.................abdominal incisions.pptx
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes9 views
Abdominal incisions are discussed by Dr. Jaya Chandra, a lecturer at SCMAT. The document provides a brief thank you note from Dr. Chandra for an unspecified topic related to abdominal incisions.
1 of 39
Download to read offline






















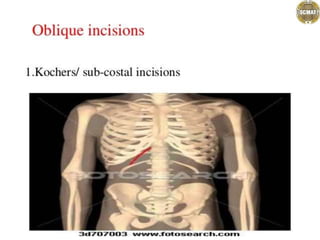

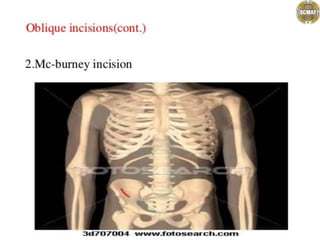
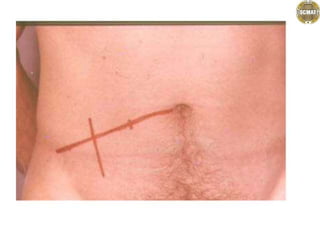

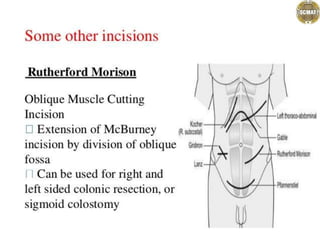



Ad
Recommended
myopathies...........................ppt
myopathies...........................pptRajveer71
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of neuromuscular disorders, focusing on various types of myopathies and their symptoms, diagnoses, and treatments. Key conditions discussed include Duchenne muscular dystrophy, myotonic dystrophy, inflammatory myopathies, and myasthenia gravis, along with their clinical features and management strategies. The document emphasizes the importance of genetic and biochemical testing in diagnosing these disorders and outlines potential therapeutic approaches.drugs, respiratory drugs, .pptx
drugs, respiratory drugs, .pptxRajveer71
╠²
This document summarizes various classes of respiratory drugs used to treat conditions like asthma. It describes 5 classes of anti-asthmatic drugs: bronchodilators, mast cell stabilizers, corticosteroids, antihistamines, and methylxanthines. Specific drugs from each class are provided along with their mechanisms of action, indications, doses, side effects and contraindications. Other drug classes discussed include mucolytics, decongestants, antitussives and expectorants which are used to treat cough and relieve nasal congestion.diabetes and exercise, Physiotherapy.pptx
diabetes and exercise, Physiotherapy.pptxRajveer71
╠²
The document discusses diabetes mellitus (DM), which is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels due to inadequate insulin production or insulin resistance. There are three main types of DM - type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 DM results from autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells, leading to absolute insulin deficiency. Type 2 DM accounts for 90% of cases and involves insulin resistance where the body does not respond properly to insulin. Regular exercise is beneficial for managing diabetes as it increases insulin sensitivity, lowers blood sugar levels, and provides various health benefits such as weight loss, improved heart health, and better management of diabetes symptoms.breathlessness breathing deficulty. .ppt
breathlessness breathing deficulty. .pptRajveer71
╠²
Breathlessness, also known as dyspnea, is an unpleasant sensation of uncomfortable, difficult, or labored breathing. It has various potential causes, both acute and chronic, including conditions affecting the heart, lungs, and other systems. A medical history, physical exam, and tests can help identify potential differential diagnoses and assess severity. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may involve oxygen supplementation, bronchodilators, opioids, anxiolytics, breathing exercises, and addressing any anxiety components.Types of delivery And Physiotherapy management after c-section.pptx
Types of delivery And Physiotherapy management after c-section.pptxRajveer71
╠²
This document provides information on different types of childbirth, including:
1. Vaginal delivery - the natural birth process where the baby passes through the birth canal. It has benefits like shorter recovery but risks like respiratory issues for babies.
2. C-section - a surgical procedure where the baby is delivered through incisions in the abdomen and uterus. It may be scheduled or due to complications. Transverse or vertical incisions can be used.
3. Post c-section exercises include belly breathing, pelvic floor exercises, low-impact exercises like wall sits and leg slides, and scar massage to improve range of motion. Always consult a doctor before beginning an exercise routine after c-section.......................VOJTA THERAPY.pptx
......................VOJTA THERAPY.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Vojta therapy is a treatment method developed by Dr. Vaclav Vojta in the 20th century that uses light pressure on specific stimulus zones of the body to elicit involuntary motor responses and movement patterns. It is intended to treat disorders of the central nervous system and musculoskeletal system. The therapy activates reflex locomotion through positions like prone, supine, and side lying, with goals of improving postural control, extension against gravity, and stepping movements. Regular application of Vojta therapy is believed to have wide-ranging benefits like improved respiratory function, autonomic regulation, motor skills, and cognitive abilities.pulmonarysurgery-141016011330-conversion-gate02.pptx
pulmonarysurgery-141016011330-conversion-gate02.pptxRajveer71
╠²
This document discusses lung surgery procedures including pneumonectomy, lobectomy, segmental resection, and wedge resection. It describes common indications for lung surgery such as lung cancer, infection, COPD, and benign tumors. Post-operative complications are outlined like infection, consolidation, pneumothorax, bronchopleural fistula, DVT, cardiac arrhythmia, hemorrhage, wound infection, and joint stiffness. Post-operative treatment includes breathing exercises, secretion clearance, pain management, mobilization, and exercise.bronchialasthmamanagement-181207213555 (1).pptx
bronchialasthmamanagement-181207213555 (1).pptxRajveer71
╠²
This document provides an overview of bronchial asthma. It begins by defining asthma as a chronic inflammatory airway disorder characterized by wheezing, breathlessness, and coughing. It then classifies asthma as atopic/extrinsic, non-atopic/intrinsic, or drug-induced. The pathophysiology section describes the chronic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness that are hallmarks of the condition. Risk factors, triggers, clinical manifestations, diagnostic tests, and treatment approaches including pharmacological and non-pharmacological options are also summarized.Anatomy and Injuries to the Wrist and Hand.ppt
Anatomy and Injuries to the Wrist and Hand.pptRajveer71
╠²
This document summarizes common injuries to the wrist and hand, including bones, joints, ligaments, and muscles. It describes injuries such as Colles' fractures, wrist sprains, tendonitis, ganglion cysts, scaphoid fractures, dislocations, and fractures of bones in the hand. For each injury, the causes, signs and symptoms, and treatment approaches are outlined. Common hand injuries involving fingers like mallet finger, jersey finger, and dislocations are also summarized.McConnell-Taping-PPT.pdf
McConnell-Taping-PPT.pdfRajveer71
╠²
Patellofemoral tracking disorder occurs when the patella shifts out of the femoral groove during knee motion. It is most common in adolescents and young athletes, and more frequent in women than men. McConnell taping is a treatment that uses rigid tape applied to the knee for up to 18 hours to center the patella in the femoral groove and reduce pain. Physical therapy focuses on strengthening the quadriceps and hip muscles through exercises while also using McConnell taping. Left untreated, patellofemoral tracking disorder can lead to further cartilage damage and osteoarthritis over time.Heart sounds ppt.pptx
Heart sounds ppt.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Heart sounds are produced during the mechanical activities of the heart during each cardiac cycle, namely the flow of blood through chambers, contraction of cardiac muscle, and closure of heart valves. There are normally four heart sounds - first, second, third, and fourth - produced during each cycle. The first and second sounds are the loudest and resemble "LUB" and "DUBB" respectively. Abnormal heart sounds can provide clinical information about cardiovascular conditions.Musculoskeletal Examination.ppt
Musculoskeletal Examination.pptRajveer71
╠²
This document provides an overview of techniques for examining the musculoskeletal system in primary care settings. It discusses taking a history and performing basic examinations of inspection, palpation, movement, and function. The GALS screening method is described for evaluating gait, arms, legs, and spine. Specific areas covered include hands, wrists, shoulders, back, hips, and feet. Common musculoskeletal conditions are demonstrated through photographs.finaldementia.pptx
finaldementia.pptxRajveer71
╠²
The document provides information on physical therapy for patients with dementia. It begins with definitions of dementia and discusses the different types, including Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body dementia. It describes the stages of dementia and tools to assess cognitive function, such as the Mini-Mental State Examination and Global Deterioration Scale. Treatment options discussed include cholinergic medications to increase acetylcholine in the brain as well as other drugs and therapeutic interventions.19-CDH-okk.ppt
19-CDH-okk.pptRajveer71
╠²
Congenital dislocation of the hip (CDH) is a multi-factorial condition where the femoral head is displaced from the acetabulum. It is more common in females and risk factors include family history, breech presentation, and foot deformities. Clinical examination involves assessing range of motion and special tests like Ortolani and Barlow. Treatment depends on age but aims to reduce the hip concentrically without disrupting blood supply to the femoral head, ranging from harness or casting for young infants to open reduction and acetabuloplasty for older children. Early detection and treatment provide the best outcomes for this endemic pediatric condition.Unit 3 NDT.pptx
Unit 3 NDT.pptxRajveer71
╠²
The document discusses the Neurodevelopmental Treatment (NDT) approach, which was developed in the 1960s by Berta and Karel Bobath. The NDT approach uses hands-on techniques to facilitate normal movement patterns and inhibit abnormal tones and postures in individuals with central nervous system impairments. It focuses on improving motor control, functional abilities, and independence through proprioceptive, vestibular, and other facilitatory and inhibitory techniques applied at key points. The goal is to help patients relearn normal movement patterns and skills to perform everyday activities.wheel chair.pptx
wheel chair.pptxRajveer71
╠²
This document discusses the key components and considerations for wheelchair design and use. It explains that wheelchairs come in different sizes for adults, children, and infants. The frame can be rigid or folding, and the tires, wheels, brakes, and other parts are selected based on indoor or outdoor use and the individual's needs. Proper fit is important for comfort and to prevent secondary disabilities. Patients should be trained on basic wheelchair skills. Regular maintenance and occasional overhauls are also recommended. Wheelchairs may be modified to facilitate transfers, positioning, self-propulsion, and transportation.Cervical spondylosis.pptx
Cervical spondylosis.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Cervical spondylosis is a degenerative condition affecting the cervical spine that commonly occurs with aging. As the cervical discs lose hydration and height, bone spurs and other degenerative changes can occur that result in compression of nerves or the spinal cord. While aging is the primary risk factor, repetitive neck movements from activities like texting or occupations involving manual labor can also contribute. Common symptoms include neck pain and stiffness, headaches, arm or hand numbness, weakness or tingling. Diagnosis involves physical examination and imaging tests like x-rays or MRI to identify the areas of involvement and damage.intro & history of rehab, epidemiology.pptx
intro & history of rehab, epidemiology.pptxRajveer71
╠²
The document provides an overview of the history and concepts of physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R), also known as physiatry. It discusses how rehabilitation therapies have evolved over thousands of years across various cultures to treat injuries and functional limitations. The document also defines key terms used in rehabilitation such as impairment, disability, and handicap according to the World Health Organization's international classification system. It emphasizes that the overall goal of rehabilitation is to minimize disability and handicap so individuals can lead productive lives.GBS.pptx
GBS.pptxRajveer71
╠²
This document provides information about Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS). It defines GBS as an acute onset demyelinating peripheral polyneuropathy that causes ascending flaccid paralysis starting in the lower limbs. Predisposing factors include viral or bacterial infections, vaccinations, surgery, and some drugs. Clinical features include rapidly progressive motor weakness, sensory symptoms, autonomic dysfunction, and increased cerebrospinal fluid albumin levels. Electrophysiology shows neurogenic abnormalities. Management involves plasmapheresis, steroid therapy, or intravenous immunoglobulin G.Presentation (3).pptx
Presentation (3).pptxRajveer71
╠²
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) is a stretching technique developed in the 1940s to enhance both active and passive range of motion. It uses patterns of diagonal and functional movements along with techniques like isometric contractions and combinations of passive stretching and muscle facilitation. The main PNF techniques are rhythmic initiation, repeated contraction, slow reversal, and contract-relax which aim to increase muscle strength and flexibility through repetition. PNF can be used to treat conditions involving muscle weakness or spasticity such as after a stroke.Scoliosis.pptx
Scoliosis.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine greater than 10 degrees. It can be classified as structural or non-structural. Structural scoliosis involves vertebral rotation and can be idiopathic, congenital, or neuromuscular. Evaluation involves history, exam, and radiographs to assess curve size and progression. Curves under 25 degrees are observed, 25-40 degrees may be braced, and over 40 degrees may require surgery like spinal fusion. Physiotherapy management focuses on posture, exercises, and breathing techniques for observation or bracing, and post-op recovery exercises.Abnormal gait patterns.pptx
Abnormal gait patterns.pptxRajveer71
╠²
The document describes different types of abnormal gaits seen in various medical conditions. It discusses hemiplegic, diplegic, myopathic, choreic, ataxic, antalgic and Trendelenburg gaits. It explains the pathomechanisms, causes and treatments for each gait type. Important muscles for normal gait include hip extensors, knee extensors, plantar flexors and dorsiflexors. Abnormalities in these muscle groups can significantly affect one's walking pattern.Gait and Gait cycle (new) mam.pptx
Gait and Gait cycle (new) mam.pptxRajveer71
╠²
This document provides an overview of gait and gait analysis. It defines gait and describes the gait cycle, which consists of the stance and swing phases. The document outlines various gait terminologies including temporal variables like single limb support time and double limb support time. It also discusses spatial variables such as step length and stride length. The document then covers causes of gait impairment, stair gait, running gait, and objective and subjective methods for analyzing gait.Handling of children with cerebral palsy PPT-vinay (1) (1).pdf
Handling of children with cerebral palsy PPT-vinay (1) (1).pdfRajveer71
╠²
Cerebral palsy is a group of disorders that affect movement and posture, caused by non-progressive damage to the developing brain before or after birth. It is diagnosed when brain damage occurs prenatally from conception to labor onset, perinatally from 28 weeks gestation to 7 days after birth, or postnatally in the first 2 years of life. The prevalence is 1-5 per 1000 live births globally and 2-2.5 per 1000 in Western countries. Etiology includes prematurity, low birth weight, infections, trauma, and complications during pregnancy, labor, or delivery. Early identification is based on risk factors and developmental delays. Diagnosis usually occurs between ages 2-5 years throughNEONATAL REFLEX.pptx
NEONATAL REFLEX.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Neonatal reflexes are involuntary responses present at birth that help assess infant development. There are several general body reflexes like the Moro reflex and plantar grasp reflex, as well as facial and oral reflexes. The presence, absence, strength, and timing of reflexes can indicate neurological abnormalities. Understanding neonatal reflexes aids in evaluating whether development is normal or if further assessment is needed.33189-Speaker-ppt.pptx
33189-Speaker-ppt.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Cupping therapy is an ancient practice over 5000 years old that is used globally to treat a broad spectrum of health disorders. It works through the body's cutivisceral reflex paths to stimulate circulation and regulate disturbed functions at the site of suction cups. This helps eliminate blockages and strengthens the body's natural healing powers without adverse side effects. Common methods include dry cupping, wet cupping, and cupping massage to improve blood flow and treat issues like bronchitis, influenza, and pain.Four_Cardiac-Rehabilitation.ppt
Four_Cardiac-Rehabilitation.pptRajveer71
╠²
This document provides information about cardiac rehabilitation. It defines cardiovascular disease and notes that it is the leading cause of death in the United States. Cardiac rehabilitation involves supervised exercise, education on lifestyle changes like nutrition, smoking cessation and stress management, and monitoring of health metrics under the guidance of a team of healthcare professionals. The benefits of cardiac rehabilitation include improved physical functioning, quality of life, disease knowledge, and adherence to a healthy lifestyle.stroke-rehabilitation.pdf
stroke-rehabilitation.pdfRajveer71
╠²
This document provides information on stroke rehabilitation techniques. It discusses principles of neuroplasticity such as use it or lose it, repetition matters, and intensity matters. Early mobilization is important to maintain cardiovascular endurance and minimize deficits. Collaboration between medical professionals and involving patients and families in setting goals is emphasized. Rehabilitation techniques discussed include neuromuscular re-education, constraint induced movement therapy, and neurodevelopmental technique. Positioning strategies are presented for patients with left or right hemiplegia. Demonstrations cover range of motion, transfers, bed mobility, gait belt use, and ambulation. Therapy typically progresses from intensive care to acute rehabilitation. References and questions are provided.Tuberculosis burden , case finding tools and management .pptx
Tuberculosis burden , case finding tools and management .pptxDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
This presentation is for educational purposes only. Comprehensive Guide on Adsorption and Partition Chromatography Techniques
Comprehensive Guide on Adsorption and Partition Chromatography TechniquesSajini
╠²
This presentation provides an in-depth overview of chromatography, focusing on adsorption and partition chromatography. It covers the principles, methodologies, types, classification, column preparation, detection methods, advantages, disadvantages, and pharmaceutical applications. A useful resource for pharmacy students and professionals in pharmaceutical chemistry.
More Related Content
More from Rajveer71 (20)
Anatomy and Injuries to the Wrist and Hand.ppt
Anatomy and Injuries to the Wrist and Hand.pptRajveer71
╠²
This document summarizes common injuries to the wrist and hand, including bones, joints, ligaments, and muscles. It describes injuries such as Colles' fractures, wrist sprains, tendonitis, ganglion cysts, scaphoid fractures, dislocations, and fractures of bones in the hand. For each injury, the causes, signs and symptoms, and treatment approaches are outlined. Common hand injuries involving fingers like mallet finger, jersey finger, and dislocations are also summarized.McConnell-Taping-PPT.pdf
McConnell-Taping-PPT.pdfRajveer71
╠²
Patellofemoral tracking disorder occurs when the patella shifts out of the femoral groove during knee motion. It is most common in adolescents and young athletes, and more frequent in women than men. McConnell taping is a treatment that uses rigid tape applied to the knee for up to 18 hours to center the patella in the femoral groove and reduce pain. Physical therapy focuses on strengthening the quadriceps and hip muscles through exercises while also using McConnell taping. Left untreated, patellofemoral tracking disorder can lead to further cartilage damage and osteoarthritis over time.Heart sounds ppt.pptx
Heart sounds ppt.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Heart sounds are produced during the mechanical activities of the heart during each cardiac cycle, namely the flow of blood through chambers, contraction of cardiac muscle, and closure of heart valves. There are normally four heart sounds - first, second, third, and fourth - produced during each cycle. The first and second sounds are the loudest and resemble "LUB" and "DUBB" respectively. Abnormal heart sounds can provide clinical information about cardiovascular conditions.Musculoskeletal Examination.ppt
Musculoskeletal Examination.pptRajveer71
╠²
This document provides an overview of techniques for examining the musculoskeletal system in primary care settings. It discusses taking a history and performing basic examinations of inspection, palpation, movement, and function. The GALS screening method is described for evaluating gait, arms, legs, and spine. Specific areas covered include hands, wrists, shoulders, back, hips, and feet. Common musculoskeletal conditions are demonstrated through photographs.finaldementia.pptx
finaldementia.pptxRajveer71
╠²
The document provides information on physical therapy for patients with dementia. It begins with definitions of dementia and discusses the different types, including Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body dementia. It describes the stages of dementia and tools to assess cognitive function, such as the Mini-Mental State Examination and Global Deterioration Scale. Treatment options discussed include cholinergic medications to increase acetylcholine in the brain as well as other drugs and therapeutic interventions.19-CDH-okk.ppt
19-CDH-okk.pptRajveer71
╠²
Congenital dislocation of the hip (CDH) is a multi-factorial condition where the femoral head is displaced from the acetabulum. It is more common in females and risk factors include family history, breech presentation, and foot deformities. Clinical examination involves assessing range of motion and special tests like Ortolani and Barlow. Treatment depends on age but aims to reduce the hip concentrically without disrupting blood supply to the femoral head, ranging from harness or casting for young infants to open reduction and acetabuloplasty for older children. Early detection and treatment provide the best outcomes for this endemic pediatric condition.Unit 3 NDT.pptx
Unit 3 NDT.pptxRajveer71
╠²
The document discusses the Neurodevelopmental Treatment (NDT) approach, which was developed in the 1960s by Berta and Karel Bobath. The NDT approach uses hands-on techniques to facilitate normal movement patterns and inhibit abnormal tones and postures in individuals with central nervous system impairments. It focuses on improving motor control, functional abilities, and independence through proprioceptive, vestibular, and other facilitatory and inhibitory techniques applied at key points. The goal is to help patients relearn normal movement patterns and skills to perform everyday activities.wheel chair.pptx
wheel chair.pptxRajveer71
╠²
This document discusses the key components and considerations for wheelchair design and use. It explains that wheelchairs come in different sizes for adults, children, and infants. The frame can be rigid or folding, and the tires, wheels, brakes, and other parts are selected based on indoor or outdoor use and the individual's needs. Proper fit is important for comfort and to prevent secondary disabilities. Patients should be trained on basic wheelchair skills. Regular maintenance and occasional overhauls are also recommended. Wheelchairs may be modified to facilitate transfers, positioning, self-propulsion, and transportation.Cervical spondylosis.pptx
Cervical spondylosis.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Cervical spondylosis is a degenerative condition affecting the cervical spine that commonly occurs with aging. As the cervical discs lose hydration and height, bone spurs and other degenerative changes can occur that result in compression of nerves or the spinal cord. While aging is the primary risk factor, repetitive neck movements from activities like texting or occupations involving manual labor can also contribute. Common symptoms include neck pain and stiffness, headaches, arm or hand numbness, weakness or tingling. Diagnosis involves physical examination and imaging tests like x-rays or MRI to identify the areas of involvement and damage.intro & history of rehab, epidemiology.pptx
intro & history of rehab, epidemiology.pptxRajveer71
╠²
The document provides an overview of the history and concepts of physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R), also known as physiatry. It discusses how rehabilitation therapies have evolved over thousands of years across various cultures to treat injuries and functional limitations. The document also defines key terms used in rehabilitation such as impairment, disability, and handicap according to the World Health Organization's international classification system. It emphasizes that the overall goal of rehabilitation is to minimize disability and handicap so individuals can lead productive lives.GBS.pptx
GBS.pptxRajveer71
╠²
This document provides information about Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS). It defines GBS as an acute onset demyelinating peripheral polyneuropathy that causes ascending flaccid paralysis starting in the lower limbs. Predisposing factors include viral or bacterial infections, vaccinations, surgery, and some drugs. Clinical features include rapidly progressive motor weakness, sensory symptoms, autonomic dysfunction, and increased cerebrospinal fluid albumin levels. Electrophysiology shows neurogenic abnormalities. Management involves plasmapheresis, steroid therapy, or intravenous immunoglobulin G.Presentation (3).pptx
Presentation (3).pptxRajveer71
╠²
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) is a stretching technique developed in the 1940s to enhance both active and passive range of motion. It uses patterns of diagonal and functional movements along with techniques like isometric contractions and combinations of passive stretching and muscle facilitation. The main PNF techniques are rhythmic initiation, repeated contraction, slow reversal, and contract-relax which aim to increase muscle strength and flexibility through repetition. PNF can be used to treat conditions involving muscle weakness or spasticity such as after a stroke.Scoliosis.pptx
Scoliosis.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine greater than 10 degrees. It can be classified as structural or non-structural. Structural scoliosis involves vertebral rotation and can be idiopathic, congenital, or neuromuscular. Evaluation involves history, exam, and radiographs to assess curve size and progression. Curves under 25 degrees are observed, 25-40 degrees may be braced, and over 40 degrees may require surgery like spinal fusion. Physiotherapy management focuses on posture, exercises, and breathing techniques for observation or bracing, and post-op recovery exercises.Abnormal gait patterns.pptx
Abnormal gait patterns.pptxRajveer71
╠²
The document describes different types of abnormal gaits seen in various medical conditions. It discusses hemiplegic, diplegic, myopathic, choreic, ataxic, antalgic and Trendelenburg gaits. It explains the pathomechanisms, causes and treatments for each gait type. Important muscles for normal gait include hip extensors, knee extensors, plantar flexors and dorsiflexors. Abnormalities in these muscle groups can significantly affect one's walking pattern.Gait and Gait cycle (new) mam.pptx
Gait and Gait cycle (new) mam.pptxRajveer71
╠²
This document provides an overview of gait and gait analysis. It defines gait and describes the gait cycle, which consists of the stance and swing phases. The document outlines various gait terminologies including temporal variables like single limb support time and double limb support time. It also discusses spatial variables such as step length and stride length. The document then covers causes of gait impairment, stair gait, running gait, and objective and subjective methods for analyzing gait.Handling of children with cerebral palsy PPT-vinay (1) (1).pdf
Handling of children with cerebral palsy PPT-vinay (1) (1).pdfRajveer71
╠²
Cerebral palsy is a group of disorders that affect movement and posture, caused by non-progressive damage to the developing brain before or after birth. It is diagnosed when brain damage occurs prenatally from conception to labor onset, perinatally from 28 weeks gestation to 7 days after birth, or postnatally in the first 2 years of life. The prevalence is 1-5 per 1000 live births globally and 2-2.5 per 1000 in Western countries. Etiology includes prematurity, low birth weight, infections, trauma, and complications during pregnancy, labor, or delivery. Early identification is based on risk factors and developmental delays. Diagnosis usually occurs between ages 2-5 years throughNEONATAL REFLEX.pptx
NEONATAL REFLEX.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Neonatal reflexes are involuntary responses present at birth that help assess infant development. There are several general body reflexes like the Moro reflex and plantar grasp reflex, as well as facial and oral reflexes. The presence, absence, strength, and timing of reflexes can indicate neurological abnormalities. Understanding neonatal reflexes aids in evaluating whether development is normal or if further assessment is needed.33189-Speaker-ppt.pptx
33189-Speaker-ppt.pptxRajveer71
╠²
Cupping therapy is an ancient practice over 5000 years old that is used globally to treat a broad spectrum of health disorders. It works through the body's cutivisceral reflex paths to stimulate circulation and regulate disturbed functions at the site of suction cups. This helps eliminate blockages and strengthens the body's natural healing powers without adverse side effects. Common methods include dry cupping, wet cupping, and cupping massage to improve blood flow and treat issues like bronchitis, influenza, and pain.Four_Cardiac-Rehabilitation.ppt
Four_Cardiac-Rehabilitation.pptRajveer71
╠²
This document provides information about cardiac rehabilitation. It defines cardiovascular disease and notes that it is the leading cause of death in the United States. Cardiac rehabilitation involves supervised exercise, education on lifestyle changes like nutrition, smoking cessation and stress management, and monitoring of health metrics under the guidance of a team of healthcare professionals. The benefits of cardiac rehabilitation include improved physical functioning, quality of life, disease knowledge, and adherence to a healthy lifestyle.stroke-rehabilitation.pdf
stroke-rehabilitation.pdfRajveer71
╠²
This document provides information on stroke rehabilitation techniques. It discusses principles of neuroplasticity such as use it or lose it, repetition matters, and intensity matters. Early mobilization is important to maintain cardiovascular endurance and minimize deficits. Collaboration between medical professionals and involving patients and families in setting goals is emphasized. Rehabilitation techniques discussed include neuromuscular re-education, constraint induced movement therapy, and neurodevelopmental technique. Positioning strategies are presented for patients with left or right hemiplegia. Demonstrations cover range of motion, transfers, bed mobility, gait belt use, and ambulation. Therapy typically progresses from intensive care to acute rehabilitation. References and questions are provided.Recently uploaded (20)
Tuberculosis burden , case finding tools and management .pptx
Tuberculosis burden , case finding tools and management .pptxDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
This presentation is for educational purposes only. Comprehensive Guide on Adsorption and Partition Chromatography Techniques
Comprehensive Guide on Adsorption and Partition Chromatography TechniquesSajini
╠²
This presentation provides an in-depth overview of chromatography, focusing on adsorption and partition chromatography. It covers the principles, methodologies, types, classification, column preparation, detection methods, advantages, disadvantages, and pharmaceutical applications. A useful resource for pharmacy students and professionals in pharmaceutical chemistry.
CEREBRAL PALSY - classification, types and Management
CEREBRAL PALSY - classification, types and ManagementSSIMS & RC
╠²
competency based classes for MBBS students.. Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...DR DHARMENDRA BINJHWAR
╠²
This slide are more importents for ayurveda students and teachers because i have mentioned in this slide night time routine in ayurveda the ancient science of India along with day and night pattern in various counteries within in one ppt. thanks for watching i will be greatful for your suggestion and feedback... please like share and suppourtWinning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs wit...
Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs wit...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair and Presenter, Naval Daver, MD, Jessica K. Altman, MD, and Ghayas Issa, MD, Alice S. Mims, MD, MSCR, discuss acute myeloid leukemia in this CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs with Innovative Targeted Strategies.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/42f1QCa. CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until June 30, 2026.Computer aided formulation development optimization
Computer aided formulation development optimizationSwami ramanand teerth marathwada university
╠²
Concept of optimization, optimization parameters, factorial design, optimization technology & screening design. Irradiation to prevent TA-GvHD by Dr. Abrar Kabir Shishir.pptx
Irradiation to prevent TA-GvHD by Dr. Abrar Kabir Shishir.pptxAbrarKabir3
╠²
This presentation discusses the role of irradiation in preventing transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GvHD). Covers pathophysiology, risk factors, investigation, prevention strategies, and irradiation procedures. Includes visuals and real-life context from Dhaka Medical College.Day care surgery anaesthesia and management of complications in postoperative...
Day care surgery anaesthesia and management of complications in postoperative...deepika582423
╠²
Day care Clinical Signs Overview: PICCKLE Mnemonic
Clinical Signs Overview: PICCKLE MnemonicDr Aman Suresh Tharayil
╠²
This presentation provides a concise yet comprehensive review of common clinical signs and their diagnostic significance, summarized under the acronym PICCKLE ŌĆō Pallor, Icterus, Clubbing, Cyanosis, Koilonychia, Lymphadenopathy, and Edema. Each condition is defined, followed by key causes, pathophysiology, diagnostic techniques, and clinical relevance. The content is tailored for undergraduate and postgraduate students in medicine and pharmacy, as well as early-career clinicians seeking to reinforce their clinical examination skillsOUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO
OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROKanhu Charan
╠²
OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...
5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...Bolan University of Medical and Health Sciences ,Quetta
╠²
Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficiency of manual lifting tasks in the workplace. It involves assessing the physical demands placed on the human body during lifting activities to prevent musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), particularly lower back injuriesELECTROMYOGRAPHY.pptX by GOKULAKRISHNAN.
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY.pptX by GOKULAKRISHNAN.GOKULAKRISHNAN JANARTHANAN
╠²
Electromyography is basically the study of motor unit activity.
In electromyography, the study of the electrical activity of contracting muscle provides information concerning the structure and function of the motor units.
Mastering the Review Article: Structure, Strategy & Success
Mastering the Review Article: Structure, Strategy & SuccessRajendra Dev Bhatt
╠²
A scoping search identified various types of review articles. For this training, most common types were selected, highlighting their key features, strengths, weaknesses, and uses.An interesting case of facial Swelling in an autoimmune rheumatic disease Ahm...
An interesting case of facial Swelling in an autoimmune rheumatic disease Ahm...Internal medicine department, faculty of Medicine Beni-Suef University Egypt
╠²
An interesting case of facial Swelling in an autoimmune rheumatic disease Ahmed Yehia EGYSIR Conference Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...DR DHARMENDRA BINJHWAR
╠²
Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs wit...
Winning GAMBITS Against AML: Guidance on Advances & Medical Breakthroughs wit...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...
5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...Bolan University of Medical and Health Sciences ,Quetta
╠²
An interesting case of facial Swelling in an autoimmune rheumatic disease Ahm...
An interesting case of facial Swelling in an autoimmune rheumatic disease Ahm...Internal medicine department, faculty of Medicine Beni-Suef University Egypt
╠²
Ad
.................abdominal incisions.pptx
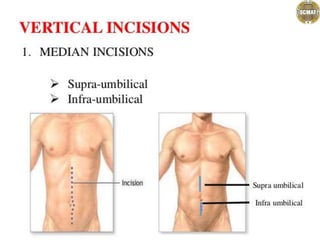
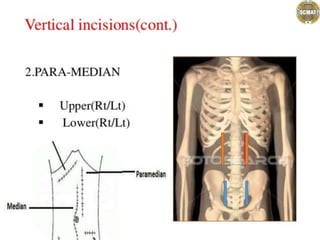
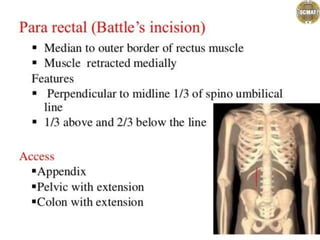
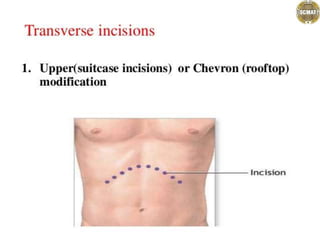
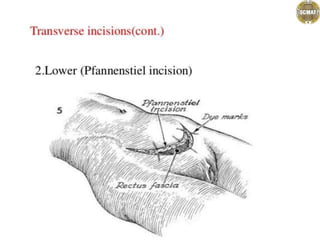
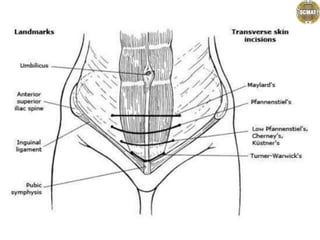
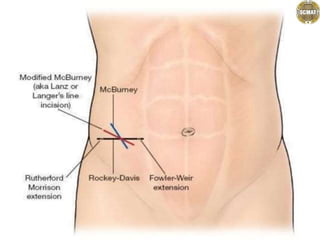
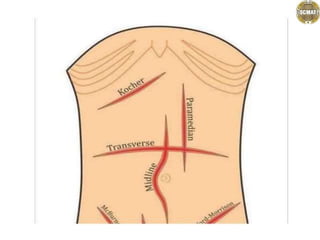
- 1. Abdominal incisions Dr. jaya chandra (pt) Lecturer scmat
- 39. Thank you