A brief introduction to cellular-mobile-communications.ppt
- 1. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction
- 2. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction ’üČSeveral Types of Mobile Radio Systems ’üČ Garage Door Controller [<100 MHz] ’üČ Remote Controllers [TV/VCR/DISH][Infra-Red: 1-100 THz] ’üČ Cordless Telephone [<100 MHz] ’üČ Hand-Held Radio [Walki-Talki] [VHF-UHF:40-480 MHz] ’üČ Pagers/Beepers [< 1 GHz] ’üČ Cellular Mobile Telephone[<2 GHz] ’üČClassification ’üČ Simplex System: Communication is possible in only one direction : Garage Door Controller, Remote Controllers [TV/VCR/DISH] Pagers/Beepers ’üČ Semi-Duplex System: Communication is possible in two directions but one talks and other listens at any time[Push to Talk System]: Walki-Talki ’üČ Duplex System: Communication is possible in both directions at any time: Cellular Telephone [FDD or TDD]
- 3. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction ’üČPaging System: For Transmission of Brief Numeric/Alpha- numeric/Voice Messages [Pages] to Subscriber ’üČ To Notify/Alert the User ’üČ Simplex Service ’üČ Modern Paging Systems Can Send News Head-Lines, Stock Info, or Fax ’üČ Application Dependent System Range [2 Km to World-wide] PAGING CONTROL CENTRE Paging Terminal PSTN Land Line Link Land Line Link Paging Terminal Paging Terminal City 1 City 2 City N
- 4. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction ’üČCordless Telephone System: To Connect a Fixed Base Station to a Portable Cordless Handset ’üČ Early Systems (1980s) have very limited range of few tens of meters [within a House Premises] ’üČ Modern Systems [PACS, DECT, PHS, PCS] can provide a limited range & mobility within Urban Centers PSTN Fixed Base Station Cordless Handset
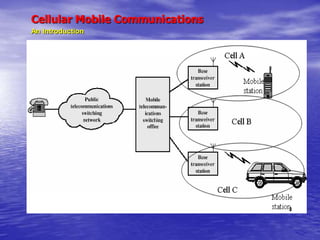
- 5. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction ’üČ Basic Components of a Cellular Telephone System ’üČ Cellular Mobile Phone: A light-weight hand-held set which is an outcome of the marriage of Graham BellŌĆÖs Plain Old Telephone Technology [1876] and MarconiŌĆÖs Radio Technology [1894] [although a very late delivery but very cute] ’üČ Base Station: A Low Power Transmitter, other Radio Equipment [Transceivers] plus a small Tower ’üČ Mobile Switching Center [MSC] /Mobile Telephone Switching Office[MTSO] ’üČ An Interface between Base Stations and the PSTN ’üČ Controls all the Base Stations in the Region and Processes User ID and other Call Parameters ’üČ A typical MSC can handle up to 100,000 Mobiles, and 5000 Simultaneous Calls ’üČ Handles Handoff Requests, Call Initiation Requests, and all Billing & System Maintenance Functions
- 6. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction
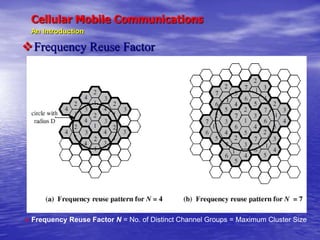
- 7. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction ’üČ The Cellular Concept ’üČRF spectrum is a valuable and scarce commodity ’üČRF signals attenuate over distance ’üČCellular network divides coverage area into cells, each served by its own base station transceiver and antenna ’üČLow (er) power transmitters used by BSs; transmission range determines cell boundary ’üČRF spectrum divided into distinct groups of channels ’üČAdjacent cells are (usually) assigned different channel groups to avoid interference ’üČCells separated by a sufficiently large distance to avoid mutual interference can be assigned the same channel group ’ā× frequency reuse among co-channel cells
- 8. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction ’üČ An Example of Frequency Reuse ’üČ Suppose we have spectrum for 100 voice channels ’üČ Scenario 1: a high power base station covering entire area ŌĆō system capacity = 100 channels ’üČ Scenario 2: divide spectrum into 4 groups of 25 channels each; cells (1, 7), (2, 4), (3, 5), 6 are assigned distinct channel groups ŌĆō system capacity = 175 channels
- 9. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction ’üČFrequency Reuse Factor ’üČ Frequency Reuse Factor N = No. of Distinct Channel Groups = Maximum Cluster Size
- 10. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction ’üČ Common Air Interface (CAI) Forward Channel Reverse Channel ’üČCommon Air Interface: A Standard that defines Communication between a Base Station and Mobile ’üČSpecifies Four Channels [Voice Channels and Control / Setup Channels] ’üČFVC: Forward Voice Channel ’üČRVC: Reverse Voice Channel ’üČFCC: Forward Control Channel ’üČRCC: Reverse Control Channel
- 11. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction ’üČ Call Setup Procedure ’üČCellular Phone Codes: Special Codes are associated with each Cell Phone to identify the phone, its owner, and service provider: ’üČElectronic Serial Number(ESN) -A Unique 32-bit Code ’üČMobile Identification Number(MIN): A SubscriberŌĆÖs Telephone Number ’üČ Station Class mark (SCM): Indicates the Max Tx Power for the User ’üČWhen a Cellular Phone is turned on and Initiates a Call:[see next slide] ’üČMonitors the Control Channels and gets hold on to the strongest one ’üČMakes a Call Initiation Request[Dials the Called part Number, MIN , ESN and SCM automatically transmitted] ’üČValidation Procedure at MSC & Voice-Frequency pair Allocation ’üČBase Station Pages the Information for the Mobile ’üČMSC Connects the Mobile with the Called Party[Another Mobile/Landline Phone] ’üČCall is Established and Communication Starts
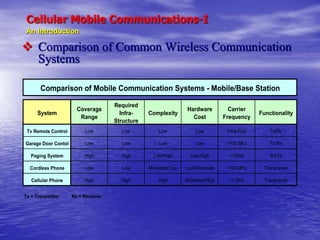
- 12. Cellular Mobile Communications-I An Introduction ’üČ Comparison of Common Wireless Communication Systems System Coverage Range Required Infra- Structure Complexity Hardware Cost Carrier Frequency Functionality Tv Remote Control Low Low Low Low Infra-Red Tx/Rx Garage Door Contol Low Low Low Low <100 Mhz Tx/Rx Paging System High High Low/High Low/High <1GHz Rx/Tx Cordless Phone Low Low Moderate/Low Low/Moderate <100 MHz Transceiver Cellular Phone High High High Moderate/High <1 GHz Transceiver Tx = Transmitter Rx = Receiver Comparison of Mobile Communication Systems - Mobile/Base Station
- 13. Cellular Mobile Communications-I An Introduction ’üČ Cellular Mobile Access Technologies ’üČFDMA Assigns each Call a Separate Frequency ’üČWorks like Radio Stations ’üČMainly Analogue Technology-used by AMPS, NAMPS, E-TACS, NMT-450, JTACS ’üČNot an Efficient Method for Digital Transmission 849 MHz 869 MHz
- 14. Cellular Mobile Communications-I An Introduction ’üČ Cellular Mobile Access Technologies ’üČTDMA Assigns each Call a certain Time-Slot on a Designated Frequency ’üČEach Mobile/User gets one-third of a total Channel Time-Slot[6.7 ms] ’üČCourtesy of Compression Techniques: Speech Data in Digital Form takes considerably less time ’üČOptimal Frequency Usage: System Capacity improves by three times ’üČOperates both in 800 MHz[IS-54] and 1900 MHz[IS-136] ’üČDigital Access Technology use by GSM, USDC, IDEN, PDC and PCS
- 15. Cellular Mobile Communications-I An Introduction ’üČ Cellular Mobile Access Technologies ’üČCDMA Assigns a Unique Code to each Call and Spreads it over the entire bandwidth available ’üČ A form of Spread Spectrum Technology ’üČSpeech Data is sent in small pieces over number of Discrete Frequencies available at any time in a specified range ’üČ Receiver uses the same unique Code to Recover the Speech Data ’üČGPS used for Exact Time Stamp ’üČCan handle 8-10 Calls in the same Channel Space as one Analogue Channel ’üČAn Access Technology for 3G Mobile Systems[IMT-2000] ’üČSupports both Bands [800 MHz and 1900 MHz]
- 16. Cellular Mobile Communications An Introduction ’üČ Trends in Cellular radio and Personal Communications ’üČ PCS/PCN: PCS calls for more personalized services whereas PCN refers to Wireless Networking Concept-any person, anywhere, anytime can make a call using PC. PCS and PCN terms are sometime used interchangeably ’üČ IEEE 802.11: A standard for computer communications using wireless links[inside building]. ’üČ ETSIŌĆÖs 20 Mbps HIPER LAN: Standard for indoor Wireless Networks ’üČ IMT-2000 [International Mobile Telephone-2000 Standard]: A 3G universal, multi-function, globally compatible Digital Mobile Radio Standard is in making ’üČ Satellite-based Cellular Phone Systems ’üČ A very good Chance for Developing Nations to Improve their Communication Networks

![Cellular Mobile Communications
An Introduction
’üČSeveral Types of Mobile Radio Systems
’üČ Garage Door Controller [<100 MHz]
’üČ Remote Controllers [TV/VCR/DISH][Infra-Red: 1-100 THz]
’üČ Cordless Telephone [<100 MHz]
’üČ Hand-Held Radio [Walki-Talki] [VHF-UHF:40-480 MHz]
’üČ Pagers/Beepers [< 1 GHz]
’üČ Cellular Mobile Telephone[<2 GHz]
’üČClassification
’üČ Simplex System: Communication is possible in only one direction : Garage Door
Controller, Remote Controllers [TV/VCR/DISH] Pagers/Beepers
’üČ Semi-Duplex System: Communication is possible in two directions but one talks
and other listens at any time[Push to Talk System]: Walki-Talki
’üČ Duplex System: Communication is possible in both directions at any time: Cellular
Telephone [FDD or TDD]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellular-mobile-communications-240520075511-a6bb450b/85/A-brief-introduction-to-cellular-mobile-communications-ppt-2-320.jpg)
![Cellular Mobile Communications
An Introduction
’üČPaging System: For Transmission of Brief Numeric/Alpha-
numeric/Voice Messages [Pages] to Subscriber
’üČ To Notify/Alert the User
’üČ Simplex Service
’üČ Modern Paging Systems Can Send News Head-Lines, Stock Info, or Fax
’üČ Application Dependent System Range [2 Km to World-wide]
PAGING CONTROL
CENTRE
Paging Terminal
PSTN
Land Line Link
Land Line Link
Paging Terminal
Paging Terminal
City 1
City 2
City N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellular-mobile-communications-240520075511-a6bb450b/85/A-brief-introduction-to-cellular-mobile-communications-ppt-3-320.jpg)
![Cellular Mobile Communications
An Introduction
’üČCordless Telephone System: To Connect a Fixed
Base Station to a Portable Cordless Handset
’üČ Early Systems (1980s) have very limited range of few tens of
meters [within a House Premises]
’üČ Modern Systems [PACS, DECT, PHS, PCS] can provide a limited
range & mobility within Urban Centers
PSTN
Fixed Base
Station
Cordless Handset](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellular-mobile-communications-240520075511-a6bb450b/85/A-brief-introduction-to-cellular-mobile-communications-ppt-4-320.jpg)
![Cellular Mobile Communications
An Introduction
’üČ Basic Components of a Cellular Telephone System
’üČ Cellular Mobile Phone: A light-weight hand-held set which is an
outcome of the marriage of Graham BellŌĆÖs Plain Old Telephone
Technology [1876] and MarconiŌĆÖs Radio Technology [1894] [although a
very late delivery but very cute]
’üČ Base Station: A Low Power Transmitter, other Radio Equipment
[Transceivers] plus a small Tower
’üČ Mobile Switching Center [MSC] /Mobile Telephone
Switching Office[MTSO]
’üČ An Interface between Base Stations and the PSTN
’üČ Controls all the Base Stations in the Region and Processes User ID and
other Call Parameters
’üČ A typical MSC can handle up to 100,000 Mobiles, and 5000 Simultaneous
Calls
’üČ Handles Handoff Requests, Call Initiation Requests, and all Billing & System
Maintenance Functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellular-mobile-communications-240520075511-a6bb450b/85/A-brief-introduction-to-cellular-mobile-communications-ppt-5-320.jpg)


![Cellular Mobile Communications
An Introduction
’üČ Common Air Interface (CAI)
Forward Channel
Reverse Channel
’üČCommon Air Interface: A Standard
that defines Communication between a
Base Station and Mobile
’üČSpecifies Four Channels [Voice
Channels and Control / Setup
Channels]
’üČFVC: Forward Voice Channel
’üČRVC: Reverse Voice Channel
’üČFCC: Forward Control Channel
’üČRCC: Reverse Control Channel](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellular-mobile-communications-240520075511-a6bb450b/85/A-brief-introduction-to-cellular-mobile-communications-ppt-10-320.jpg)
![Cellular Mobile Communications
An Introduction
’üČ Call Setup Procedure
’üČCellular Phone Codes: Special Codes are associated with each Cell
Phone to identify the phone, its owner, and service provider:
’üČElectronic Serial Number(ESN) -A Unique 32-bit Code
’üČMobile Identification Number(MIN): A SubscriberŌĆÖs Telephone Number
’üČ Station Class mark (SCM): Indicates the Max Tx Power for the User
’üČWhen a Cellular Phone is turned on and Initiates a Call:[see
next slide]
’üČMonitors the Control Channels and gets hold on to the strongest one
’üČMakes a Call Initiation Request[Dials the Called part Number, MIN , ESN and SCM
automatically transmitted]
’üČValidation Procedure at MSC & Voice-Frequency pair Allocation
’üČBase Station Pages the Information for the Mobile
’üČMSC Connects the Mobile with the Called Party[Another Mobile/Landline Phone]
’üČCall is Established and Communication Starts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellular-mobile-communications-240520075511-a6bb450b/85/A-brief-introduction-to-cellular-mobile-communications-ppt-11-320.jpg)

![Cellular Mobile Communications-I
An Introduction
’üČ Cellular Mobile Access Technologies
’üČTDMA Assigns each Call a
certain Time-Slot on a Designated
Frequency
’üČEach Mobile/User gets one-third of
a total Channel Time-Slot[6.7 ms]
’üČCourtesy of Compression
Techniques: Speech Data in Digital
Form takes considerably less time
’üČOptimal Frequency Usage: System
Capacity improves by three times
’üČOperates both in 800 MHz[IS-54]
and 1900 MHz[IS-136]
’üČDigital Access Technology use by
GSM, USDC, IDEN, PDC and PCS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellular-mobile-communications-240520075511-a6bb450b/85/A-brief-introduction-to-cellular-mobile-communications-ppt-14-320.jpg)
![Cellular Mobile Communications-I
An Introduction
’üČ Cellular Mobile Access Technologies
’üČCDMA Assigns a Unique Code to
each Call and Spreads it over the entire
bandwidth available
’üČ A form of Spread Spectrum
Technology
’üČSpeech Data is sent in small pieces
over number of Discrete Frequencies
available at any time in a specified range
’üČ Receiver uses the same unique Code
to Recover the Speech Data
’üČGPS used for Exact Time Stamp
’üČCan handle 8-10 Calls in the same
Channel Space as one Analogue Channel
’üČAn Access Technology for 3G Mobile
Systems[IMT-2000]
’üČSupports both Bands [800 MHz and
1900 MHz]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellular-mobile-communications-240520075511-a6bb450b/85/A-brief-introduction-to-cellular-mobile-communications-ppt-15-320.jpg)
![Cellular Mobile Communications
An Introduction
’üČ Trends in Cellular radio and Personal
Communications
’üČ PCS/PCN: PCS calls for more personalized services whereas
PCN refers to Wireless Networking Concept-any person,
anywhere, anytime can make a call using PC. PCS and PCN
terms are sometime used interchangeably
’üČ IEEE 802.11: A standard for computer communications using
wireless links[inside building].
’üČ ETSIŌĆÖs 20 Mbps HIPER LAN: Standard for indoor Wireless
Networks
’üČ IMT-2000 [International Mobile Telephone-2000
Standard]: A 3G universal, multi-function, globally compatible
Digital Mobile Radio Standard is in making
’üČ Satellite-based Cellular Phone Systems
’üČ A very good Chance for Developing Nations to Improve
their Communication Networks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellular-mobile-communications-240520075511-a6bb450b/85/A-brief-introduction-to-cellular-mobile-communications-ppt-16-320.jpg)