7 standard costing
- 1. Standard Costing ï· A standard cost is a carefully predetermined estimated unit cost. ï· Usually a standard cost per unit of production, per unit of service rendered, per routine task completed or standard cost per Rs 1/= of sale. Standard costing is defined basically as a technique of cost accounting, which compares the âstandard costâ of each product or service with the actual cost, to determine the efficiency of the operation, so that any remedial action may be taken immediately. ï· Standard costing involves: o Setting of standards o Ascertaining actual results o Comparing standard and actual costs to determine the variances o Investigating the variances and taking appropriate actions where necessary ï· Standard cost may be used in both marginal and absorption costing systems. Difference between Budgeted and standard costing methods Budgeted Cost Standard Cost Total Cost Unit cost Possible to have budgeting without Not possible to have standard cost standard cost system without total cost budgeting system Full note set with Examples and Questions: http://www.executioncycle.lkblog.com/2012/06/my- business-economics-and-financial.html
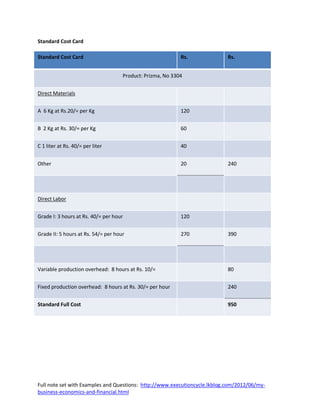
- 2. Standard Cost Card Standard Cost Card Rs. Rs. Product: Prizma, No 3304 Direct Materials A 6 Kg at Rs.20/= per Kg 120 B 2 Kg at Rs. 30/= per Kg 60 C 1 liter at Rs. 40/= per liter 40 Other 20 240 Direct Labor Grade I: 3 hours at Rs. 40/= per hour 120 Grade II: 5 hours at Rs. 54/= per hour 270 390 Variable production overhead: 8 hours at Rs. 10/= 80 Fixed production overhead: 8 hours at Rs. 30/= per hour 240 Standard Full Cost 950 Full note set with Examples and Questions: http://www.executioncycle.lkblog.com/2012/06/my- business-economics-and-financial.html
- 3. Setting Standards Revised once a year People concern with setting standards, ï· The production controller : Production requirements in term of material, labor and overhead ï· The buyer : schedules of prices and details of market price trends ï· The personnel Manager : labor rates of pay and possible forecasts of any changes in rates ï· The time study engineer : standard times for operations ï· The cost accountant: labor requirements, overhead recovery rates, etc. Advantages of standard costing ï· Yardstick against the actual costs ï· Involves determining best materials and methods, which may lead to economies. ï· Costing procedures are often simplified ï· Stock evaluation is easy ï· The operation of cost centers defines responsibilities ï· A target efficiency is set for employees to reach The standard Hours ï· Production is frequently expressed in terms of units, kilos, liters etc. ï· Nevertheless, in standard costing system production can be expressed in terms of a measure common to all products, as âstandard hourâ. Example: ABC Jam Co.Ltd produces and markets three types of Jam: Orange, Marmalade and Mixed Fruits. It is estimated that the following number of jars could be filed within one hour. Orange 2000 jars, Marmalade 6000 jars, Mixed Fruit 4000 jars. The production in February 2003 is 300,000 jars of orange 1,000,000 jars of Marmalade and 600,000 jars of Mixed Fruit. Type of Jam Production Standards units per Production in standard hour hours Orange 300,000 jars 2000 150 Marmalade 1,000,000 jars 6000 166 Mixed Fruit 600,000 jars 4000 150 466 Full note set with Examples and Questions: http://www.executioncycle.lkblog.com/2012/06/my- business-economics-and-financial.html
- 4. Full note set with Examples and Questions: http://www.executioncycle.lkblog.com/2012/06/my- business-economics-and-financial.html