6-sigma green belt introduction
- 1. 1 SIX SIGMA GREEN BELT TRAINING INTRODUCTION TO
- 2. 2 Six Sigma has evolved over the last two decades and so has its definition. Six Sigma has literal, conceptual, and practical definitions. Six Sigma has three different levels: 1. As a metric 2. As a methodology 3. As a management system Essentially, Six Sigma is all three at the same time. WHAT IS SIX SIGMA?
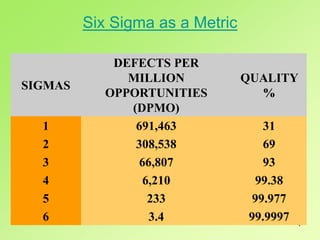
- 3. 3 The term "Sigma" is often used as a scale for levels of "goodness" or quality. Using this scale, "Six Sigma" equates to 3.4 defects per one million opportunities (DPMO). Therefore, Six Sigma started as a defect reduction effort in manufacturing and was then applied to other business processes for the same purpose. Six Sigma as a Metric
- 4. 4 SIGMAS DEFECTS PER MILLION OPPORTUNITIES (DPMO) QUALITY % 1 691,463 31 2 308,538 69 3 66,807 93 4 6,210 99.38 5 233 99.977 6 3.4 99.9997 Six Sigma as a Metric
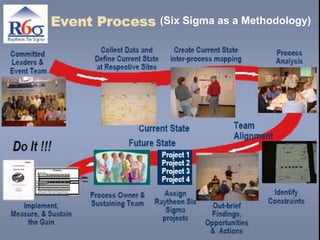
- 5. 5 Six Sigma is a business improvement methodology that focuses an organization on: Understanding and managing customer requirements Aligning key business processes to achieve those requirements Utilizing rigorous data analysis to minimize variation in those processes Driving rapid and sustainable improvement to business processes At the heart of the methodology is the DMAIC model for process improvement. DMAIC is commonly used by Six Sigma project teams and is an acronym for: Define opportunity Measure performance Analyze opportunity Improve performance Control performance Six Sigma as a Methodology
- 6. 6 The DMAIC Model Define Control Measure Improve Analyze Voice of the Customer Institutionalization Six Sigma as a Methodology
- 7. 7 (Six Sigma as a Methodology)
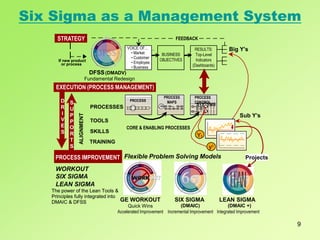
- 8. 8 When practiced as a management system, Six Sigma is a high performance system for executing business strategy. Six Sigma is a top-down solution to help organizations: Align their business strategy to critical improvement efforts Mobilize teams to attack high impact projects Accelerate improved business results Govern efforts to ensure improvements are sustained The Six Sigma Management System drives clarity around the business strategy and the metrics that most reflect success with that strategy. It provides the framework to prioritize resources for projects that will improve the metrics, and it leverages leaders who will manage the efforts for rapid, sustainable, and improved business results. Six Sigma as a Management System
- 9. 9 Six Sigma as a Management System PROCESSES TOOLS SKILLS TRAINING LEAN SIGMA (DMAIC +) Integrated Improvement Y1 y1 VOICE OF... ? Market Customer ? Employee ? ? Business FEEDBACK CORE & ENABLING PROCESSES PROCESS MAPS SYSTEMS EXECUTION (PROCESS MANAGEMENT) WORKOUT SIX SIGMA LEAN SIGMA STRATEGY If new product or process Big Y’s Sub Y’s PROCESS DFSS(DMADV) Fundamental Redesign D R I V E S S U P P O R T S Flexible Problem Solving Models Y1 y1 VOICE OF... ? Market ? Customer ? Employee ? Business BUSINESS OBJECTIVES RESULTS: Top-Level Indicators (Dashboards) PROCESS MAPS SYSTEMS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT STRATEGY If new product or process Projects PROCESS DFSS D R I V E S S U P P O R T S PROCESS CONTROL ALIGNMENT SIX SIGMA (DMAIC) Incremental Improvement GE WORKOUT Quick Wins Accelerated Improvement The power of the Lean Tools & Principles fully integrated into DMAIC & DFSS The power of the Lean Tools & Principles fully integrated into DMAIC & DFSS
- 10. 10 Six Reasons Why Business Leaders Love Six Sigma? 1. Six Sigma impacts the bottom line 2. Six Sigma drives strategy execution 3. Six Sigma generates robust, flexible business processes 4. Six Sigma improves human performance across the enterprise 5. Six Sigma is highly scalable 6. Six Sigma is a low risk investment Note: Robustness is the condition of a product or process design that remains relatively stable with a minimum of variation even though factors that influence operations or usage, such as environment and wear, are constantly changing.
- 11. 11 Six Habits of Six Sigma Leaders 1. Delivering customer value (exhibit passion, listen actively, communicate partnership) 2. Focusing on execution (result-driven, resource conscious, process-oriented) 3. Making sound, data-driven decisions (critical thinking, decisiveness, accountability) 4. Managing performance (set goals, track progress, manage details) 5. Advocating breakthrough improvements (assertiveness, influence, tenacity) 6. Supporting team-based implementations (manage teams, reward teams)
- 12. 12 Six Tools Every SS BB/GB Loves 1. Quality Function Deployment (QFD)—helps to drive customer-focused development across the design process 2. Cause and Effect (C&E) Matrix—helps to facilitate team decision making 3. Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)—helps to identify and address weaknesses in a product or process before they occur 4. Control Charts—helps to assess process stability 5. T-Student Test (t-test)—helps to validate test results using small sample size 6. Design of Experiments (DOE)—helps to make the most of valuable resources Business and/or Customer Requirement 1 2 3 4 5 6? Defects Good
- 13. 13 Six Reason Why Six Sigma Fails? 1. Lack of visible senior leader sponsorhip 2. Lack of alignment to a clear organization strategy 3. Lack of performance tracking and accountability 4. Failure to link projects to bottom-line impact 5. Insufficient or ineffective alocation of human resources 6. Over-emphasis on rigid approach and technical tools
- 14. 14 SIX SIGMA IMPLEMENTATION AT PT MATTEL INDONESIA
- 15. 15 PT Mattel’s Vision: “A globally competitive manufacturer of premier toy brands through continuous improvement”
- 16. 16 PRACTICAL PROBLEM (PT Mattel’s Needs) STATISTICAL PROBLEM STATISTICAL SOLUTION PRACTICAL SOLUTION (MATTEL’S SMART OBJECTIVES) PT MATTEL’S VISION S I X S I G M A L E A N S U P P L Y C H A I N SMART = Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Actionable, Result-oriented, Time-bound
- 17. 17 PT Mattel’s COPIS IDENTIFICATION Vision: A globally competitive manufacturer of premier toy brands through CI SMART OBJECTIVES 1. To Increase Direct Labor Efficiency from ____% to ____% 2. To Reduce Scrap from _______ PPM to ______ PPM 3. To Improve Production Schedule Adherence from ______ % to ______ % 4. To Improve Daily Schedule Adherence from _____% to ______% 5. To Reduce Lot Buy Off from _____ PPM to ______ PPM 6. To Reduce Containment Audit from _______ PPM to ______ PPM 7. To Maintain Lost Day Incident Case at Zero Level (Always Zero Goal) Product Type Customers Outputs Processes Inputs Suppliers #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 etc Customers’ Needs (Voice of Customer = VOC) KPOV (Key Per- formance Outputs Variables) – CTQ (Critical To Quality),CTS (CT Schedule, CTC (CT Cost) Processes Needs (Voice of Processes = VOP) Inputs Requi- rements Suppliers Require- Ments & Selection COPIS = Customer, Outputs, Processes, Inputs, Suppliers
- 18. 18 Six Sigma COPIS Model The Voice of the Customer (VOC) is aggressively evaluated and used to determine needed outputs and hence the optimal process configuration needed to yield those outputs and their necessary inputs for which the best suppliers are identified and allied with. From Mattel’s Concept to Market: the Voice of the Customer Customers Suppliers Outputs Inputs Process Steps How does Six Sigma Work?
- 19. 19 PT MATTEL’S SIPOC PROJECTS PT MATTEL’S LEAN SUPPLY CHAIN Product Type #1 #2 #3 #4 etc Suppliers ? Inputs ? Processes ? Outputs ? Customers LEAN-SIX SIGMA PROJECTS (PT MATTEL’S PROJECTS) APPROACH (DMAIC) LEAN-SIX SIGMA PROJECTS Define Measure Analyze Improve Control PROJECT’S OBJECTIVES ? LEAN SIX SIGMA TOOLS
- 20. 20 Six Sigma Way is a best- in-class change strategy for accelerating improvements in manufacturing processes and services. Six Sigma Way is: ? Mindset/Way of thinking ? A way of doing manufacturing/servi ce business ? Methodology/Tools for continual improvement Six Sigma Way of Transformation Six Sigma Way