1 of 10
Download to read offline







Recommended
Marche, Arco di Traiano, Ancona



Marche, Arco di Traiano, AnconaAdriana Stanzione
Ěý
The Arch of Trajan in Ancona, Italy was erected between 100-116 AD by the Syrian architect Apollodorus of Damascus to honor Emperor Trajan. Trajan had expanded and fortified the port of Ancona at his own expense, which is why the arch is located in the port area. Made of Turkish marble, the arch originally featured an equestrian statue of Trajan on top and statues of his wife and sister on the sides. Inscriptions on the arch were gilded bronze but were stolen in the 9th century. It has since been renovated with new lighting to accentuate its structure.Chapter13



Chapter13tonicalder
Ěý
The document summarizes key aspects of Islamic art and architecture between 600-1600 CE. It provides an overview of three main mosque types: hypostyle, iwan, and central-plan. Examples of important mosques are given for each type, including the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem and the Great Mosque of Kairouan in Tunisia. Decorative arts such as calligraphy, tilework, miniatures, and carpets are also summarized. Important terms related to Islamic culture, architecture, and decorative arts are defined.Armenia



Armeniawheelman
Ěý
Armenia is one of the oldest countries in the world with a rich history evident throughout its capital city of Yerevan and outskirts. It survived numerous empires and attempts at conquest while remaining largely independent over centuries. Armenia embraced capitalism after the Soviet Union which improved living standards somewhat. The country's Orthodox Christian heritage and numerous historic monasteries and temples dating back over 2000 years demonstrate Armenia's long and varied history.The Roman Colony of Emerita Augusta.



The Roman Colony of Emerita Augusta.Carmen_29
Ěý
The city of MĂ©rida was founded in 25 BC by Octavian Augustus as the capital of the Roman province of Lusitania to settle retired Roman soldiers. Today it contains some of the largest and most extensive archaeological remains in Spain, including a Roman theater, amphitheater, aqueduct, and bridge over the Guadiana River, all dating back to the Roman colonial period. The archaeological site was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1993.





LUXEMBOURG CREATIVE 2015 : Innovation managériale en entrepriseLUXEMBOURG CREATIVE
Ěý
Innovation managériale en entreprise. Le patron est-il amené à disparaître ?



Etude 1 ministere kb-vdbViviane de Beaufort
Ěý
L’objectif de cette étude est d’analyser la féminisation des conseils d’administration ou de surveillance concernés par la loi du 27 janvier 2011 (dite « loi Copé-Zimmermann ») telle que modifiée par la loi du 4 août 2014.
L’étude est menée en France sur les SA de plus de 500 salariés et réalisant un chiffre d’affaires de plus de 50 millions d’euros en dehors des groupes cotés au SBF 120 sur les années 2013 et 2014, concernées par l’échéance de 2017. Sur les 2462 mandats d’administrateurs identifiés pour ces 341 SA, 391 mandats sont attribués à des femmes. • Un taux de féminisation des conseils largement en deçà du seuil de 40% fixé par la loi Copé-Zimmermann avec un taux moyen de 15,5% en 2014 aant les AG...
auteures Karima BOUAISS et Viviane de BEAUFORT


Clase i SEMIOTICA DE LA IMAGENMonica Cohendoz
Ěý
Este documento trata sobre la semiĂłtica de la imagen. Explica que la imagen es un soporte de comunicaciĂłn material que representa un fragmento del mundo real o posible. Luego describe los diferentes grados de figuraciĂłn, iconicidad, complejidad y normalizaciĂłn que puede tener una imagen, y las distintas competencias e ideologĂas que influyen en su interpretaciĂłn. Finalmente, plantea algunas preguntas sobre el significado y la interpretaciĂłn de las imágenes visuales, y los cĂłdigos como la realidad, la retĂłrica y el lenguaje fotográfico que guĂan su

Analisis desarrollo economico local caso chiquitos 1Vivi Ondarza
Ěý
Este proyecto creó las Comisiones de Desarrollo Económico Local en los municipios de San José de Chiquitos, Roboré y Pailón en la provincia de Chiquitos, Bolivia. Esto involucró a los gobiernos municipales en actividades como apoyar asociaciones de productores, capacitación en microempresas y proyectos productivos, mejorando la capacidad económica local y la calidad de vida. El proyecto contó con apoyo de organizaciones internacionales.

Système financier de La liberté à tout prixLaliberteatoutprix
Ěý
Voici le système financier que j'utilise pour gagner ma liberté. Gérer ses finances personnelles est important pour une vie plus sereine et plus heureuse.
Découvrez toutes mes expériences sur :
http://laliberteatoutprix.fr

Juego BadmintonJugar Con Juegos
Ěý
Entra y Juega Gratis a este divertido juego de Badminton para 1 o 2 jugadores. Echa una partida contra la máquina o contra un amigo a ver quien gana el partido. Para jugar Flechas del teclado o teclas A, S, W, D para mover Jugador 1 o el 2. Barra espacio para golpear la bola y devolverla al campo contrario. Un juego épico de bádminton con figuras de palo. Elige tu jugador y llevale a la victoria en la cancha de badminton. 

Ppt twitter # et chats Com'en VraiLpCoMeN ComenVrai
Ěý
Twitter est un formidable outil de veille mais il réserve également de nombreuses autres possibilités dont les chats. Que ce soit pour trouver et/ou échanger des informations avec des personnes du même secteur, fidéliser un public ou encore développer son carnet d'adresses, voici quelques pistes et outils pour vous aider à bien utiliser les chats Twitter.

Présentation de Jonathan GrayCblogculture
Ěý
Présentation de Jonathan Gray directeur politiques publiques et idées de l'OKFN, lors de la journée de conférence « Transmettre la culture à l’ère du numérique » le 7 novembre 2013, Ministère de la culture et de la communication.

Campaña solar iluminemos el altiplano-DLCHCristian O'Ryan
Ěý
Este documento describe el proyecto "iluminemosel Altiplano", cuyo objetivo es proveer energĂa renovable y agua caliente a escuelas rurales en el altiplano chileno a travĂ©s de paneles y termos solares para mejorar las condiciones educativas, promover el desarrollo sostenible y preservar la cultura aymara. El proyecto comenzará instalando sistemas en 12 escuelas beneficiando a más de 1,400 personas y busca recaudar fondos a travĂ©s de donaciones para expandirse a más escuel

Flexible Workstyle: le Poste et les modes de travail réconciliés (mobilité, s...Microsoft Ideas
Ěý
Changez le paradigme du poste de travail: Venez découvrir dans cette session les solutions que Microsoft apporte aux besoins des différents modes de travail tout en répondant aux contraintes et enjeux IT: Mobilité et sécurisation des données, multiples équipements et gestion intégrée...



La biblia esta viva, es la palabraPablo Palomo
Ěý
Este tema es importante para que todos lo dejemos pasar por alto, la palabra de Dios dice que debemos obecer los estatuos de Dios, porque seremos juzgados por esos estatutos, para los que hemos creido en Cristo esta es serio cuanto más para los que todavia no lo han hecho.



±·±đłó±đłľĂ˛ą˛őbc16alcantara
Ěý
Este documento describe el Trastorno Adaptativo con estado de ánimo depresivo de ±·±đłó±đłľĂ˛ą˛ő. Resume que ±·±đłó±đłľĂ˛ą˛ő se entera de la triste situaciĂłn de los judĂos repatriados a JerusalĂ©n y se consterna profundamente, orando y ayunando dĂa y noche. Tres meses despuĂ©s muestra un semblante melancĂłlico y aflicciĂłn en su corazĂłn debido al estrĂ©s emocional y desgaste de cargar con los problemas de su pueblo sin descanso.

Iniciación a KinectJosé Vicente Sogorb Morón
Ěý
Este documento resume las funciones y aplicaciones del sensor Kinect y del sistema operativo ROS para robots. Explica que Kinect es un periférico de videojuegos de Microsoft que incluye una cámara y detecta la posición del esqueleto a través de sensores de tiempo de vuelo. También describe cómo ROS es un sistema operativo basado en Linux que ayuda a crear sistemas modulares de control para robots mediante nodos y mensajes. El documento concluye explicando algunas aplicaciones como el control de humanoides, navegación de quadcopters y ma

MotivacionAlejandro Cano
Ěý
Este documento presenta una introducciĂłn a la motivaciĂłn en el lugar de trabajo. Define la motivaciĂłn y explica cĂłmo las necesidades insatisfechas generan tensiĂłn y conducen al comportamiento. Luego clasifica las teorĂas de la motivaciĂłn en teorĂas de contenido (centradas en necesidades internas) y de proceso (describen cĂłmo se estimula la conducta). Presenta varias teorĂas de la motivaciĂłn como las de Maslow, Herzberg, McClelland y la teorĂa de la equidad. Finalmente, discute cĂłmo la motivaciĂłn puede ser manejada por los gerentes para mejorar



Wayma creative and design bookwaymagroup
Ěý
View some design and concepts of mobile UX and interfaces
Best practices in designing mobiles sites, applications and tablets
Webdesign has to adaptated to be simple and efficient



11 the results of the reformation



11 the results of the reformationfasteddie
Ěý
The Protestant Perspective:
Civilization And The Protestant Reformation, by John W. Robbins
Martin Luther nailed 95 theological propositions challenging the sale of indulgences by the Catholic Church in 1517, sparking the Protestant Reformation. The Reformation established principles of democracy, constitutionalism, religious liberty, and a free market economy. It promoted the idea that all individuals have equal standing before God and law, weakening political and religious hierarchies. By translating the Bible into common languages, Luther empowered individuals to interpret scripture for themselves rather than rely on clergy. The Reformation transformed Western society, politics, law, and economics.10 new world and columbian exchange reading



10 new world and columbian exchange readingfasteddie
Ěý
The document discusses the results of the Age of Exploration following Columbus' voyage to the Americas in 1492. It notes that over 2,000 English words have Native American origins, including common words like barbecue, hammock, and hurricane. It also discusses how Europeans introduced new crops, minerals, and goods to the Americas and brought horses, cattle, and pigs, while devastating native populations through disease and warfare. Over the centuries, this exchange of people, plants, animals, technologies, and ideas fundamentally reshaped societies on both sides of the Atlantic.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (20)


Etude 1 ministere kb-vdbViviane de Beaufort
Ěý
L’objectif de cette étude est d’analyser la féminisation des conseils d’administration ou de surveillance concernés par la loi du 27 janvier 2011 (dite « loi Copé-Zimmermann ») telle que modifiée par la loi du 4 août 2014.
L’étude est menée en France sur les SA de plus de 500 salariés et réalisant un chiffre d’affaires de plus de 50 millions d’euros en dehors des groupes cotés au SBF 120 sur les années 2013 et 2014, concernées par l’échéance de 2017. Sur les 2462 mandats d’administrateurs identifiés pour ces 341 SA, 391 mandats sont attribués à des femmes. • Un taux de féminisation des conseils largement en deçà du seuil de 40% fixé par la loi Copé-Zimmermann avec un taux moyen de 15,5% en 2014 aant les AG...
auteures Karima BOUAISS et Viviane de BEAUFORT


Clase i SEMIOTICA DE LA IMAGENMonica Cohendoz
Ěý
Este documento trata sobre la semiĂłtica de la imagen. Explica que la imagen es un soporte de comunicaciĂłn material que representa un fragmento del mundo real o posible. Luego describe los diferentes grados de figuraciĂłn, iconicidad, complejidad y normalizaciĂłn que puede tener una imagen, y las distintas competencias e ideologĂas que influyen en su interpretaciĂłn. Finalmente, plantea algunas preguntas sobre el significado y la interpretaciĂłn de las imágenes visuales, y los cĂłdigos como la realidad, la retĂłrica y el lenguaje fotográfico que guĂan su

Analisis desarrollo economico local caso chiquitos 1Vivi Ondarza
Ěý
Este proyecto creó las Comisiones de Desarrollo Económico Local en los municipios de San José de Chiquitos, Roboré y Pailón en la provincia de Chiquitos, Bolivia. Esto involucró a los gobiernos municipales en actividades como apoyar asociaciones de productores, capacitación en microempresas y proyectos productivos, mejorando la capacidad económica local y la calidad de vida. El proyecto contó con apoyo de organizaciones internacionales.

Système financier de La liberté à tout prixLaliberteatoutprix
Ěý
Voici le système financier que j'utilise pour gagner ma liberté. Gérer ses finances personnelles est important pour une vie plus sereine et plus heureuse.
Découvrez toutes mes expériences sur :
http://laliberteatoutprix.fr

Juego BadmintonJugar Con Juegos
Ěý
Entra y Juega Gratis a este divertido juego de Badminton para 1 o 2 jugadores. Echa una partida contra la máquina o contra un amigo a ver quien gana el partido. Para jugar Flechas del teclado o teclas A, S, W, D para mover Jugador 1 o el 2. Barra espacio para golpear la bola y devolverla al campo contrario. Un juego épico de bádminton con figuras de palo. Elige tu jugador y llevale a la victoria en la cancha de badminton. 

Ppt twitter # et chats Com'en VraiLpCoMeN ComenVrai
Ěý
Twitter est un formidable outil de veille mais il réserve également de nombreuses autres possibilités dont les chats. Que ce soit pour trouver et/ou échanger des informations avec des personnes du même secteur, fidéliser un public ou encore développer son carnet d'adresses, voici quelques pistes et outils pour vous aider à bien utiliser les chats Twitter.

Présentation de Jonathan GrayCblogculture
Ěý
Présentation de Jonathan Gray directeur politiques publiques et idées de l'OKFN, lors de la journée de conférence « Transmettre la culture à l’ère du numérique » le 7 novembre 2013, Ministère de la culture et de la communication.

Campaña solar iluminemos el altiplano-DLCHCristian O'Ryan
Ěý
Este documento describe el proyecto "iluminemosel Altiplano", cuyo objetivo es proveer energĂa renovable y agua caliente a escuelas rurales en el altiplano chileno a travĂ©s de paneles y termos solares para mejorar las condiciones educativas, promover el desarrollo sostenible y preservar la cultura aymara. El proyecto comenzará instalando sistemas en 12 escuelas beneficiando a más de 1,400 personas y busca recaudar fondos a travĂ©s de donaciones para expandirse a más escuel

Flexible Workstyle: le Poste et les modes de travail réconciliés (mobilité, s...Microsoft Ideas
Ěý
Changez le paradigme du poste de travail: Venez découvrir dans cette session les solutions que Microsoft apporte aux besoins des différents modes de travail tout en répondant aux contraintes et enjeux IT: Mobilité et sécurisation des données, multiples équipements et gestion intégrée...



La biblia esta viva, es la palabraPablo Palomo
Ěý
Este tema es importante para que todos lo dejemos pasar por alto, la palabra de Dios dice que debemos obecer los estatuos de Dios, porque seremos juzgados por esos estatutos, para los que hemos creido en Cristo esta es serio cuanto más para los que todavia no lo han hecho.



±·±đłó±đłľĂ˛ą˛őbc16alcantara
Ěý
Este documento describe el Trastorno Adaptativo con estado de ánimo depresivo de ±·±đłó±đłľĂ˛ą˛ő. Resume que ±·±đłó±đłľĂ˛ą˛ő se entera de la triste situaciĂłn de los judĂos repatriados a JerusalĂ©n y se consterna profundamente, orando y ayunando dĂa y noche. Tres meses despuĂ©s muestra un semblante melancĂłlico y aflicciĂłn en su corazĂłn debido al estrĂ©s emocional y desgaste de cargar con los problemas de su pueblo sin descanso.

Iniciación a KinectJosé Vicente Sogorb Morón
Ěý
Este documento resume las funciones y aplicaciones del sensor Kinect y del sistema operativo ROS para robots. Explica que Kinect es un periférico de videojuegos de Microsoft que incluye una cámara y detecta la posición del esqueleto a través de sensores de tiempo de vuelo. También describe cómo ROS es un sistema operativo basado en Linux que ayuda a crear sistemas modulares de control para robots mediante nodos y mensajes. El documento concluye explicando algunas aplicaciones como el control de humanoides, navegación de quadcopters y ma

MotivacionAlejandro Cano
Ěý
Este documento presenta una introducciĂłn a la motivaciĂłn en el lugar de trabajo. Define la motivaciĂłn y explica cĂłmo las necesidades insatisfechas generan tensiĂłn y conducen al comportamiento. Luego clasifica las teorĂas de la motivaciĂłn en teorĂas de contenido (centradas en necesidades internas) y de proceso (describen cĂłmo se estimula la conducta). Presenta varias teorĂas de la motivaciĂłn como las de Maslow, Herzberg, McClelland y la teorĂa de la equidad. Finalmente, discute cĂłmo la motivaciĂłn puede ser manejada por los gerentes para mejorar



Wayma creative and design bookwaymagroup
Ěý
View some design and concepts of mobile UX and interfaces
Best practices in designing mobiles sites, applications and tablets
Webdesign has to adaptated to be simple and efficient





















Flexible Workstyle: le Poste et les modes de travail réconciliés (mobilité, s...Microsoft Ideas
Ěý




















More from fasteddie (20)
11 the results of the reformation



11 the results of the reformationfasteddie
Ěý
The Protestant Perspective:
Civilization And The Protestant Reformation, by John W. Robbins
Martin Luther nailed 95 theological propositions challenging the sale of indulgences by the Catholic Church in 1517, sparking the Protestant Reformation. The Reformation established principles of democracy, constitutionalism, religious liberty, and a free market economy. It promoted the idea that all individuals have equal standing before God and law, weakening political and religious hierarchies. By translating the Bible into common languages, Luther empowered individuals to interpret scripture for themselves rather than rely on clergy. The Reformation transformed Western society, politics, law, and economics.10 new world and columbian exchange reading



10 new world and columbian exchange readingfasteddie
Ěý
The document discusses the results of the Age of Exploration following Columbus' voyage to the Americas in 1492. It notes that over 2,000 English words have Native American origins, including common words like barbecue, hammock, and hurricane. It also discusses how Europeans introduced new crops, minerals, and goods to the Americas and brought horses, cattle, and pigs, while devastating native populations through disease and warfare. Over the centuries, this exchange of people, plants, animals, technologies, and ideas fundamentally reshaped societies on both sides of the Atlantic.9 reformation chart



9 reformation chartfasteddie
Ěý
The document summarizes some of the key differences between Protestant and Catholic theology and practices during the Reformation period. The Protestant view emphasized salvation through faith alone, access to God for all believers without priests, and interpreting scripture independently. The Catholic view maintained that good works and the priesthood were necessary along with faith for salvation. Catholics saw scripture and tradition as revealing doctrine, while Protestants viewed the Bible as the sole source. Other differences included the number of sacraments, whether communion represented a repeated sacrifice, and the concept of predestination.8 reformation timeline 1 page



8 reformation timeline 1 pagefasteddie
Ěý
This document provides a condensed timeline of key events during the Protestant Reformation from 1440 to 1564. It highlights the roles of important figures like Martin Luther, John Calvin, Henry VIII and key Anabaptist leaders. Major events included Luther posting his 95 Theses in 1517, his appearance before the Diet of Worms in 1521 where he refused to recant, the Peasant's War from 1524-1526, and the publication of Calvin's Institutes of the Christian Religion in 1536. The timeline also notes the growing persecution of Anabaptists and their beliefs in martyrdom, as well as developments like the English Act of Supremacy in 1534 that made Henry VIII the head of7 reformation docs packet 1



7 reformation docs packet 1fasteddie
Ěý
Martin Luther critiques the power and authority of the papacy in three key ways:
1) He argues that the Roman Catholics have built "three walls" to protect themselves from reform - claiming sole authority over temporal power, sole right to interpret scripture, and sole right to call councils.
2) Luther asserts that these claims of sole authority have no basis in scripture and are only valid if not harmful to Christianity. When the pope deserves punishment, these claims no longer apply.
3) He contends that when necessity demands it, such as when the pope is an offense to Christianity, any person able should call a council without the pope's approval in order to punish the pope and6 protestant reformation in one page



6 protestant reformation in one pagefasteddie
Ěý
Martin Luther initiated the Protestant Reformation in 1517 by posting his 95 theses criticizing the Catholic Church. He advocated for a church founded on faith alone rather than works, in opposition to the corruption and power of the Papacy. Other reformers like Ulrich Zwingli and the Anabaptists further split from Luther over issues like the sacraments. Henry VIII broke from Rome for political reasons when the Pope did not grant his divorce. John Calvin split over the concept of predestination, and Protestantism continued fragmenting into various denominations like Calvinism. The Catholic Church launched a Counter-Reformation to combat the spread of Protestantism through measures like the Inquisition and Council of Trent.5 renaissance figures speak for themselves



5 renaissance figures speak for themselvesfasteddie
Ěý
This document contains quotes from several Renaissance figures that demonstrate key ideas of the time period. Giovanni Pico della Mirandola's quote emphasizes humanism and individualism by saying man can fashion himself however he prefers and is not limited by nature. William Shakespeare's quote about man's nobility and infinite abilities shows classical ideas about humanity. Laura Cereta's quote argues for women's abilities and talents, highlighting the growing focus on individualism.4 renaissance and reformation timeline short



4 renaissance and reformation timeline shortfasteddie
Ěý
This document provides a timeline of major events from 1452 to 1648 that occurred during the Renaissance and Reformation periods in Europe. Some of the key events included Leonardo da Vinci's work as an artist, the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453, Johann Gutenberg's invention of the printing press in 1455, Martin Luther posting his 95 Theses criticizing the Catholic Church in 1517, and the Thirty Years' War beginning in Germany in 1618. The timeline covers major developments in art, religion, exploration, science, and warfare that transformed Europe during this period.3 renaissance packet



3 renaissance packetfasteddie
Ěý
This document provides an overview of several websites containing resources for studying European history, including notes, review sheets, quizzes, and timelines. It recommends some specific sites as being particularly comprehensive or well-designed, such as http://www.homestead.com/chaffeyaphistory/european.html. The document then shifts to providing multi-paragraph summaries of topics related to the Renaissance in Italy, including the meaning and characteristics of the Renaissance, the Italian city-states, the intellectual Renaissance, art of the period, and the development of states in France and England.2 medieval europe overview reading



2 medieval europe overview readingfasteddie
Ěý
The document provides an overview of medieval Europe from the fall of Rome to the Renaissance. It summarizes that the Western Roman Empire fell in 476 AD due to various internal and external factors. While Rome fell, the Eastern Roman Empire continued on as the Byzantine Empire based in Constantinople. After the fall of Rome, Europe was politically fragmented with no central government and was dominated by invading Germanic tribes. Charlemagne was able to unite much of Western Europe under the Frankish Kingdom in the 9th century, which became known as the Holy Roman Empire. Feudalism developed as a political and economic system during this period characterized by a hierarchy of land ownership and obligations between lords and vassals. The1 ap euro chronological and thematic outline



1 ap euro chronological and thematic outlinefasteddie
Ěý
The document outlines the AP European History course which covers history from 1450 to present day. It is divided into chronological periods such as Renaissance/Reformation from 1450-1550 and Industrialization/Enlightenment from 1700-1800. Within each period, the course focuses on 3 major themes: intellectual/cultural history, political/diplomatic history, and social/economic history. Themes include developments in art, science, government, nationalism, and changes in social structures from hierarchy to social classes with industrialization.12 scientific revolution and enlightenment quotations



12 scientific revolution and enlightenment quotationsfasteddie
Ěý
The document provides quotes from prominent figures of the Scientific Revolution and Enlightenment era on a variety of topics including science, reason, liberty, justice, and human nature. Some of the key ideas expressed are that mathematics reveals the order of the universe (Galileo), liberty requires virtue (Rousseau), laws should aim to perfect education over punishment (Beccaria), and reason and science lead to happiness and knowledge (Franklin, Hume, Jefferson). Overall, the quotes illustrate the intellectual foundations and values of the Enlightenment period.6 reformationwpics1



6 reformationwpics1fasteddie
Ěý
The document summarizes the major events and figures of the Protestant Reformation. It describes how Martin Luther protested abuses within the Catholic Church and sparked the growth of Protestantism. Over time, various Protestant denominations emerged like Lutheranism, Calvinism, and Anglicanism under leaders such as Luther, John Calvin, and Henry VIII respectively. The Reformation destroyed unity within Christianity and led to religious conflicts across Europe for over a century.4 rise of nation states



4 rise of nation statesfasteddie
Ěý
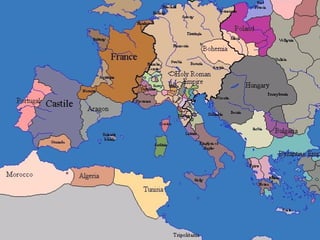
Between 1400 and 1500, Europe transitioned from decentralized feudal systems to centralized nation-states. This was driven by several factors, including the rise of the middle class which weakened feudal lords, war between feudal lords that led to unified kingdoms, and the development of ideas around political states and divine rights of kings. Key events included the marriage of Ferdinand and Isabella in 1469 which unified Spain, and the War of the Roses in England which ended in 1485 with the victory of Henry Tudor, establishing a strong centralized English nation-state. By 1500, several large European powers like France, Spain, and England had established themselves as nation-states with centralized governments and bureaucrac3 renaissance in rome



3 renaissance in romefasteddie
Ěý
The document provides an overview of important people and events during the Italian Renaissance from 1300-1527. It summarizes the rise of Florence as the center of the Renaissance under the Medici family and their patronage of the arts. It also discusses the power struggles between foreign powers like France and Spain vying for control of the Italian peninsula, the rise and fall of various popes, and the start of the Protestant Reformation challenging the Catholic Church.2 the catholic church background and overview



2 the catholic church background and overviewfasteddie
Ěý
The document discusses the history and structure of Christianity and the Catholic Church. It describes how Christianity split into the Roman Catholic, Protestant, and Eastern Orthodox branches. It outlines the Catholic Church's hierarchical structure headed by the Pope, and key events like the Great Schism of 1054 which divided Western and Eastern Christianity.7 post reformation scientific rev and exploration



7 post reformation scientific rev and explorationfasteddie
Ěý
The document provides an overview of major developments in Europe between 1550-1648, including:
1) The Scientific Revolution led to a shift from Aristotle's geocentric view to the theories of Copernicus, Kepler, Galileo and Newton that the earth revolves around the sun.
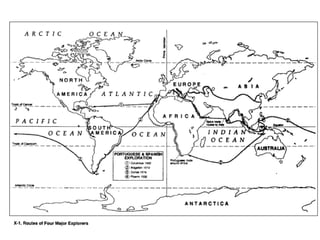
2) The Age of Exploration drove expansion by European powers like Spain, Portugal, and England between the 15th-17th centuries as they sought new trade routes, resources, and lands.
3) Religious wars erupted across Europe during this time period as conflicts arose between Catholic and Protestant groups in countries like France and Germany.1 Renaissance in Florence



1 Renaissance in Florencefasteddie
Ěý
The document provides an overview of the Renaissance period in Europe between the 14th and 16th centuries. It discusses the major developments including the rebirth of humanism and individualism, the development of nation-states, drastic changes in artistic methods and thinking, voyages of discovery to the New World, and the Protestant Reformation and resulting civil wars. It then focuses on the specific causes and events of the Renaissance in Italy, with Florence emerging as the birthplace due to factors like trade, wealthy banking families like the Medicis, and great individual artists and thinkers including Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Brunelleschi.AP Byzantine Empire And Islam Timeline



AP Byzantine Empire And Islam Timelinefasteddie
Ěý
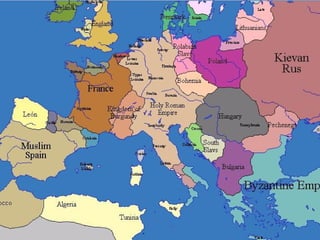
The Byzantine Empire lasted from 330-1453 CE with its capital of Constantinople, founded by Constantine in 330 CE. Under Emperor Justinian in the 6th century, the Byzantine Empire reached its greatest extent but then lost territory to invaders. The Byzantine Empire preserved Greek and Roman culture and spread Eastern Orthodox Christianity and the Cyrillic alphabet to eastern Europe through missionaries like Cyril and Methodius.AP Ming Dynasty Powerpoint



AP Ming Dynasty Powerpointfasteddie
Ěý
The document summarizes the Ming Dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644. Some key aspects include:
- The Ming Dynasty was established after the Mongol Yuan Dynasty lost the Mandate of Heaven.
- The Ming Dynasty saw a period of economic and cultural prosperity in China, with a large population and advances in agriculture, industry, arts, and naval exploration.
- However, corruption and natural disasters in the 17th century weakened the Ming and led to its eventual collapse, with the Manchu people establishing the Qing Dynasty in China in 1644.