5.opththalmology Uveitis.over view pptx
- 1. 1 Uveitis By Bekuma Jima (MD) Ophthalmology Resident- (R4)
- 2. 2 ’é¦ Introduction ŌĆō ŌĆ£UveaŌĆØ = ŌĆ£GrapeŌĆØ (Latin). ŌĆō Uveal Tract = Three parts --- Iris + Ciliary body + Choroid.
- 3. 3 ŌĆō Ciliary body --- two parts: ŌĆō Pars plicata --- anterior part. ŌĆō Pars plana --- posterior part.
- 4. 4 ’é¦ Uveitis ŌĆō It is an inflammation of the uvea --- and, it can affect: ŌĆō Any part of the uveal tract: ŌĆó Iris ---> iritis. ŌĆó Choroid ---> choroiditis. ŌĆó Ciliary body --- cyclitis. ŌĆó Pars plicata ---> anterior cyclitis. ŌĆó Pars plana ---> pars planitis (intermediate uveitis). ŌĆō More than one part of the uveal tract: ŌĆó Iris and ciliary body ---> iridocyclitis. ŌĆó Whole uveal tract ---> panuveitis.
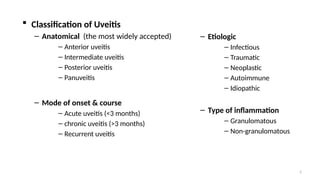
- 5. 5 ’é¦ Classification of Uveitis ŌĆō Anatomical (the most widely accepted) ŌĆō Anterior uveitis ŌĆō Intermediate uveitis ŌĆō Posterior uveitis ŌĆō Panuveitis ŌĆō Mode of onset & course ŌĆō Acute uveitis (<3 months) ŌĆō chronic uveitis (>3 months) ŌĆō Recurrent uveitis ŌĆō Etiologic ŌĆō Infectious ŌĆō Traumatic ŌĆō Neoplastic ŌĆō Autoimmune ŌĆō Idiopathic ŌĆō Type of inflammation ŌĆō Granulomatous ŌĆō Non-granulomatous
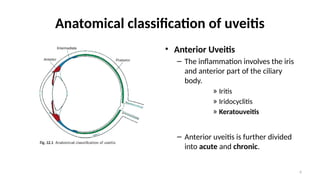
- 6. 6 Anatomical classification of uveitis ŌĆó Anterior Uveitis ŌĆō The inflammation involves the iris and anterior part of the ciliary body. ┬╗ Iritis ┬╗ Iridocyclitis ┬╗ Keratouveitis ŌĆō Anterior uveitis is further divided into acute and chronic.
- 7. 7 ŌĆō Causes of anterior uveitis: ŌĆō Arthritis --- JRA, ankylosing spondylitis, ReiterŌĆÖs syndrome, psoriasis ŌĆō Sarcoidosis ŌĆō BehcetŌĆÖs disease ŌĆō Infections ---bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic, others. ┬╗ HSV, HZV, Syphilis, TB, Lyme disease ŌĆō Trauma ŌĆō Surgery --- esp. associated with lens ŌĆō Idiopathic (unknown cause)
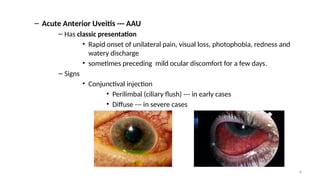
- 8. 8 ŌĆō Acute Anterior Uveitis --- AAU ŌĆō Has classic presentation ŌĆó Rapid onset of unilateral pain, visual loss, photophobia, redness and watery discharge ŌĆó sometimes preceding mild ocular discomfort for a few days. ŌĆō Signs ŌĆó Conjunctival injection ŌĆó Perilimbal (ciliary flush) --- in early cases ŌĆó Diffuse --- in severe cases
- 9. 9 ŌĆó Miosis due to pupillary sphincter spasm ŌĆó Endothelial dusting or Keratic precipitates (KPŌĆÖs) ŌĆó Inflamm. cells and flare (protein influx) in A/C ŌĆó Sometimes inflamm. membrane covering pupil ŌĆó Posterior synechiae
- 10. 10
- 11. 11
- 12. 12 ŌĆō Chronic Anterior Uveitis --- CAU ŌĆō Gradual onset, persistent inflammation, lasts > 3months. ŌĆō Symptoms: ŌĆó Variable --- redness, discomfort, photophobia. ŌĆó Sometimes --- asymptomatic until complications develop --- E.g., cataract.
- 13. 13 ŌĆō Signs: ŌĆó Aqueous cells and flare ŌĆó Old KPŌĆÖs (endothelial aggregates of inflammatory cells) ŌĆó Posterior synechiae ŌĆó Iris atrophy or nodules
- 14. 14 ŌĆó Intermediate Uveitis ŌĆō Inflammation of the middle portion of the uvea. ŌĆō Presentation: ŌĆō Insidious onset of blurred vision and floaters. ŌĆō Externally, the eye looks quiet and normal. ŌĆō Anterior vitreous cells. ŌĆō Snow ball --- aggregation of inflammatory cells in the anterior part of vitreous. ŌĆō Snow banking --- grey-white fibrovascular plaque in the inferior peripheral retina
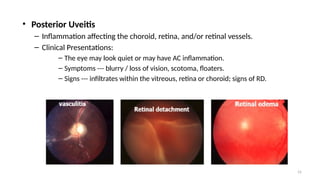
- 15. 15 ŌĆó Posterior Uveitis ŌĆō Inflammation affecting the choroid, retina, and/or retinal vessels. ŌĆō Clinical Presentations: ŌĆō The eye may look quiet or may have AC inflammation. ŌĆō Symptoms --- blurry / loss of vision, scotoma, floaters. ŌĆō Signs --- infiltrates within the vitreous, retina or choroid; signs of RD.
- 16. 16 ŌĆó Panuveitis --- Diffuse Uveitis ŌĆō Inflammation of the entire inner eye. ŌĆō Presentation --- findings of the anterior and posterior uveitis. ŌĆō Endophthalmitis ŌĆō A type of panuveitis which is of infectious cause --- usually unilateral.
- 17. 17 ’é¦ Investigation for Uveitis ŌĆō Diagnosis often made on clinical grounds --- as in: ŌĆō Mild unilateral acute anterior uveitis. ŌĆō Systemic diagnosis already made --- E.g., sarcoidosis. ŌĆō Distinct features --- E.g., toxoplasmosis, CMV retinitis, sympathetic ophthalmia. ŌĆō When investigations is needed, it should be done based on the most likely cause clinically.
- 18. 18 ŌĆō General investigations: ŌĆō CBC, ESR, CRP ŌĆō Serology for syphilis --- VDRL, rapid plasma reagin (RPR), ŌĆō Chest x-ray ŌĆō Specific workups: ŌĆō Infectious workup --- HIV test, toxoplasma IgG/IgM, Sputum AFB ŌĆō ANA --- for children with arthritis ŌĆō Serum ACE, lysozyme ŌĆō Biopsy --- from conj., aqueous, vitreous, retina, choroid ŌĆō Imaging tests --- Ultrasound, Fluorescein angiography, OCT, CT scan, MRI
- 19. 19 ’é¦ Treatment of Uveitis ŌĆō Steps of management: ŌĆō Proper workup and diagnosis. ŌĆó Especially, differentiate infectious from the non infectious causes. ŌĆō Treatment of the underlying cause, if any. ŌĆō Supportive management.
- 20. 20 ŌĆō Treatment of underlying causes: ŌĆō TB --- initiate proper anti-TB ŌĆō CMV retinitis --- Gancyclovir, Foscarnet ŌĆō HSV --- Acyclovir ŌĆō Toxoplasmosis: ŌĆó 1st line --- pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, folinic acid, and prednisolone. ŌĆó 2nd Line --- Clindamycin. ŌĆó 3rd Line --- trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole. ŌĆō Systemic inflammatory dŌĆÖses: ŌĆó Systemic corticosteroids ŌĆó Immunomodulatory agents
- 21. 21 ŌĆō Supportive treatment: ŌĆō Important for both infectious & non infectious causes. ŌĆō Include: ŌĆó Cycloplegics ŌĆó Uses --- relieve pain, prevent synechiae. ŌĆó Tropicamide, cyclopentolate, atropine. ŌĆó Corticosteroids --- to control inflammation. ŌĆó Immunosuppressive drugs --- indications being: ŌĆó Sight threatening uveitis despite steroid use. ŌĆó Steroid resistant or steroid dependent cases. ŌĆó Intolerable side effects of steroids. ŌĆó If corticosteroid use is contraindicated.
- 22. 22 ŌĆō Possible routes for corticosteroids: ŌĆō Topical --- for treatment of anterior uveitis. ŌĆō Sub-Tenon injection --- for intermediate or posterior uveitis. ŌĆō Intravitreal --- as injection or implant --- for posterior uveitis. ŌĆō Systemic --- for: ŌĆó Vision threatening uveitis --- posterior uveitis, panuveitis. ŌĆó Simultaneous treatment of underlying systemic inflammatory dŌĆÖses.
- 23. 23 Thank you!