5 Ways to Use Spark to Enrich your Cassandra Environment
- 1. Jim Hatcher DFW Cassandra Users - Meetup 5/18/2016 5 Ways to use Spark to Enrich your Cassandra Environment C*
- 2. Agenda ŌĆó Introduction ŌĆó Data Systems ŌĆó What is Cassandra? ŌĆó Tradeoffs vs. RDBMS ŌĆó Addressing Limitations ŌĆó What is Spark? ŌĆó Five Ways to Use Spark in a Cassandra Environment ŌĆó ETL ŌĆó Data Migrations ŌĆó Consistency Checking / Syncing Denormalized Data ŌĆó Analytics ŌĆó Machine Learning ŌĆó Spark Resources
- 3. Introduction Jim Hatcher james_hatcher@hotmail.com At IHS, we take raw data and turn it into information and insights for our customers. Automotive Systems (CarFax) Defense Systems (JaneŌĆÖs) Oil & Gas Systems (Petra) Maritime Systems Technology Systems (Electronic Parts Database, Root Metrics) Sources of Raw Data Structure Data Add Value Customer-facing Systems
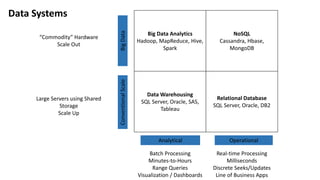
- 4. Data Systems Big Data Analytics Hadoop, MapReduce, Hive, Spark NoSQL Cassandra, Hbase, MongoDB Data Warehousing SQL Server, Oracle, SAS, Tableau Relational Database SQL Server, Oracle, DB2 Analytical Operational ConventionalScaleBigData Batch Processing Minutes-to-Hours Range Queries Visualization / Dashboards ŌĆ£CommodityŌĆØ Hardware Scale Out Real-time Processing Milliseconds Discrete Seeks/Updates Line of Business Apps Large Servers using Shared Storage Scale Up
- 5. Hadoop, MapReduce, Hive, Spark Cassandra, Hbase, MongoDb SQL Server, Oracle, SAS, Tableau SQL Server, Oracle, DB2 Analytical Operational ConventionalScaleBigDataData Systems Factors: ŌĆó Size/Scale of Data ŌĆó Multi-Data Center (with writes) ŌĆó Rate of Data Ingest ŌĆó Massive Concurrency ŌĆó Uptime Requirements ŌĆó Operational Complexity
- 6. What is Cassandra? Cassandra Cluster B C D E F Client -9223372036854775808 through -6148914691236517207 -6148914691236517206 through -3074457345618258605 -3074457345618258604 through -3 -2 through 3074457345618258599 3074457345618258600 through 6148914691236517201 6148914691236517202 through 9223372036854775808 CREATE KEYSPACE orders WITH replication = { 'class': 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor': 3 }; CREATE TABLE orders.customer ( customer_id uuid, customer_name varchar, customer_age int, PRIMARY KEY ( customer_id ) ) INSERT INTO customer (feb2b9e6-613b-4e6b-b470-981dc4d42525, ŌĆśBobŌĆÖ, 35) SELECT customer_name, customer_age FROM customer WHERE customer_id = feb2b9e6-613b-4e6b-b470-981dc4d42525 A
- 7. What is Cassandra? Cassandra is ŌĆó A NoSQL (i.e., non-relational) operational database ŌĆó Distributed (the data lives on many nodes) ŌĆó Highly Scalable (no scale ceiling) ŌĆó Highly Available (no single point of failure) ŌĆó Open Source ŌĆó Fast (optimized for fast reads and fast writes) Cassandra uses: ŌĆó Commodity Hardware (no SAN/NAS or high-end hardware) ŌĆó Ring Architecture (not master/slave) ŌĆó Flexible Data Model ŌĆó CQL (abstraction layer for data access; not tied to a particular language) DataStax provides consulting, support, and additional software around Cassandra.
- 8. What you gain with Cassandra: ŌĆó Linear Horizontal Scale (HUGE!) ŌĆó Multi-Data Center / Active-Active ŌĆó Fast, Scalable writes ŌĆó Fast Reads (by the key(s)) ŌĆó Continuous Availability ŌĆó High Concurrency ŌĆó Schema Flexibility ŌĆó Cheaper (commodity hardware)? What you give up with Cassandra: ŌĆó Tables only queryable by key ŌĆó 3rd Normal Form ŌĆó Data Integrity Checks ŌĆó Foreign Keys ŌĆó Unique Indexes ŌĆó Joins ŌĆó Secondary Indexes ŌĆó Grouping / Aggregation ŌĆó ACID Tradeoffs (vs. RDBMS)
- 9. Limitations Solutions DenormalizeData IdempotentDataModel IndexinAnotherTool ConsistencyChecker BatchAnalytics BatchETL Tables only Queryable by Key X X No Foreign Keys / Unique Indexes X X No JOINs X X No GROUP BYs / Aggregation X Keeping Denormalized Data in Sync X Creating New Tables for New Queries X Addressing Limitations
- 10. What is Spark? Spark is a processing framework designed to work with distributed data. ŌĆ£up to 100X faster than MapReduceŌĆØ according to spark.apache.org Used in any ecosystem where you want to work with distributed data (Hadoop, Cassandra, etc.) Includes other specialized libraries: ŌĆó SparkSQL ŌĆó Spark Streaming ŌĆó MLLib ŌĆó GraphX Spark Facts Conceptually Similar To MapReduce Written In Scala Supported By DataBricks Supported Languages Scala, Java, or Python
- 11. Spark Architecture Spark Client Driver Spark Context Spark Master Spark Worker Spark Worker Spark Worker Executor Executor Executor 1. Request Resources 2. Allocate Resources 3.StartExecutors 4.PerformComputation Credit: https://academy.datastax.com/courses/ds320-analytics-apache-spark/introduction-spark-architecture
- 12. Spark Terms / Concepts Resilient Distributed Dataset (RDD) Represents an immutable, partitioned collection of elements that can be operated on in parallel. Dataframe RDD + schema This is the ŌĆ£way that everything in Spark is goingŌĆØ Actions and Transformations Transformations ŌĆō create a new RDD but are executed in a lazy fashion (i.e., when an action fires) Actions ŌĆō cause a computation to be run and return a response to the driver program Executing Spark Code Spark Shell ŌĆō run Spark commands interactively via the Spark REPL Spark Submit ŌĆō execute Spark jobs (i.e., JAR files); you can build a JAR file in the Java IDE of your choice ŌĆō Eclipse, IntelliJ, etc.
- 13. Spark with Cassandra Credit: https://academy.datastax.com/courses/ds320- analytics-apache-spark/introduction-spark- architecture Cassandra Cluster A CB Spark Worker Spark WorkerSpark Worker Spark Master Spark Client Spark Cassandra Connector ŌĆō open source, supported by DataStax https://github.com/datastax/spark-cassandra-connector
- 14. ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Text File JDBC Data Source Cassandra Hadoop Extract Data Spark: Create RDD Data Source(s) Spark Code Transform Data Spark: Map function Spark Code Cassandra Data Source(s) Load Data Spark: Save Spark Code
- 15. ETL import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} //Create a SparkConfig and a SparkContext val sparkConf = new SparkConf(true) .setAppName("MyEtlApp") .setMaster("spark://10.1.1.1:7077") .set("spark.cassandra.connection.host", "10.2.2.2") ) val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf) //EXTRACT: Using the SparkContext, read a text file and expose it as an RDD val logfile = sc.textFile("/weblog.csv") //TRANSFORM: split the CSV into fields and then put the fields into a tuple val split = logfile.map { line => line.split(",") } val transformed = split.map { record => ( record(0), record(1) ) } //LOAD: write the tuple structure into Cassandra transformed.saveToCassandra("test", "weblog")
- 16. Data Migrations Cassandra Extract Data Spark: Create RDD Data Source(s) Spark Code Transform Data Spark: Map function Spark Code Cassandra Data Source(s) Load Data Spark: Save Spark Code
- 17. Data Migrations import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} //Create a SparkConfig and a SparkContext val sparkConf = new SparkConf(true) .setAppName("MyEtlApp") .setMaster("spark://10.1.1.1:7077") .set("spark.cassandra.connection.host", "10.2.2.2") ) val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf) //EXTRACT: Using the SparkContext, read a C* table and expose it as an RDD val weblogRecords = sc.cassandraTable("test", "weblog").select("logtime", "page") //TRANSFORM: pull fields out of the CassandraRow and put the fields into a tuple val transformed = weblogRecords.map { row => ( row.getString(1), row.getLong(0) ) } //LOAD: write the tuple structure into Cassandra into a different table transformed.saveToCassandra("test", "weblog_bypage")
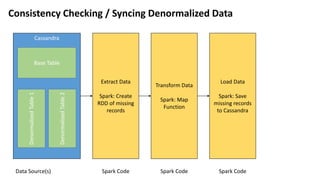
- 18. Consistency Checking / Syncing Denormalized Data Cassandra Extract Data Spark: Create RDD of missing records Data Source(s) Spark Code Base Table DenormalizedTable1 DenormalizedTable2 Transform Data Spark: Map Function Spark Code Spark Code Load Data Spark: Save missing records to Cassandra
- 19. Consistency Checking / Syncing Denormalized Data import org.apache.spark.sql.hive.HiveContext val hc = new HiveContext(sc) val query1 = """ SELECT w1.logtime, w1.page FROM test.weblog w1 LEFT JOIN test.weblog_bypage w2 ON w1.page = w2.page WHERE w2.page IS NULL""" val results1 = hc.sql(query1) results1.collect.foreach(println) val newRecord = Array(("2016-05-17 2:00:00", "page6.html")) val newRecordRdd = sc.parallelize(newRecord) newRecordRdd.saveToCassandra("test", "weblog") results1.collect.foreach(println) val transformed = results1.map { row => ( row.getString(1), row.get(0) ) } transformed.saveToCassandra("test", "weblog_bypage")
- 20. Analytics //EXAMPLE of a JOIN val query2 = """ SELECT w.page, w.logtime, p.owner FROM test.weblog w INNER JOIN test.webpage p ON w.page = p.page""" val results2 = hc.sql(query2) results2.collect.foreach(println) //EXAMPLE of a GROUP BY val query3 = """ SELECT w.page, COUNT(*) AS RecordCount FROM test.weblog w GROUP BY w.page ORDER BY w.page""" val results3 = hc.sql(query3) results3.collect.foreach(println)
- 21. Machine Learning import org.apache.spark.ml.Pipeline import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.LogisticRegression import org.apache.spark.ml.feature.{HashingTF, Tokenizer} import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vector import org.apache.spark.sql.{DataFrame, Row, SQLContext} case class LabeledDocument(id: Long, text: String, label: Double) case class DataDocument(id: Long, text: String) lazy val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc) import sqlContext.implicits._ // Load the training data val modelTrainingRecords = sc.cassandraTable("test", "ml_training") .select("id", "text", "label") val labeledDocuments = modelTrainingRecords.map { record => LabeledDocument(record.getLong("id") , record.getString("text"), record.getDouble("label")) }.toDF
- 22. Machine Learning // Create the pipeline val pipeline = { val tokenizer = new Tokenizer() .setInputCol("text") .setOutputCol("words") val hashingTF = new HashingTF() .setNumFeatures(1000) .setInputCol(tokenizer.getOutputCol) .setOutputCol("features") val lr = new LogisticRegression() .setMaxIter(10) .setRegParam(0.001) new Pipeline() .setStages(Array(tokenizer, hashingTF, lr)) } // Fit the pipeline to training documents. val model = pipeline.fit(labeledDocuments)
- 23. Machine Learning // Load the data to run against the model val modelTestRecords = sc.cassandraTable("test", "ml_text") val dataDocuments = modelTestRecords.map { record => DataDocument(record.getLong(0), record.getString(1)) }.toDF model.transform(dataDocuments) .select("id", "text", "probability", "prediction") .collect() .foreach { case Row(id: Long, text: String, prob: Vector, prediction: Double) => println(s"($id, $text) --> prob=$prob, prediction=$prediction") }
- 24. Resources Spark ŌĆó Books http://shop.oreilly.com/product/0636920028512.do Scala (Knowing Scala with really help you progress in Spark) ŌĆó Functional Programming Principles in Scala (videos) https://www.youtube.com/user/afigfigueira/playlists?shelf_id=9&view=50&sort=dd ŌĆó Books http://www.scala-lang.org/documentation/books.html Spark and Cassandra ŌĆó DataStax Academy http://academy.datastax.com/ ŌĆó Self-paced course: DS320: DataStax Enterprise Analytics with Apache Spark ŌĆō Really Good! ŌĆó Tutorials ŌĆó Spark Cassandra Connector website ŌĆō lots of good examples https://github.com/datastax/spark-cassandra-connector