7 Organizational Structure Deepak Agrawal
- 1. Presented by: Deepak Agrawal (08MTHYD023) Organizational Structure
- 2. Is it related to your behavior??? How you form a group.. How you sit in a group.. How you react at any situation.. How you respect position.. How much freedom you have.. How much authority and responsibilities you have.. How much power you have.. Organizational Structure If Yes Then obviously Organization structure also lead to individual(employee) behaviorŌĆ”.
- 3. FLOW of Presentation Elements that define organizationŌĆÖs structure Different Organizational Designs Three traditional organizational designs Simple, Bureaucracy, Matrix structure Some new design options Team Structure, Virtual Organization, Boundaryless organization Contrast Mechanistic and organic structure Influencing factors Strategy, Organization size, Technology, Environment Organizational Design and Employee Behavior Organizational Structure
- 4. Defining Organizational Structure Organizational Structure defines how job tasks are formally divided, grouped, and coordinated. Organizational Design A process involving decisions about six key elements: Work specialization Departmentalization Chain of command Span of control Centralization and decentralization Formalization Organizational Structure
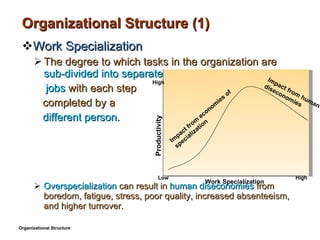
- 5. Organizational Structure (1) Work Specialization The degree to which tasks in the organization are sub-divided into separate jobs with each step completed by a different person. Overspecialization can result in human diseconomies from boredom, fatigue, stress, poor quality, increased absenteeism, and higher turnover. Organizational Structure Productivity Work Specialization Low High High Impact from economies of specialization Impact from human diseconomies
- 6. Organizational Structure (2) Functional Grouping jobs by functions performed Product Grouping jobs by product line Geographical Grouping jobs on the basis of territory or geography Process Grouping jobs on the basis of product or customer flow Customer Grouping jobs by type of customer and needs Organizational Structure Departmentalization by Type
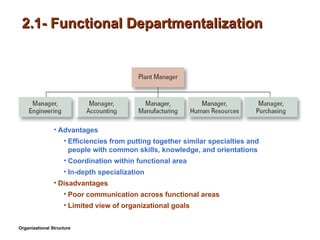
- 7. 2.1- Functional Departmentalization Advantages Efficiencies from putting together similar specialties and people with common skills, knowledge, and orientations Coordination within functional area In-depth specialization Disadvantages Poor communication across functional areas Limited view of organizational goals Organizational Structure
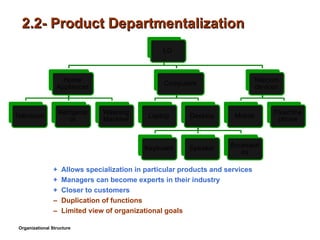
- 8. 2.2- Product Departmentalization + Allows specialization in particular products and services + Managers can become experts in their industry + Closer to customers ŌĆō Duplication of functions ŌĆō Limited view of organizational goals Organizational Structure
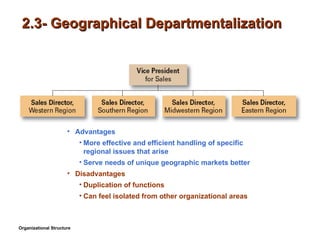
- 9. 2.3- Geographical Departmentalization Advantages More effective and efficient handling of specific regional issues that arise Serve needs of unique geographic markets better Disadvantages Duplication of functions Can feel isolated from other organizational areas Organizational Structure
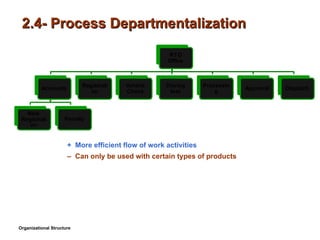
- 10. 2.4- Process Departmentalization + More efficient flow of work activities ŌĆō Can only be used with certain types of products Organizational Structure
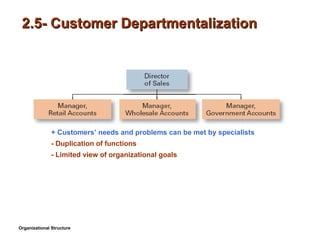
- 11. 2.5- Customer Departmentalization + CustomersŌĆÖ needs and problems can be met by specialists - Duplication of functions - Limited view of organizational goals Organizational Structure
- 12. Organization Structure (3) Chain of Command The continuous line of authority that extends from upper levels of an organization to the lowest levels of the organization and clarifies who reports to whom. Authority The rights inherent in a managerial position to tell people what to do and to expect them to do it. Unity of Command The concept that a person should have one boss and should report only to that person. Organizational Structure
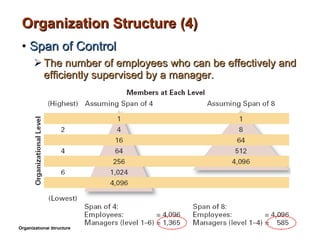
- 13. Organization Structure (4) Span of Control The number of employees who can be effectively and efficiently supervised by a manager. Organizational Structure
- 14. 4.1- Span of Control Width of span is affected by: Skills and abilities of the manager Employee characteristics Characteristics of the work being done Similarity of tasks Complexity of tasks Physical proximity of subordinates Standardization of tasks Organizational Structure
- 15. Organization Structure (5) Centralization The degree to which decision-making is concentrated at a single point in the organizations. Reduced information overload on upper managers. Increased motivation and accountability throughout organization. Fewer managers; lower bureaucratic costs . Decentralization Organizations in which decision-making is pushed down to the managers who are closest to the action . Easier coordination of organizational activities. Exercise of strong leadership in crisis . Faster decision making and response. Organizational Structure
- 16. Organization Structure (6) Formalization The degree to which jobs within the organization are standardized and the extent to which employee behavior is guided by rules and procedures . Highly formalized jobs offer little discretion over what is to be done. Low formalization means fewer constraints on how employees do their work. Organizational Structure
- 17. DIFFERENT ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGNS Part-2 Organizational Structure
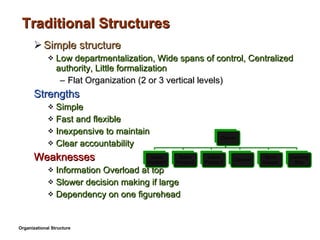
- 18. Traditional Structures Simple structure Low departmentalization, Wide spans of control, Centralized authority, Little formalization Flat Organization (2 or 3 vertical levels) Strengths Simple Fast and flexible Inexpensive to maintain Clear accountability Weaknesses Information Overload at top Slower decision making if large Dependency on one figurehead Organizational Structure
- 19. Traditional Structures The Bureaucracy High departmentalization by function, Narrow span of control , Centralized authority, High formalization Strengths Efficiency to perform standardized tasks Economies of scale Minimum duplication of personnel & equipment Cost advantage by less talent hunting Weaknesses Subunit Conflicts (ŌĆ£ BureaupathologiesŌĆØ ) Fails to take environment into account Is less effective during change or turbulence, requiring flexibility and action Ignores interpersonal relationships Organizational Structure
- 20. Traditional Structures The Matrix structure Departmentalized by both functions and products, No unity of command Strengths Strength of both function and product departmentalization Better and direct communication More Flexibility Reduce Bureaupathologies Maximizes use of employeesŌĆÖ skills Weaknesses Dual chain of command Power struggle Role conflict Less predictability Organizational Structure ’ü¼ Two-boss employee
- 21. New Design Options Team structures The entire organization is made up of work groups or self-managed teams. Require Generalists as well as specialists employee No departmentalization, Decentralized Strengths Flexibility Empowered employees Reduced barriers among functional areas (Cross-functional) Weaknesses No clear chain of command Pressure on teams to perform Organizational Structure
- 22. New Design Options Virtual Organization A small core organization that outsources its major business functions in order to concentrate what it does best. Highly centralized, no departmentalization Only coordination and controlling relationships Strengths Choosing best alternatives always Best for finite period existence (e.g. Olympics) Maximum flexibility Weaknesses Reduces managementŌĆÖs control over key parts Organizational Structure
- 23. New Design Options Boundaryless Organization (Concept) It behaves more like an organism encouraging better integration among employees and closer partnerships with Stakeholders. No chain of command, limitless spans of control Strengths Highly flexible and responsive Draws on talent wherever itŌĆÖs found Cross hierarchical team, Cross functional team No external boundaries Weaknesses Lack of control Communication difficulties Organizational Structure
- 24. ORGANIZATION DESIGN DECISIONS Part-3 Organizational Structure
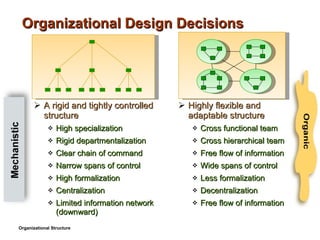
- 25. A rigid and tightly controlled structure High specialization Rigid departmentalization Clear chain of command Narrow spans of control High formalization Centralization Limited information network (downward) Organizational Design Decisions Highly flexible and adaptable structure Cross functional team Cross hierarchical team Free flow of information Wide spans of control Less formalization Decentralization Free flow of information Organizational Structure
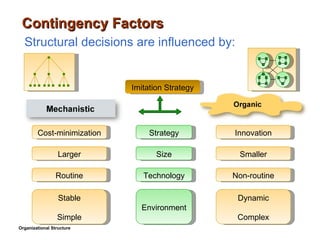
- 26. Contingency Factors Organizational Structure Innovation Cost-minimization Imitation Strategy Larger Smaller Routine Non-routine Strategy Size Technology Environment Stable Simple Dynamic Complex Structural decisions are influenced by:
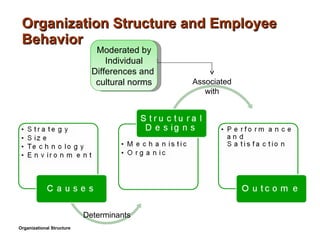
- 27. Organization Structure and Employee Behavior Organizational Structure Determinants Associated with Moderated by Individual Differences and cultural norms
- 28. THANK YOU FOR YOUR PATIENCEŌĆ”