7440326.ppt
- 2. Parametric & Non-parametric Parametric Non-Parametric ? A parameter to compare Mean, S.D. ?Normal Distribution & Homogeneity ? No parameter is compared Significant numbers in a category plays the role ? No need of Normal Distribution & Homogeneity ? Used when parametric is not applicable.
- 3. Parametric & Non-parametric Parametric Vs Non-parametric Which is good ? If parametric is not applicable, then only we go for a non-parametric Both are applicable, we prefer parametric. Why? In parametric there is an estimation of values. Null hypothesis is based on that estimation. In non-parametric we are just testing a Null Hypothesis.
- 4. Normality ? How do you check Normality ? ? The mean and median are approximately same. ? Construct a Histogram and trace a normal curve. Example ? Level of Significance / p-value / Type I error / ¶¡ ? Degree of Freedom
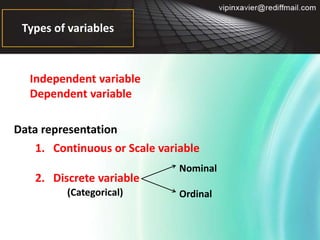
- 5. Types of variables Independent variable Dependent variable Data representation 1. Continuous or Scale variable 2. Discrete variable Nominal Ordinal (Categorical)
- 8. Paired t-test Areas of application >> When there is one group pre & post scores to compare. >> In two group studies, if there is pre & post assessment, paired t is applied to test whether there is significant change in individual group. S = S.E. = t = S.E. Example
- 9. Unpaired/independent t-test Areas of application >> When there is two group scores to compare. (One time assessment of dependent variable). >> In two group studies, if there is pre & post assessment, paired t is applied to test whether there is significant change in individual group. After this, the pre-post differences in the two groups are taken for testing. Example
- 10. Areas of application ANOVA >> When there is more than two group scores to compare. Group A x Group B x Group C Post-HOC procedures after ANOVA helps to compare the in-between groups A x B , A x C , B x C Similar to doing 3 unpaired t tests Example
- 11. Wilcoxon Matched Pairs A Non-parametric procedure >> This is the parallel test to the parametric paired t-test ? Before after differences are calculated with direction + ve or ®Cve ? 0 differences neglected. ? Absolute differences are ranked from smallest to largest ? Identical marks are scored the average rank ? T is calculated from the sum of ranks associated with least frequent sign ? If all are in same direction T = 0 Example
- 12. Mann Whitney U A Non-parametric procedure >> This is the parallel test to the parametric unpaired t-test ? Data in both groups are combined and ranked ? Identical marks are scored the average rank ?Sum of ranks in separate groups are calculated ? Sum of ranks in either group can be considered for U. ? n1 is associated with °∆R1i , n2 is associated with °∆R2j Example
- 13. Median Test A Non-parametric procedure Similar to the cases of Mann Whitney >> This is the parallel test to the parametric unpaired t-test ? Data in both groups are combined and median is calculated ? Contingency table is prepared as follows
- 14. Kruskal Walis A Non-parametric procedure >> This is the parallel test to the parametric ANOVA >> ANOVA was an extension of 2-group t-test >> Kruskal Walis is an extension of Mann Whitney U ? Data in all groups are combined and ranked ? Identical marks are scored the average rank ?Sum of ranks in separate groups are calculated Areas of application >> Areas similar to ANOVA >> Comparison of dependent variable between categories in a demographic variable Example
- 15. Mc Nemar°Øs Test Areas of application >> Similar to the parametric paired t-test, but the dependent variable is discrete, qualitative.