Acano Solution Resilient Archicture
- 1. ACANO SOLUTION Resilient Architecture
- 2. Why Resilience? Because maintaining service under any circumstance is critical for a superior use experience For Acano, resilience means that there must be no single point of failure anywhere in the system ŌĆō the Acano software, network between the components, and integration points.
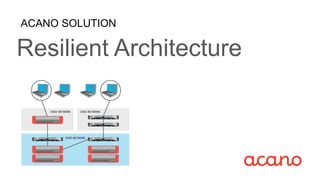
- 3. Acano Resilient Architecture Edge Instance Core Instance NAT traversal Media processing and signaling Instant messaging, presence and call control WebRTC database Configuration information and stored messages A single Acano software image is divided into components Each system running the software is referred to as an ŌĆ£instanceŌĆØ Each instance can: ŌĆó run a subset of components ŌĆó be on a Virtual Machine (VM) or Acano Server Multiple instances can work together to form a single system where each instance is self-sufficient typical deployment where edge functions in the DMZ are split from core functions
- 4. Achieving Resiliency Acano client connects to the best Edge instance Each Edge instance connects to the best Core instance (typically local) Core instances have mesh of connections between them for distributed conferences/coSpaces ŌĆ£best of bothŌĆØ: any mix of VMs and/or Acano Servers 1 2 3 3 1 2
- 5. Resiliency at Edge and Core Failure of a Core instance -- Only calls currently on those instances are affected, the rest of the system carries on Failure of an Edge instance -- Calls routed via an alternative edge instance in same or other location 4 4
- 6. Resilient Integration Multiple trunk connections can be configured for automatic failover Dialplan supports different SIP trunks configured at different Acano instances in the distributed system
- 7. Other Resiliency Measures Secure Data Management All persistent states of the system are in a fully distributed and redundant SQL database Changing Network Conditions TURN/STUN/ICE to perform NAT traversal and to route media optimally between locations Distributed By default all calls/conferences fully distributed Media processing for single call/conference split across multiple instances Those instances can be co-located in the same datacenter or geographically distributed