Abdomen exam
- 2. Important history ïŪ Dyspepsia- heartburn ïŪ Dysphagia- difficulty swallowing ïŪ Altered bowel habit- diarrhea/constipation ïŪ Pain- colicky, stretch, radiation, referred ïŪ Bleeding- UGI/LGI ïŪ Jaundice ïŪ Urinary symptoms- hematuria, dysuria, frequency, urgency, hesitancy, retention ïŪ Appetite ïŪ Dietary history
- 3. Examination ïŪ Oral cavity ïŪ Abdomen ïŪ Male genitalia ïŪ Anus/rectum
- 4. Oral cavity ïŪ Angular stomatitis, cheilitis ïŪ Teeth- number, color, ridges, caries ïŪ Gums- swelling, bleeding, pyorrhea ïŪ Buccal mucosa- ulcer, pigmentation ïŪ Tongue- size, color, papillae ïŪ Palate, tonsils, pharynx
- 5. Abdomen- regions ïŪ 4- vertical & horizontal planes thru umbilicus- RUQ, RLQ, LUQ, LLQ ïŪ 9- vertical planes thru 9th costal cartilage & femoral artery; horizontal planes are subcostal & interiliac- R & L hypochondrium, lumbar, iliac and epigastrium, umbilical, hypogastrium
- 7. Quadrants & organs ïŪ RUQ- liver, GB, upper pole of R kidney, hepatic flexure of colon ïŪ LUQ- stomach, spleen, pancreas, upper pole of L kidney, splenic flexure of colon ïŪ RLQ- lower pole of R kidney, appendix, terminal ileum, R colon, R ovary ïŪ LLQ- lower pole L kidney, L colon, L ovary
- 8. Pre-examination ïŪ Comfortable room & couch ïŪ Adequate light ïŪ Patient lying supine ïŪ Adequate exposure ïŪ Examinerâs hand at the level of patientâs abdomen
- 9. Examination- components ïŪ Inspection- see, donât touch ïŪ Palpation- touch ïŪ Percussion- tap ïŪ Auscultation- use stethoscope
- 10. Inspection ïŪ Shape- scaphoid, normal, distended ïŪ Umbilicus- shape, inverted/everted ïŪ Movements- normal or restricted, pulsation, visible peristalsis ïŪ Striae or scars ïŪ Prominent veins ïŪ Genitalia & groin
- 11. Palpation ïŪ Relaxed patient & abdominal wall ïŪ Start from the point farthest from possible area of involvement e.g. for liver start from LLQ & for spleen from RLQ ïŪ Palpate whole abdomen in an order
- 12. Special techniques ïŪ Deep palpation- in obese, muscular or poorly relaxed ïŪ Dipping- tense ascites ïŪ Bimanual- for kidney & spleen ïŪ Ballotable- kidney ïŪ Shifting dullness & fluid thrill- for ascitis
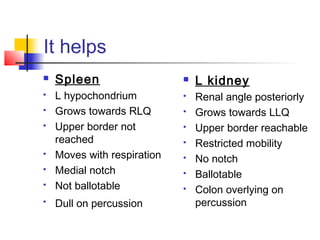
- 13. It helps ïŪ Spleen ï§ L hypochondrium ï§ Grows towards RLQ ï§ Upper border not reached ï§ Moves with respiration ï§ Medial notch ï§ Not ballotable ï§ Dull on percussion ïŪ L kidney ï§ Renal angle posteriorly ï§ Grows towards LLQ ï§ Upper border reachable ï§ Restricted mobility ï§ No notch ï§ Ballotable ï§ Colon overlying on percussion
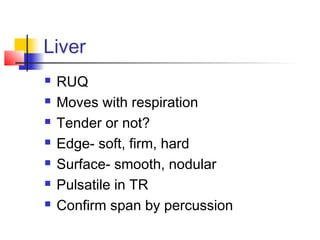
- 14. Liver ïŪ RUQ ïŪ Moves with respiration ïŪ Tender or not? ïŪ Edge- soft, firm, hard ïŪ Surface- smooth, nodular ïŪ Pulsatile in TR ïŪ Confirm span by percussion
- 15. Gall bladder ïŪ Underlies liver in RUQ ïŪ Moves with respiration ïŪ Usually not palpable ïŪ Tender- Murphyâs sign- +ve in acute cholecystitis ïŪ Palpable GB- mucocoele, cancer, CBD obstruction
- 16. Urinary bladder ïŪ Midline, suprapubic ïŪ Usually not palpable ïŪ When palpable- smooth, symmetrical, lower border not reached, ïŪ Urge to micturate on palpation ïŪ Dull on percussion
- 17. Percussion ïŪ Only light percussion required ïŪ Resonant note allover, except over liver where it is dull ïŪ Used to confirm liver or spleen or bladder enlargement & ascitis
- 18. Auscultation ïŪ Paraumbilical ïŪ For bowel sounds or bruit ïŪ Normal BS- intermittent gurgles interspersed with tinkles ïŪ Increased- intestinal obstruction ïŪ Decreased- paralytic ileus ïŪ Bruit- over aorta, iliac/renal arteries
- 19. Donât forget ïŪ Groin- LNE, hernia ïŪ Male genitalia ïŪ PR examination- for local pathology, prostate examination in males
- 20. Stigmata of CLD ïŪ Muscle wasting ïŪ Pallor, jaundice ïŪ Clubbing ïŪ Palmar erythema ïŪ Dupuytrenâs contracture ïŪ Spider nevi ïŪ Gynecomastia ïŪ Testicular atrophy ïŪ Caput medusae ïŪ Ascites
- 21. Supported by X-ray, US/CT, Endoscopy