4.reproductive health medical termination of pregnancy (mtp),
- 1. REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH MEDICALTERMINATION OF PREGNANCY (MTP), SEXUALLYTRANSMITTED DISEASES (STDs) AND INFERTILITY PREPARED BY: INDERJIT SINGH PGT BIOLOGY KV SECTOR 31 D CHANDIGARH
- 2. MEDICAL TERMINATION OFPREGNANCY(MTP) • Intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy is called medical termination of pregnancy (MTP)orinduced abortion. • 45 to 50 million MTPs/ year-world • Decreases population- not meant for thatpurpose • Accept/ legalise is debated due toemotional, ethical, religious & social issues • Government of India legalized- 1971, with strict restrictions to check indiscriminate & illegal femalefoeticide • MTP-rid of unwanted pregnancy due to unprotected intercourse, failure of contraceptive, rapes, pregnancy which may fatal to mother or foetus • Thismethod is safewithin 1st trimester (12 weeks), 2ndtrimester abortions areriskier • Illegal- unqualified quacks, unsafe & fatal- avoided bycounselling • Misuse of amniocentesis, followed by MTP-avoided
- 3. SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (STDs) • Diseasesor infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are called Sexually transmitted diseases(STDs)/Venereal diseases(VD)/ Reproductive tract infections(RTI) • Gonorrhea, Syphilis, Genital herpes, Chlamydiasis, genitalwarts, Trichomoniasis, hepatitis-B andHIV. • Mode of transmission- Hepatitis- B & HIV 1. Sexualcontact with infectedperson 2. Sharing of injectionneedles 3. Sharing the unsterilized surgical instruments 4. Transfusion of blood from infected person to healthy person 5. Infected mother to foetus • Except hepatitis-B, genital herpes and HIVinfections, othersare curable.
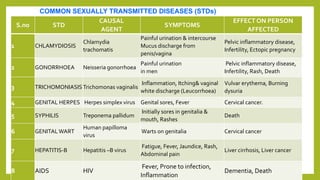
- 4. S.no STD CAUSAL AGENT SYMPTOMS EFFECT ON PERSON AFFECTED 1 CHLAMYDIOSIS Chlamydia trachomatis Painful urination & intercourse Mucus discharge from penis/vagina Pelvic inflammatory disease, Infertility, Ectopic pregnancy 2 GONORRHOEA Neisseria gonorrhoea Painful urination in men Pelvic inflammatory disease, Infertility, Rash, Death 3 TRICHOMONIASIS Trichomonas vaginalis Inflammation, Itching& vaginal white discharge (Leucorrhoea) Vulvar erythema, Burning dysuria 4 GENITAL HERPES Herpes simplex virus Genital sores, Fever Cervical cancer. 5 SYPHILIS Treponema pallidum Initially sores in genitalia & mouth, Rashes Death 6 GENITALWART Human papilloma virus Warts on genitalia Cervical cancer 7 HEPATITIS-B Hepatitis –B virus Fatigue, Fever, Jaundice, Rash, Abdominal pain Liver cirrhosis, Liver cancer 8 AIDS HIV Fever, Prone to infection, Inflammation Dementia, Death COMMON SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (STDs)
- 5. KNOWTHE SYMPTOMS OF STDs • Men • • Swelling or tenderness in genital area. • Blisters ,sores or bumps around the mouth or genitals. • Fever, chills and aches. • Unusual itching. • Burning sensation when you pass urine or move your bowels. •White, watery or yellow discharge from the penis. • Women • • Have fewer symptoms than men, often none at all. STDs can lead to cancer. Women should watch for- • Bleeding that is not part of their period. • Pelvic or vaginal pain. • Discharge from the vagina. • Painful urination. • Unusual rash, sore or growth in the genital area.
- 6. • Symptoms are minor- early stages: 1. Itching, fluid discharge, slight pain, swelling in the genital region. 2. STDsremain asymptomatic in female and remain undetectedfor long. 3. In the later stage it may leads to Pelvic inflammatory diseases (PID), abortion, still birth, ectopic pregnancy, infertility or even cancer in reproductive tract. • Preventions: 1. Avoiding sexwith unknown partners or multiplepartners. 2. Always using condoms during coitus. 3. In caseof doubt, consult adoctor forearly detection. 4. Getting complete treatment for diagnoseddisease.
- 7. • Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Overview • Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is infection of a woman's reproductive organs. Infection spreads upward from the cervix to the uterus, Fallopian tubes, ovaries, and surrounding structures Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Symptoms: - • If a woman has PID, she may have any of these symptoms: • Abdominal pain (especially lower abdominal pain) or tenderness • Back pain • Abnormal uterine bleeding • Unusual or heavy vaginal discharge • Painful urination • Painful sexual intercourse • Symptoms not related to the female reproductive organs include fever, nausea, and vomiting. PID symptoms may be worse at the end of a menstrual period and during the first several days following a period.
- 8. INFERTILITY • Thecouple unable to produce children in spite of unprotected sexis due to Infertility. Problems of infertility may be in male or female. • Thereason of infertility may be:- physical, congenial,diseases, drugs, immunological or evenpsychological. • Female are blamed often in India • Specialized Health care units like Infertility clinics-diagnose, corrective treatments to havechild • When treatments are not enough, couple are assisted with techniques called assisted reproductive technologies (ART)
- 9. • Methods of infertility control: 1. IVF- ET (In Vitro Fertilization- Embryo Transfer) • Testtube baby, fertilization takes place outside & embryois transferred • Female is induced to produce multiple egg/ova • Eggis then collected from wife/ donor & sperm collected from husband/ donor • Incubated in culture medium- fertilization & form zygote • It is then transferred to the uterus of wife, implants & pregnancy continues • Two types a. ZIFT (Zygote Intra fallopian Transfer)- Zygote/ Embryo with 8 blastomeres transferred to fallopian tube b. IUT (Intra- Uterine Transfer)- Embryo transferred at 32 celled stage to uterus
- 10. IN MALES IN FEMALES Oligospermia: Low sperm count Anovulation:Absence of ovulation. Azoospermia: Absence of sperm. Oligoovulation: Deficient ovulation. Asthenospermia: Low sperm motility. Hyperprolactinemia: excess of prolactin can lead to anovulation. Teratozoospermia: Defective sperm morphology. Idiopathic Infertility: Failure or abnormal fertilization. Cryptorchidism: Failure ofTestes to descend in the scrotal sac. Tubal Infertility: Damaged/ligated fallopian tube INFERTILITY IN HUMAN: - Causes & Consequences
- 11. • Significance: a. Boon to infertile mother b. Men with Oligospermia (low sperm count) c. Embryos canbe frozen & used forfuture
- 12. 2. GIFT (Gamete Intra Fallopian transfer) • Ovum collected from donor & transferred to female who cannot produce one but provide suitable environment forfertilization • Washedsperms & ova are transferred to the ampulla of fallopian tube with the help of laparoscope- fertilization & cleavage • Useful when fimbriae fail to capture ovum & females having sperm antibodies in their cervicalsecretion
- 13. 3. Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) • Sperm is directly injected into the ovum in culture medium • Zygote or Embryo- transferred to fallopian tube or uterus
- 14. 4. Artificial insemination (AI) • It is useful in cases either the male partner unable to inseminate the female or very lowsperm counts (oligospermia) • Semenof male partner/ donor is collected, concentrated& introduced into vagina or uterus of female- intra -uterine insemination (IUI) Drawbacks: 1. Thesetechniques are not possible with female withdamaged uterine wall. 2. Require high precision, specialized professional & expensive instrumentation & so available in few centers & available to few people only. 3. Raisedseveral ethical, emotional, religious & moral issues inthe society.