Introduction to Zoology Lecture 2
- 1. Cellular Metabolism and Division Animals Among Us August 29th, 2013 1
- 3. Organic Molecules ŌĆó Anything with carbon in it ŌĆó The Building Blocks of Life 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Amino Acids and Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids 3
- 4. Organic Molecules ŌĆó Anything with carbon in it ŌĆó The Building Blocks of Life 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Amino Acids and Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids 4
- 5. Carbohydrates ŌĆó Carbohydrates ŌĆō Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen ŌĆō 1 C: 2 H: 1 O ŌĆō Sugars, starches, cellulose ŌĆō Where do carbohydrates come from? 5
- 6. Carbohydrates ŌĆó Photosynthesis ŌĆó Water + Carbon Dioxide -> solar -> Carbs! 1. Monosaccharides ŌĆō Simple sugars 2. Disaccharides ŌĆō Double sugars 3. Polysaccharides ŌĆō Complex sugars 6
- 7. Monosaccharides ŌĆó Glucose/dextrose ŌĆó Fructose ŌĆó Galactose 7
- 8. Disaccharides ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó Combined monosaccharides Maltose = 2 glucose Sucrose = 1 glucose + 1 fructose Lactose = 1 glucose + 1 galactose 8
- 9. Polysaccharides ŌĆó Many molecules of simple sugars in long chains ŌĆó Glycogen ŌĆō How sugars are stored in animal tissues ŌĆō When needed, converted into glucose ŌĆó Cellulose ŌĆō Principal structural carbohydrate of plants 9
- 10. Organic Molecules ŌĆó Anything with carbon in it ŌĆó The Building Blocks of Life 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Amino Acids and Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids 10
- 11. Lipids ŌĆó Fuel storage and building material 1. Neutral Fats ŌĆō ŌĆ£TrueŌĆØ fats ŌĆō Storage from dietary fats or carbs 2. Phospholipids ŌĆō Structurally important 3. Steroids ŌĆō Complex alcohols 11
- 12. Neutral Fats ŌĆó Saturated ŌĆō Typically animal fats ŌĆō Every carbon atom is bonded with two hydrogen atoms ŌĆō Usually solid at room temperature ŌĆó Unsaturated ŌĆō Typically plant fats (ŌĆ£oilsŌĆØ) ŌĆō 2 or more carbon atoms are joined by double bonds, not ŌĆ£saturatedŌĆØ with hydrogen atoms 12
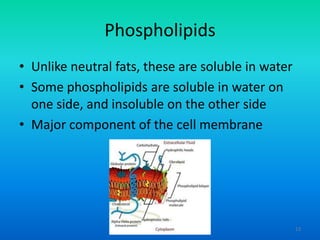
- 13. Phospholipids ŌĆó Unlike neutral fats, these are soluble in water ŌĆó Some phospholipids are soluble in water on one side, and insoluble on the other side ŌĆó Major component of the cell membrane 13
- 14. Steroids ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó Structurally unlike fats Other chemical properties are similar Cholesterol Hormones 14
- 15. Organic Molecules ŌĆó Anything with carbon in it ŌĆó The Building Blocks of Life 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Amino Acids and Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids 15
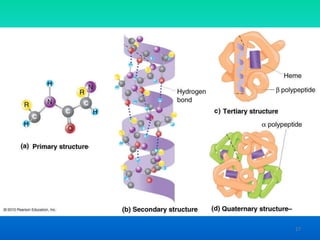
- 16. Amino Acids and Proteins ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó 20 amino acids Amino acid + amino acid = protein Organized into 3 dimensional structures Often interlinked with other proteins 16
- 17. 17
- 18. Organic Molecules ŌĆó Anything with carbon in it ŌĆó The Building Blocks of Life 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Amino Acids and Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids 18
- 19. Nucleic Acids ŌĆó RNA ŌĆō Ribonucleic Acid ŌĆó DNA ŌĆō Deoxyribonucleic Acid ŌĆó Store codes for replication 19
- 20. Miller Experiment ŌĆó Methane, hydrogen, ammonia, water ŌĆó Circulate 1 week with electric spark ŌĆō Solar energy, hydrothermic vents, lightning ŌĆó 15% into complex molecules ŌĆō 4 amino acids ŌĆó Add a couple of billion yearsŌĆ” 20
- 21. Animal ID #1 21
- 22. Scissor-Grinder Cicada ŌĆó Annual cicada ŌĆó Important food source for many bird species ŌĆó Lives underground in nymph stage for several years, feeding on tree roots 22
- 23. Metabolism ŌĆó Photosynthesis CO2 + H2O + Solar Energy = Sugar + O2 ŌĆó First law of thermodynamics ŌĆō Energy cannot be created or destroyed ŌĆō Solar energy becomes stored energy in the plant 23
- 24. Cellular Respiration 1. Heterotroph eats food, food is broken down and absorbed into the bloodstream 2. Molecules enter cells 3. Molecules are turned into ATP in the cytoplasm 4. Mitochondria break bonds of ATP to provide energy for the cell 24
- 25. Metabolism ŌĆó ATP ŌĆō Adenosine Tri-Phosphate ŌĆō High-energy bonds (ŌĆ£potential energyŌĆØ) ŌĆó ATP + Water = ADP + Energy 25
- 26. Cellular Respiration ŌĆó Aerobic ŌĆō ATP + Water + O2 = ADP + Energy + CO2 ŌĆó Anaerobic ŌĆō ATP + Water = ADP + Energy + Lactic Acid ŌĆō 1/18th as efficient as aerobic 26
- 27. Anaerobic is Unavoidable ŌĆó Difficult to get oxygen to muscles fast enough in enough quantity 27
- 28. Many Animals Require Anaerobic ŌĆó Diving birds and mammals use anaerobic metabolism under water 28
- 29. Metabolism of Lipids ŌĆó Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Proteins can be stored as fats ŌĆó Stored fats contain huge amounts of potential energy 29
- 30. Animal ID #2 30
- 31. Northern True Katydid ŌĆó Life cycle within one year ŌĆó Prefers oak leaves ŌĆó Usually in tree canopy 31
- 32. Cellular Division ŌĆó Mitosis ŌĆō ŌĆ£My ToesŌĆØ sis ŌĆō NOT Meiosis (forming gametes) ŌĆó Each new cell contains complete genetic code of ŌĆ£parentŌĆØ cell ŌĆó For animals that reproduce asexually, this is the whole story 32
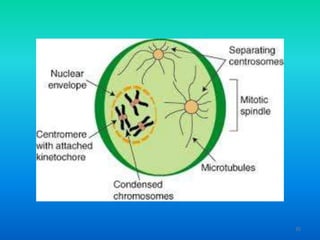
- 33. Mitosis ŌĆó 5 stages ŌĆō Interphase (MOST OF THE TIME) ŌĆō Prophase ŌĆō Metaphase ŌĆō Anaphase ŌĆō Telophase ŌĆó IPMAT ŌĆō I Poop More After Tacos 33
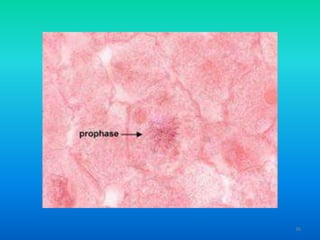
- 34. 1. Prophase ŌĆó Chromatin copies itself ŌĆó Chromatin ’āĀ Chromosomes ŌĆō Separates and becomes dense ŌĆō Each chromosome is two chromatids ŌĆó Sister chromatids are identical ŌĆó Fibers in the cell arrange themselves to prepare for separation 34
- 35. 35
- 36. 36
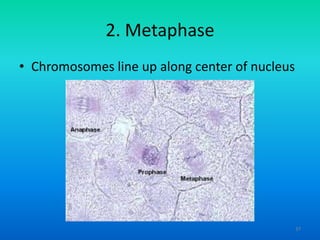
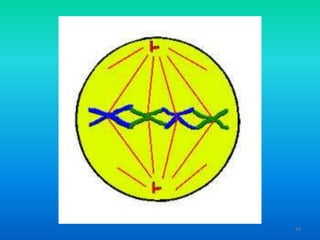
- 37. 2. Metaphase ŌĆó Chromosomes line up along center of nucleus 37
- 38. 38
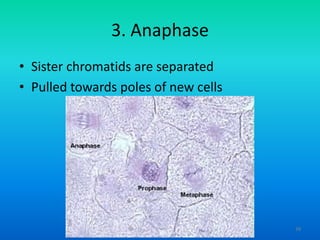
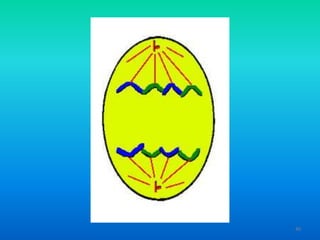
- 39. 3. Anaphase ŌĆó Sister chromatids are separated ŌĆó Pulled towards poles of new cells 39
- 40. 40
- 41. 4. Telophase ŌĆó Fibers disappear ŌĆó Chromosomes relax into chromatin ŌĆó Nuclear membrane is formed 41
- 42. 42
- 43. 43
- 44. Animal ID #3 44
- 45. European Earthworm ŌĆó Nightcrawler, red wriggler ŌĆó Areas that were glaciated during the Ice Age do not have native earthworms ŌĆó European earthworms were transported by the colonials, probably by accident, when they transplanted their plant stocks 45
- 46. Meiosis ŌĆó Same basic process as mitosis, except ŌĆō Two cycles ŌĆō Four resulting cells ŌĆō Resulting cells have half of the DNA 46
- 47. Meiosis I Prophase I ŌĆó Chromatin condenses into chromosomes ŌĆó Chromosome line up with homologues 47
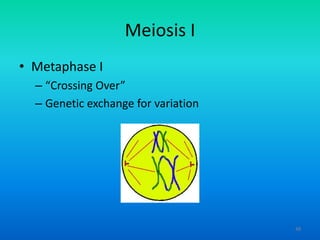
- 48. Meiosis I ŌĆó Metaphase I ŌĆō ŌĆ£Crossing OverŌĆØ ŌĆō Genetic exchange for variation 48
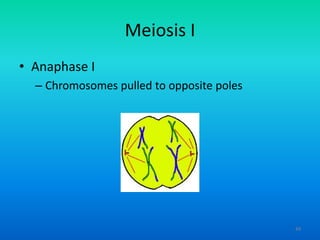
- 49. Meiosis I ŌĆó Anaphase I ŌĆō Chromosomes pulled to opposite poles 49
- 50. Meiosis I ŌĆó NO TELOPHASE I!!! 50
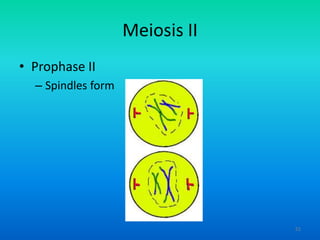
- 51. Meiosis II ŌĆó Prophase II ŌĆō Spindles form 51
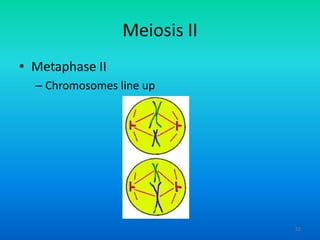
- 52. Meiosis II ŌĆó Metaphase II ŌĆō Chromosomes line up 52
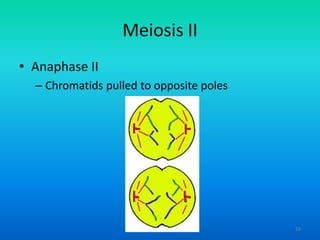
- 53. Meiosis II ŌĆó Anaphase II ŌĆō Chromatids pulled to opposite poles 53
- 54. Meiosis II ŌĆó Telophase II ŌĆō Nuclear membranes form ŌĆō Chromosomes relax into chromatin ŌĆō Each cell contains only half of the DNA necessary for an organism 54