Abdominal ct scan by nadia sarwar (khyber medical university peshawar)
- 1. Abdominal CT scan Submitted by: NADIA SARWAR
- 2. How the CT is performed? ? You will lie on a narrow table that slides into the center of the CT scanner. Most often, you will lie on your back with your arms raised above your head. ? Once you are inside the scanner, the machine's x-ray beam rotates around you. Modern spiral scanners can perform the exam without stopping. ? A computer creates separate images of the belly area. These are called slices. These images can be stored, viewed on a monitor, or printed on film. Three-dimensional models of the belly area can be made by stacking the slices together. ? You must be still during the exam, because movement causes blurred images. You may be told to hold your breath for short periods of time.
- 3. Why the Test is Performed An abdominal CT scan makes detailed pictures of the structures inside your belly (abdomen) very quickly. This test may be used to look for: ? Cause of abdominal pain or swelling ? Hernia ? Cause of a fever ? Masses and tumors, including cancer ? Infections or injury ? Kidney stones ? Appendicitis
- 4. What Abnormal Results Mean The abdominal CT scan may show some cancers, including: ? Cancer of the renal pelvis or ureter ? Colon cancer ? Hepatocellular carcinoma ? Lymphoma ? Melanoma ? Ovarian cancer ? Pancreatic cancer ? Pheochromocytoma ? Renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer) ? Testicular cancer
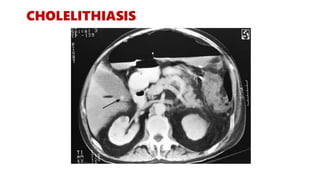
- 5. The abdominal CT scan may show problems with the gallbladder, liver, or pancreas, including: Acute cholecystitis Alcoholic liver disease Cholelithiasis Pancreatic abscess Pancreatic pseudocyst Pancreatitis Blockage of bile ducts Kidney stones Kidney or ureter damage Polycystic kidney disease
- 6. Abnormal results may also be due to: Abdominal aortic aneurysm Abscesses Appendicitis Bowel wall thickening Retroperitoneal fibrosis Renal artery stenosis Renal vein thrombosis
- 8. ABDOMINAL CYST An abdominal CT scan revealed a large right upper quadrant cyst measuring 14x17x21 cm ( lateral, anteroposterior and craniocaudal)There was mass effect upon the liver and duodenum. The cyst had a thin smooth wall with internal fluid and high density material consistent with a blood clot.
- 9. HEPATOMEGALY
- 10. SPLENOMEGALY
- 11. RENAL CYST NO CONTRAST CONTRAST
- 12. DIVERTICULITS
- 13. ABDOMINAL ABSCESS Psoas abscess (blue arrow), and abscess dissecting anteriorly in transversalis fascia.
- 14. RENAL STONE
- 15. PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA Pheochromocytoma is a tumor of the adrenal gland that causes excess release of epinephrine and norepinephrine, hormones that regulate heart rate and blood pressure
- 16. CIRRHOSIS
- 17. CHOLELITHIASIS
- 18. CHOLECYSTITIS
- 20. PANCREATITIS
- 22. Because answers EXISTS only to questions! Thank you!