internet is also very costly. Limitations of 4G
- 14. Bharti Airtel launched India's first 4G service, using TD-LTE technology, in Kolkata on April 10, 2012. Bharti Airtel 4G services are available in Kolkata, Bangalore, Pune and Chandigarh region (The Tricity or Chandigarh region consists of a major city Chandigarh, Mohali and Panchkula). RIL is launching 4G services through its subsidiary, Jio Infocomm. RIL 4G services are currently available only in Jamnagar, where it is testing the new TD-LTE technology. Scope of 4G
- 15. 1. The World in 2010: ICT Facts & Figures. [Online]. http://www.itu.int/ITU-D/ict/material/FactsFigures2010.pdf 2. S. Nigam and P. Siljerud. (August2006). On 4G (fourthŌĆō generationwireless). [Online]. http://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/4G 3. 4G Wireless Systems. [Online]:http://google.com 4. DRouffet, S. Kerboeuf and V. Capdevielle, On 4G Mobile. [Online].http://66.14.166.45/whitepapers/wirelessforensics/c ell/4G%20Mobile.pdf References













![1. The World in 2010: ICT Facts & Figures. [Online].
http://www.itu.int/ITU-D/ict/material/FactsFigures2010.pdf
2. S. Nigam and P. Siljerud. (August2006). On 4G (fourthŌĆō
generationwireless). [Online].
http://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/4G
3. 4G Wireless Systems. [Online]:http://google.com
4. DRouffet, S. Kerboeuf and V. Capdevielle, On 4G Mobile.
[Online].http://66.14.166.45/whitepapers/wirelessforensics/c
ell/4G%20Mobile.pdf
References](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4gmobiletechnologyanditscomparisons-141115235115-conversion-gate02/85/4g-mobile-technology-and-it-s-comparisons-15-320.jpg)