A szÃv ÃĐs az ÃĐrrendszer anatÃģmiÃĄja
Download as ppt, pdf1 like5,646 views
1 of 8
Downloaded 30 times

Ad
Recommended
Adrenal hormones
Adrenal hormonesDr.M.Prasad Naidu
Ėý
The document summarizes adrenal hormones and their functions. It discusses that the adrenal glands are composed of the adrenal cortex and medulla. The cortex produces steroid hormones like cortisol, aldosterone and androgens. The medulla produces catecholamines including epinephrine and norepinephrine. It describes the synthesis, regulation and effects of these hormones. It also discusses adrenal disorders like Cushing's syndrome, Conn's syndrome and adrenal insufficiency.Acid base balance
Acid base balanceJayprakash Shahjayprakash978
Ėý
This document discusses acid-base balance and disorders. It covers 3 key mechanisms to maintain blood pH: 1) blood buffers, 2) respiratory regulation, and 3) renal regulation. The blood's bicarbonate buffer system uses carbonic acid, while tissues also use phosphate and protein buffers. Respiration controls pH by regulating CO2 exhalation. The kidneys compensate for acid-base imbalances over hours by regulating bicarbonate reabsorption and acid excretion. Acid-base disorders include respiratory and metabolic acidosis and alkalosis.Porphyrin Metabolism
Porphyrin MetabolismRehmanRaheem
Ėý
Porphyrin metabolism involves the biosynthesis of heme through a series of enzymatic reactions in the liver and erythroid tissues. Deficiencies in enzymes involved in this pathway can result in porphyrias, characterized by accumulation of porphyrin intermediates and excessive porphyrin excretion in urine, sometimes with neurovisceral symptoms. Heme is degraded through the action of heme oxygenase to form biliverdin and ultimately bilirubin, which is conjugated and excreted in bile and urine. Elevated bilirubin levels can cause jaundice through various mechanisms of liver dysfunction or increased heme breakdown. Proteomic Strategies for purification of lactate dehydrogenase ...
Proteomic Strategies for purification of lactate dehydrogenase ...Gaurav Dwivedi
Ėý
The document summarizes proteomic strategies for purifying lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) from chicken muscle. Key steps included homogenizing muscle tissue, removing debris via centrifugation, precipitating proteins with ammonium sulfate, dialyzing to remove salts, and purifying LDH using blue sepharose affinity chromatography. SDS-PAGE and activity assays confirmed the isolation of a single 35 kDa protein band corresponding to LDH. The multi-step process successfully extracted and purified LDH from chicken muscle for further study.Dna damage and repair
Dna damage and repairMadurai kamaraj university
Ėý
DNA in cells can become damaged through radiation, chemicals, and errors during replication. There are several pathways cells use to repair DNA damage, including direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, and mismatch repair. Double strand breaks can be repaired through direct joining of broken ends or homologous recombination using the sister chromatid as a template. Failure to properly repair DNA damage can lead to mutations and genetic disorders.Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney diseaseQuratulann bader
Ėý
This document discusses chronic kidney disease (CKD), including its definition as structural or functional abnormalities of the kidneys for over 3 months, stages of progression from normal kidney function to kidney failure, prevalence, clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis and management, classification based on etiology and diagnosis, and remaining treatment options for end-stage renal disease.Liver cirrhosis, Clinical Presentation, Complications and Treatment.
Liver cirrhosis, Clinical Presentation, Complications and Treatment.DrSyedMansoorRashid
Ėý
The document provides a comprehensive overview of liver cirrhosis, including its etiology, pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment options. It highlights the complications associated with cirrhosis, such as ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and hepatocellular carcinoma, and emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate management. Treatment strategies focus on addressing the underlying cause, managing complications, and considering liver transplantation for decompensated patients.HYPOTHALAMUS CONTROLS PITUITARY SECRETION.pptx
HYPOTHALAMUS CONTROLS PITUITARY SECRETION.pptxFatimaSundus1
Ėý
The hypothalamus controls secretion of the pituitary gland. It sends signals via nerve connections to the posterior pituitary and releases hormones into the hypothalamic-hypophysial portal system that influence the anterior pituitary. These hypothalamic releasing and inhibitory hormones are synthesized in neurons of the hypothalamus and secreted into the median eminence, then carried via blood vessels to the anterior pituitary to regulate its hormone secretion. In this way, the hypothalamus integrates information from the body and nervous system to control the pituitary and many other physiological functions.Disorder of sodium imbalance
Disorder of sodium imbalancePradip Katwal
Ėý
This case discusses a 67-year-old female who presented with fever, vomiting, and loose stool for several days. On examination, she was found to be hypotensive and dehydrated. Initial tests showed hyponatremia, hypokalemia, and metabolic acidosis. She was diagnosed with acute infectious gastroenteritis complicated by hypovolumic shock and electrolyte imbalances. She was treated with IV fluids and antibiotics. Her condition improved over three days with correction of her volume status and electrolytes. The discussion then reviews hyponatremia, its causes, assessment of volume status, and treatment approaches depending on the underlying condition.Renal tubular reabsorption, secretion, regulation & renal function tests
Renal tubular reabsorption, secretion, regulation & renal function testsDipti Magan
Ėý
Renal tubular reabsorption and secretion involves the transport of substances across tubular epithelial cells. Substances may be reabsorbed from the tubular fluid back into the blood (reabsorption exceeds filtration) or secreted from the blood into the tubular fluid (secretion exceeds filtration). Clearance tests can measure glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and renal plasma flow. Substances like inulin that are freely filtered but not reabsorbed/secreted will have a clearance equal to GFR, while clearance of substances like para-aminohippuric acid (PAH) that are secreted can estimate renal plasma flow. Hormones and other factors regulate tubular transport and fluid/electroly15 Cox Acute Renal Failure
15 Cox Acute Renal FailureDang Thanh Tuan
Ėý
The document discusses acute renal failure (ARF), including its definition, classification into pre-renal, renal and post-renal types, and common causes. It describes the pathophysiology of pre-renal azotemia and acute tubular necrosis (ATN). Diagnostic tools for ARF including urinary sediment examination, urine indices, and radiologic imaging are also summarized.Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathyFahim Ahmad
Ėý
Diabetic nephropathy is a chronic kidney disease that develops over many years in people with diabetes. It is characterized by increased urinary albumin excretion, hyperglycemia, high blood pressure, declining kidney function, and the absence of other kidney diseases. According to studies, 20-44% of people with diabetes develop kidney failure and require renal replacement therapy like dialysis. The pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy involves metabolic pathways like increased polyol pathway flux, hexosamine pathway flux, formation of advanced glycation end products, and activation of protein kinase C, as well as hemodynamic changes and genetic factors. Major therapeutic interventions include controlling blood glucose, blood pressure, lipids, restricting protein intake,Respiracijska acidoza i alkaloza
Respiracijska acidoza i alkalozaDomina Petric
Ėý
Dokument opisuje respiracijsku acidozu i alkalozu, naglaÅĄavajuÄi uzroke, mehanizme kompenzacije i kliniÄke manifestacije tih stanja. Akutna respiracijska acidoza brzo se razvija uz opasnosti po Åūivot, dok kroniÄna forma moÅūe biti kompenzirana, ali ne uvijek. Terapija ukljuÄuje lijeÄenje osnovnog uzroka, s posebnim mjerama za izbjegavanje pogorÅĄanja hiperkapnijske situacije kod pacijenata s kroniÄnom acidozom.PoremeÄaj prometa vode i elektrolita
PoremeÄaj prometa vode i elektrolitaAntonio KobaÅĄ
Ėý
Dokument opisuje raspodjelu tjelesnih tekuÄina, njihovu funkciju i vaÅūnost elektrolita u regulaciji prometa vode i elektrolita. PoremeÄaji prometa vode i elektrolita, kao ÅĄto su dehidracija, hiperhidracija, hiponatrijemija i hiperkalcijemija, objaÅĄnjeni su kroz njihove uzroke i simptome. TakoÄer se razmatraju mehanizmi nastanka edema i vaÅūnost pravilne regulacije tjelesnih tekuÄina za odrÅūavanje zdravlja.Fejezetek a keresztmetszeti anatÃģmiÃĄbÃģl - 4. A mellkas ÃĐs szÃv keresztmetszet...
Fejezetek a keresztmetszeti anatÃģmiÃĄbÃģl - 4. A mellkas ÃĐs szÃv keresztmetszet...Dr. Jakab AndrÃĄs
Ėý
AnatomÃa coronaria bÃĄsica - CoronariografÃa. VisualizaciÃģn de las arterias co...
AnatomÃa coronaria bÃĄsica - CoronariografÃa. VisualizaciÃģn de las arterias co...CardioTeca
Ėý
The document details the anatomy of coronary arteries, specifically the right and left coronary systems, including their branches and anatomical landmarks. It describes the dominance patterns of coronary circulation, the average dimensions of the left main artery, and the various views used to visualize these structures during imaging. Key branches of both coronary arteries are highlighted, along with their respective vascular supplies and important collateral connections.Angiografia coronariaDaniel Meneses
Ėý
El documento presenta una revisiÃģn de las limitaciones de la angiografÃa coronaria, incluyendo la sobrestimaciÃģn de la severidad de las estenosis, las dificultades en la interpretaciÃģn de las calcificaciones y las lesiones en bifurcaciones, y la subestimaciÃģn de la ganancia luminal tras angioplastia. TambiÃĐn compara los resultados de la angiografÃa con tÃĐcnicas cuantitativas y con la fisiologÃa, mostrando una sobreestimaciÃģn de la enfermedad coronaria.AnatomÃa coronariaJesus Custodio
Ėý
Este documento describe la anatomÃa coronaria y las proyecciones angiogrÃĄficas utilizadas para visualizar las arterias coronarias. Explica que la arteria coronaria derecha suele ser dominante y proporciona detalles sobre las vistas angiogrÃĄficas optimas para evaluar las diferentes secciones de las arterias coronarias izquierda y derecha.arterias coronariasMedicineStudent
Ėý
El documento describe la anatomÃa de las arterias coronarias. Explica que las arterias coronarias izquierda y derecha nacen de la aorta y suministran sangre al mÚsculo cardÃaco. Describe las ramas y territorios de cada arteria coronaria, asà como los conceptos de dominancia coronaria y circulaciÃģn balanceada. TambiÃĐn cubre variaciones anatÃģmicas y el uso de la angiografÃa coronaria para evaluar obstrucciones.Irrigacion del corazonGabriela Capa
Ėý
Este documento describe la irrigaciÃģn arterial del corazÃģn. Las arterias coronarias principales son la arteria coronaria derecha y la izquierda, las cuales se originan de la aorta y proveen irrigaciÃģn al miocardio. Cada arteria provee irrigaciÃģn a diferentes regiones del corazÃģn y existe variaciÃģn en los patrones de irrigaciÃģn entre individuos. Existen tambiÃĐn conexiones colaterales entre las ramas de las arterias coronarias.irrigacion del CorazonKANINO15
Ėý
El documento describe la irrigaciÃģn sanguÃnea del corazÃģn. Las arterias coronarias salen de la aorta ascendente y suministran sangre a travÃĐs de ramas a las paredes de los ventrÃculos y aurÃculas. La sangre oxigenada llega al miocardio a travÃĐs de mÚltiples vasos pequeÃąos. Luego, la sangre desoxigenada drena al seno coronario y de ahà a la aurÃcula derecha.More Related Content
What's hot (7)
HYPOTHALAMUS CONTROLS PITUITARY SECRETION.pptx
HYPOTHALAMUS CONTROLS PITUITARY SECRETION.pptxFatimaSundus1
Ėý
The hypothalamus controls secretion of the pituitary gland. It sends signals via nerve connections to the posterior pituitary and releases hormones into the hypothalamic-hypophysial portal system that influence the anterior pituitary. These hypothalamic releasing and inhibitory hormones are synthesized in neurons of the hypothalamus and secreted into the median eminence, then carried via blood vessels to the anterior pituitary to regulate its hormone secretion. In this way, the hypothalamus integrates information from the body and nervous system to control the pituitary and many other physiological functions.Disorder of sodium imbalance
Disorder of sodium imbalancePradip Katwal
Ėý
This case discusses a 67-year-old female who presented with fever, vomiting, and loose stool for several days. On examination, she was found to be hypotensive and dehydrated. Initial tests showed hyponatremia, hypokalemia, and metabolic acidosis. She was diagnosed with acute infectious gastroenteritis complicated by hypovolumic shock and electrolyte imbalances. She was treated with IV fluids and antibiotics. Her condition improved over three days with correction of her volume status and electrolytes. The discussion then reviews hyponatremia, its causes, assessment of volume status, and treatment approaches depending on the underlying condition.Renal tubular reabsorption, secretion, regulation & renal function tests
Renal tubular reabsorption, secretion, regulation & renal function testsDipti Magan
Ėý
Renal tubular reabsorption and secretion involves the transport of substances across tubular epithelial cells. Substances may be reabsorbed from the tubular fluid back into the blood (reabsorption exceeds filtration) or secreted from the blood into the tubular fluid (secretion exceeds filtration). Clearance tests can measure glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and renal plasma flow. Substances like inulin that are freely filtered but not reabsorbed/secreted will have a clearance equal to GFR, while clearance of substances like para-aminohippuric acid (PAH) that are secreted can estimate renal plasma flow. Hormones and other factors regulate tubular transport and fluid/electroly15 Cox Acute Renal Failure
15 Cox Acute Renal FailureDang Thanh Tuan
Ėý
The document discusses acute renal failure (ARF), including its definition, classification into pre-renal, renal and post-renal types, and common causes. It describes the pathophysiology of pre-renal azotemia and acute tubular necrosis (ATN). Diagnostic tools for ARF including urinary sediment examination, urine indices, and radiologic imaging are also summarized.Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathyFahim Ahmad
Ėý
Diabetic nephropathy is a chronic kidney disease that develops over many years in people with diabetes. It is characterized by increased urinary albumin excretion, hyperglycemia, high blood pressure, declining kidney function, and the absence of other kidney diseases. According to studies, 20-44% of people with diabetes develop kidney failure and require renal replacement therapy like dialysis. The pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy involves metabolic pathways like increased polyol pathway flux, hexosamine pathway flux, formation of advanced glycation end products, and activation of protein kinase C, as well as hemodynamic changes and genetic factors. Major therapeutic interventions include controlling blood glucose, blood pressure, lipids, restricting protein intake,Respiracijska acidoza i alkaloza
Respiracijska acidoza i alkalozaDomina Petric
Ėý
Dokument opisuje respiracijsku acidozu i alkalozu, naglaÅĄavajuÄi uzroke, mehanizme kompenzacije i kliniÄke manifestacije tih stanja. Akutna respiracijska acidoza brzo se razvija uz opasnosti po Åūivot, dok kroniÄna forma moÅūe biti kompenzirana, ali ne uvijek. Terapija ukljuÄuje lijeÄenje osnovnog uzroka, s posebnim mjerama za izbjegavanje pogorÅĄanja hiperkapnijske situacije kod pacijenata s kroniÄnom acidozom.PoremeÄaj prometa vode i elektrolita
PoremeÄaj prometa vode i elektrolitaAntonio KobaÅĄ
Ėý
Dokument opisuje raspodjelu tjelesnih tekuÄina, njihovu funkciju i vaÅūnost elektrolita u regulaciji prometa vode i elektrolita. PoremeÄaji prometa vode i elektrolita, kao ÅĄto su dehidracija, hiperhidracija, hiponatrijemija i hiperkalcijemija, objaÅĄnjeni su kroz njihove uzroke i simptome. TakoÄer se razmatraju mehanizmi nastanka edema i vaÅūnost pravilne regulacije tjelesnih tekuÄina za odrÅūavanje zdravlja.Viewers also liked (8)
Fejezetek a keresztmetszeti anatÃģmiÃĄbÃģl - 4. A mellkas ÃĐs szÃv keresztmetszet...
Fejezetek a keresztmetszeti anatÃģmiÃĄbÃģl - 4. A mellkas ÃĐs szÃv keresztmetszet...Dr. Jakab AndrÃĄs
Ėý
AnatomÃa coronaria bÃĄsica - CoronariografÃa. VisualizaciÃģn de las arterias co...
AnatomÃa coronaria bÃĄsica - CoronariografÃa. VisualizaciÃģn de las arterias co...CardioTeca
Ėý
The document details the anatomy of coronary arteries, specifically the right and left coronary systems, including their branches and anatomical landmarks. It describes the dominance patterns of coronary circulation, the average dimensions of the left main artery, and the various views used to visualize these structures during imaging. Key branches of both coronary arteries are highlighted, along with their respective vascular supplies and important collateral connections.Angiografia coronariaDaniel Meneses
Ėý
El documento presenta una revisiÃģn de las limitaciones de la angiografÃa coronaria, incluyendo la sobrestimaciÃģn de la severidad de las estenosis, las dificultades en la interpretaciÃģn de las calcificaciones y las lesiones en bifurcaciones, y la subestimaciÃģn de la ganancia luminal tras angioplastia. TambiÃĐn compara los resultados de la angiografÃa con tÃĐcnicas cuantitativas y con la fisiologÃa, mostrando una sobreestimaciÃģn de la enfermedad coronaria.AnatomÃa coronariaJesus Custodio
Ėý
Este documento describe la anatomÃa coronaria y las proyecciones angiogrÃĄficas utilizadas para visualizar las arterias coronarias. Explica que la arteria coronaria derecha suele ser dominante y proporciona detalles sobre las vistas angiogrÃĄficas optimas para evaluar las diferentes secciones de las arterias coronarias izquierda y derecha.arterias coronariasMedicineStudent
Ėý
El documento describe la anatomÃa de las arterias coronarias. Explica que las arterias coronarias izquierda y derecha nacen de la aorta y suministran sangre al mÚsculo cardÃaco. Describe las ramas y territorios de cada arteria coronaria, asà como los conceptos de dominancia coronaria y circulaciÃģn balanceada. TambiÃĐn cubre variaciones anatÃģmicas y el uso de la angiografÃa coronaria para evaluar obstrucciones.Irrigacion del corazonGabriela Capa
Ėý
Este documento describe la irrigaciÃģn arterial del corazÃģn. Las arterias coronarias principales son la arteria coronaria derecha y la izquierda, las cuales se originan de la aorta y proveen irrigaciÃģn al miocardio. Cada arteria provee irrigaciÃģn a diferentes regiones del corazÃģn y existe variaciÃģn en los patrones de irrigaciÃģn entre individuos. Existen tambiÃĐn conexiones colaterales entre las ramas de las arterias coronarias.irrigacion del CorazonKANINO15
Ėý
El documento describe la irrigaciÃģn sanguÃnea del corazÃģn. Las arterias coronarias salen de la aorta ascendente y suministran sangre a travÃĐs de ramas a las paredes de los ventrÃculos y aurÃculas. La sangre oxigenada llega al miocardio a travÃĐs de mÚltiples vasos pequeÃąos. Luego, la sangre desoxigenada drena al seno coronario y de ahà a la aurÃcula derecha.Fejezetek a keresztmetszeti anatÃģmiÃĄbÃģl - 4. A mellkas ÃĐs szÃv keresztmetszet...
Fejezetek a keresztmetszeti anatÃģmiÃĄbÃģl - 4. A mellkas ÃĐs szÃv keresztmetszet...Dr. Jakab AndrÃĄs
Ėý
Ad
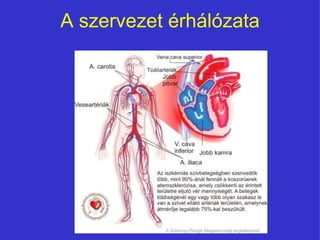
A szÃv ÃĐs az ÃĐrrendszer anatÃģmiÃĄja
- 1. A szÃv ÃĐs az ÃĐrrendszer anatÃģmiÃĄja Magyar Nemzeti SzÃvalapÃtvÃĄny 2008
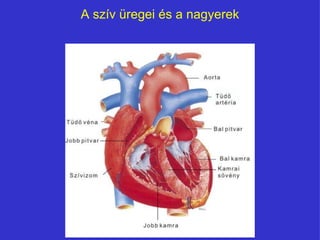
- 3. A szÃv Þregei ÃĐs a nagyerek
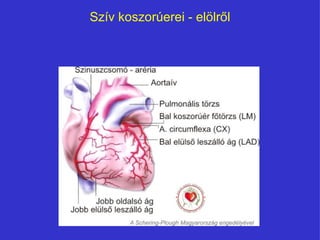
- 4. SzÃv koszorÚerei - ąðąôÃķąô°ųÅąô
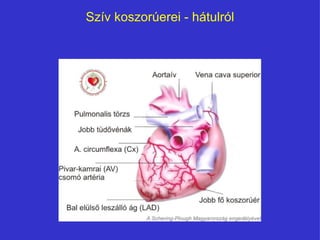
- 5. SzÃv koszorÚerei - ģóÃĄģŲģÜąô°ųÃģąô
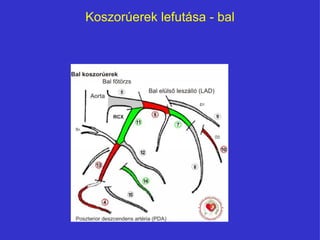
- 6. KoszorÚerek lefutÃĄsa - bal
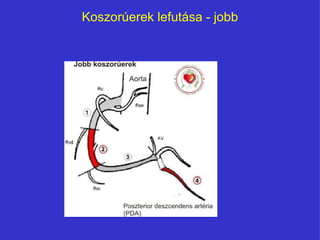
- 7. KoszorÚerek lefutÃĄsa - jobb
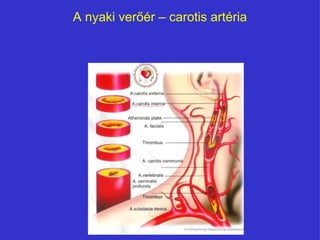
- 8. A nyaki verÅÃĐr â carotis artÃĐria
