823963 body-fluids
- 1. www.Examville.com Online practice tests, live classes, tutoring, study guides Q&A, premium content and more .
- 2. The Body Fluid Compartments : Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids: Interstitial Fluid and Edema Body Fluids and The Kidneys
- 3. The maintenance of a relatively constant volume and a stable composition of the body fluids is essential for homeostasis Fluid Intake and Output are Balanced During Steady-State Conditions
- 5. 1. Extracellular Fluid Compartment - 14.0 L Interstitial - 11.0 L = 3/4 Plasma - 3.0 L = 1/4 2. Extracellular Fluid Compartment = 28.0 L 3. Transcellular Fluid Compartment 1to 2 liters - includes fluid in the following Spaces: Synovial Peritoneal Pericardial Intraocular Cerebrospinal fluid
- 6. Total Body Water is 60% of the body weight = 42 liters Extracellular Fluid 20% = 14.0L Intracellular Fluid 40% = 28.0L Blood Volume Blood contains both extracellular fluid (the fluid in the plasma) and intracellular fluid ( the fluid in the red blood cells)
- 7. Constituents of Extracellular Fluid and Intracellular Fluid
- 8. Ěý
- 9. Regulation of Fluid Exchange and Osmotic Equilibrium Between Intracellular and Extracellular Fluid Basic Principles of Osmosis and Osmotic Pressure Osmotic Equilibrium is Maintain Between Intracellular Fluid and Extracellular Fluid
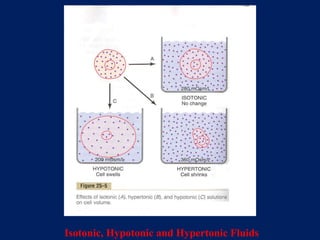
- 10. Isotonic, Hypotonic and Hypertonic Fluids
- 11. Osmotic Equilibrium Between Intracellular and Extracellular Fluids is Rapidly Attained Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular Fluid in Abnormal States Basic Principles to Calculate Changes in Intracellular and Extracellular Fluid Volumes and Types of Therapy 1. Water moves rapidly across cell membrane ; therefore the osmolarities of ICF and ECF remain almost exactly equal to each other. 2. Cell membranes are most completely impermeable to many solutes ; therefore the number of osmoles in the ECF or ICF remain constant.
- 12. Effect of Adding Saline Solution to the Extracellular Fluid
- 13. Ěý
- 14. Ěý
- 15. Clinical Abnormalities of Fluid Volume Regulation: Hyponatremia and Hypernatremia
- 16. Causes of Hyponatremia: - Excess Water - Loss of Sodium Causes of Hypernatremia: - Water loss - Excess of Sodium
- 17. EDEMA : presence of excess fluid in the body tissues A. Intracellular Edema A. depression of the metabolic systems of the tissues B. lack of adequate nutrition to the cells C. Inflammation B. Extracellular Edema A. abnormal leakage of fluid from the plasma to the interstitial spaces across the capillaries B. failure of the lymphatics to return fluid from the interstitium back into the blood
- 18. The most common clinical cause of interstitial fluid accumulation is excessive capillary fluid filtration Factors That Can Increase Capillary Filtration 1. Increase Filtration Coefficient - product of permeability and surface area of the capillaries ( k f ) 2.Increase Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure ( Pc ) 3. Decrease capillary Colloid Osmotic Pressure ( iic) Filtration = Kf x ( Pc - Pif - iic +iiif )
- 19. Major Factors that cause Increased Capillary Filtration of Fluid and Protein into the Interstitium: 1. Increased capillary Hydrostatic Pressure 2. Decreased Plasma Colloid Osmotic Pressure 3. Increased Capillary Permeability
- 20. Summary of Causes of Extracellular Edema 1. Increased capillary pressure A. Excessive kidney retention of salt and water 1. Acute and chronic kidney failure 2. Mineralocorticoid excess B. High venous pressure 1. Heart failure 2. Venous obstruction 3. Failure of venous pump A. paralysis of muscle B. immobilized parts of body C. Failure of venous valves
- 21. C. Decreased arteriolar resistance 1. Excessive body heat 2. Insufficiency of sympathetic nervous system 3. Vasodilator drugs II. Decreased plasma proteins A. Loss of proteins in urine ( nephrotic syndrome ) B. Loss of proteins from denuded skin areas 1. Burns 2. Wounds C. Failure to produce proteins 1. Liver disease 2. Serious protein or caloric malnutrition
- 22. III. Increased capillary permeability A. Immune reactions that cause release of histamine B. Toxins C. Bacterial infections D. Vitamin deficiency, especially vitamin C E. Prolonged ischemia F. Burns IV. Blockage of lymph return A. Cancer B. Infections ( filarial nematodes) C. Surgery D. Congenital absence or abnormality of lymphatic vessels
- 23. Safety Factors That Prevent Edema 1. The safety factors caused by low tissue compliance ( -3 mmHg ) 2. The safety factor caused by increased lymph flow ( 7 mmHg ) 3. The safety factor caused by washdown of proteins from the interstitial spaces ( 7 mmHg )
- 24. Ěý
- 25. It’s FREE to join. http://www.examville.com