A Common Country Assessment of the Philippines 103-118
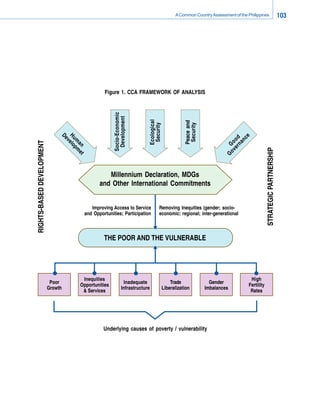
- 1. A Common Country Assessment of the Philippines 103 Figure 1. CCA FRAMEWORK OF ANALYSIS Socio-Economic Development Ecological Peace and Security Security d ce H u elo De o o nan v RIGHTS-BASED DEVELOPMENT m pm G er a n et v STRATEGIC PARTNERSHIP Go Millennium Declaration, MDGs and Other International Commitments Improving Access to Service Removing Inequities (gender; socio- and Opportunities; Participation economic; regional; inter-generational THE POOR AND THE VULNERABLE Inequities High Poor Inadequate Trade Gender Opportunities Fertility Growth Infrastructure Liberalization Imbalances & Services Rates Underlying causes of poverty / vulnerability
- 2. 104 A Common View, A Common Journey
- 3. A Common Country Assessment of the Philippines 105
- 4. 106 A Common View, A Common Journey Figure 4. An ENR Conceptual Framework on Environment, Population and Poverty Within the Context of Sustainable Development ENR Forest, Biodiversity and Water Resources Mineral Resources Land Resources Coastal/Marine Reosurces Provides Goods and Services Sustains ecological stability Waste assimilation Nutrient cycling Natural Life Water cycling Capital Support Oxygen generation Resource Carbon sequestration Services Climate balance control Wildlife habitat Pests and diseases control Sustains productive and regenerative capacity Conservation Protection Generate funds for Food (crops, livestock, ENR Management Management Framework fisheries) Resource use planning Water (drinking, irrigation, and allocation power) Wealth Ecosystem Regulatory measures Industrial Products Economic measures (wood, chemicals, cement, Creation Stability Shared governance steel, pharmaceuticals, IEC/Info system development chemicals and other Rehabilitation measures manufactured materials) Sustains production Research and development Tourist/recreation Poverty reduction programs Technical advisory services Sustains conservation and protection efforts Income and employment Stable ecological systems Savings and investments Economic Ecological Clean air and water Foreign revenues Development Balance Production resource base Sustains ENR quality and quantity Improves human capital QOL, breaks poverty Investments in Physical capital (infrastructures, Social Quality of life plans, equipment, etc.) Capital Society’s Peace and security Human capital (Knowledge Formation Well-being Sustainable population and skills) Social justice Intellectual capital (technol- ogy and institutions, knowledge industries) Improves economic productivity Sustained Sustained Economic ENR Development Management Environment and Natural Resources (ENR) Management
- 5. A Common Country Assessment of the Philippines 107
- 6. 108 A Common View, A Common Journey
- 7. A Common Country Assessment of the Philippines 109
- 8. 110 A Common View, A Common Journey
- 9. A Common Country Assessment of the Philippines 111
- 10. 112 A Common View, A Common Journey
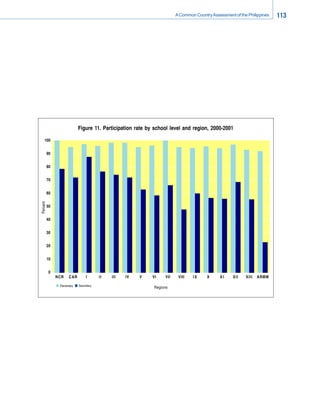
- 11. A Common Country Assessment of the Philippines 113 Figure 11. Participation rate by school level and region, 2000-2001 100 90 80 70 60 Percent 50 40 30 20 10 0 NCR CAR I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X XI XII XIII ARMM Elementary Secondary Regions
- 12. 114 A Common View, A Common Journey
- 13. A Common Country Assessment of the Philippines 115 Figure 13. Cohort survival rate by school level and region, 2000-2001 100 90 80 70 60 Percent 50 40 30 20 10 0 NCR CAR I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X XI XII XIII ARMM Elementary Secondary Regions
- 14. 116 A Common View, A Common Journey Figure 14. Cohort survival rate to grade 6 by gender and region, 2000-2001 100 90 80 70 60 Percent 50 40 30 20 10 0 NCR CAR I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X XI XII XIII ARMM Male Female Regions
- 15. A Common Country Assessment of the Philippines 117
- 16. 118 A Common View, A Common Journey