Accounting Equation
- 1. Assets, Liabilities, Ownersâ equity, Revenues, Expenses and Net income. Six elements of accounting: Point 3 Accounting Equation
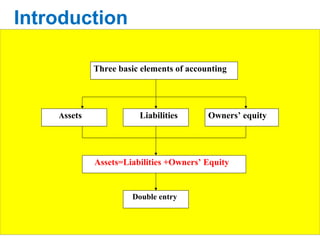
- 2. Assets Liabilities Ownersâ equity Assets=Liabilities +Ownersâ Equity Double entry Three basic elements of accounting Introduction
- 3. Study objectives âĒ Use the accounting equation to present accounting elements and their increases and decreases. âĒ Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. 4 Accounting Equation
- 4. ïž 1 ïž The basic Equation The accounting equation is the same for all economic entities.
- 5. The expanded Accounting Equation
- 6. Example ïž Classify the following items as assets, liabilities, or Owner's equity: âĒ(1) cash, (2) service revenue, âĒ(3) drawings, (4) accounts receivable, âĒ(5) accounts payable, âĒ(6) salaries expense.
- 7. Transaction identification process: ïž 2 ïž Transaction Analysis
- 8. âĒ Transaction (1): Investment by Owner. On September 1, 2015, Marc Douket invests $15,000 cash in the business .
- 9. âĒ Transaction (2): Purchase of Equipment for Cash. Softbyte purchases computer equipment for $7,000 cash.
- 10. âĒ Transaction (3): Purchase of Supplies on Credit. Softbyte purchases from the Tuch Supply Company $1,600 of computer paper and other supplies on Credit.
- 11. Summarizing 1. Each transaction must have effects on the three components (assets, liabilities, and Owner's equity) of the accounting equation 2. The two sides of the equation must always be equal.