Acids & Bases
109 likes40,964 views
Acids and bases can be identified by their names or chemical formulas. Acids contain hydrogen (H) or a carboxyl group (COOH) and have a pH below 7. Bases contain a metallic or ammonium ion and hydroxide (OH) and have a pH above 7. Acid-base indicators change color at specific pH levels and can be used to determine if a solution is acidic or basic. A neutralization reaction occurs between an acid and base, producing water and a salt.
1 of 32





























Recommended
Acid and base



Acid and baseJimnaira Abanto
Ėý
Acids produce H+ ions in water and taste sour, while bases produce OH- ions in water and taste bitter. Acids react with metals to produce hydrogen gas and with bases to form salts and water. The pH scale ranges from 0-14 and is used to measure whether a substance is acidic (below 7) or basic (above 7). Common indicators like litmus paper and the pH scale can be used to identify substances as acidic or basic. Maintaining the proper pH is important for processes like food preservation, plant growth, and human bodily functions.Salt preparation 



Salt preparation Zainab Yahya
Ėý
The document discusses four methods for preparing salts: 1) Reacting a metal with an acid, 2) Reacting an insoluble base with an acid, 3) Neutralizing an alkali with an acid through titration, and 4) Precipitation. It then provides examples of soluble and insoluble compounds, and explains how to specifically prepare zinc sulfate by reacting zinc powder with sulfuric acid. The document asks to describe how to prepare several example salts using these methods.ACIDS and BASES.



ACIDS and BASES.Analiza Secillano
Ėý
Properties/characteristics of Acid and Base.
Understanding the pH scale.
Acid-Base Indicator.
Neutralization.
Example of acids and basesThe PH Scale 



The PH Scale Supreme Student Government
Ėý
The document discusses pH and the pH scale. It defines pH as the negative logarithm of the molar concentration of hydrogen ions and explains that pH values below 7 indicate increasing acidity while values above 7 indicate increasing basicity. It provides examples of calculating pH from given hydrogen ion concentrations and vice versa. It also discusses buffer solutions and how they resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.CHEMICAL REACTIONS



CHEMICAL REACTIONSJimnaira Abanto
Ėý
Chemical reactions involve the transformation of one or more substances into different substances. There are two types of substances involved: reactants present at the beginning of the reaction and products formed by the reaction. Chemical reactions obey the law of conservation of mass, meaning the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products. Evidence of a chemical reaction may include the absorption or release of energy, a change in color or odor, the formation of a gas, or the production of a precipitate. Chemical equations are used to represent chemical reactions, and must be balanced so the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the reaction.Acids, bases and salts



Acids, bases and saltsAyush Patel
Ėý
This document discusses acids, bases, salts, and indicators. It defines acids as sour substances that produce hydrogen ions in solution and have a pH below 7. Bases are defined as having a pH above 7 and forming hydroxide ions in solution. Examples of common acids and bases are provided. Indicators are substances that change color in acidic versus basic solutions, allowing the pH to be determined. Strong acids and bases fully ionize in solution, while weak ones only partially ionize. Neutralization occurs when an acid and base react to form a salt and water. Salts are neutral compounds composed of acid anions and base cations.Periodic table ppt



Periodic table pptbherren
Ėý
The periodic table organizes the chemical elements in an orderly fashion according to their atomic number and properties. Dmitri Mendeleev created one of the first periodic tables in 1869 by arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic mass, which allowed for the prediction of undiscovered elements. The modern periodic table arranges elements by atomic number and places them into rows called periods and columns called groups based on their chemical and physical properties. Elements within the same group have similar properties including their valence electrons and the types of ions they form.Acids & Bases



Acids & Basessondang29
Ėý
This document discusses acids and bases. It defines acids as substances that produce H+ ions in aqueous solution and bases as substances that produce OH- ions. The document describes the pH scale for measuring acidity and alkalinity. It provides examples of the characteristic reactions of acids with metals, bases, and carbonates. It also discusses the importance of controlling acidity in the environment and describes how acids and bases are encountered in everyday life such as in soil, water, and air.Properties and Formation of Ionic Compounds Powerpoint



Properties and Formation of Ionic Compounds PowerpointNeQuelle DeFord
Ėý
Ionic compounds form when ions bond through electrostatic attraction. Metals form cations by losing electrons to achieve a full outer shell, while nonmetals form anions by gaining electrons. Cations and anions are attracted due to their opposite charges. Ionic compounds have high melting points, are crystalline solids, and dissolve in water due to the separation of ions. They do not conduct electricity as solids but do so as liquids or dissolved solutions.Introduction to periodic table



Introduction to periodic tableitutor
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to the periodic table, including:
1) It explains how to read the periodic table and what the atomic number, symbol, element name, and atomic weight represent.
2) It describes the main sections and groups of the periodic table, including metals and nonmetals, and how properties change across periods and groups.
3) It provides examples of different types of elements, including alkali metals, alkali earth metals, transition metals, noble gases, halogens, and metalloids.Naming Ionic and Covalent Compounds



Naming Ionic and Covalent CompoundsJohn Canuel
Ėý
1. The document provides an overview of writing formulas and naming ionic and covalent compounds. It reviews the periodic table and properties of metals, nonmetals and metalloids.
2. Key concepts covered include ion formation, the octet rule, polyatomic ions, oxidation numbers, naming conventions for ionic compounds containing metals or transition metals, and prefixes used in naming covalent compounds.
3. The document distinguishes between ionic and covalent bonding, lattice structures, and molecular structures of compounds.Acids and Bases



Acids and BasesKevin Cram
Ėý
This document discusses the chemistry of acids and bases. It outlines three definitions of acids and bases: Arrhenius, BrÃļnsted-Lowry, and Lewis. The Arrhenius definition states that acids produce hydrogen ions in water and bases produce hydroxide ions. The BrÃļnsted-Lowry definition broadened this to include acids as hydrogen ion donors and bases as acceptors. The Lewis definition focuses on electron pair donation and acceptance. Acids react with bases to form salts and water in a neutralization reaction. Common acids include sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and acetic acid.Chapter 15.1 : Properties of Acids and Bases



Chapter 15.1 : Properties of Acids and BasesChris Foltz
Ėý
This document discusses the properties and nomenclature of acids and bases. It defines acids as substances that increase the hydrogen ion concentration in aqueous solutions, and bases as substances that increase the hydroxide ion concentration. Strong acids fully ionize in water, producing hydronium ions, while weak acids only partially ionize. Common strong acids include sulfuric acid and nitric acid. Common bases, such as sodium hydroxide, fully dissociate in water to produce hydroxide ions. The document also provides examples of uses for several acids in industry and food processing.Acids and bases



Acids and basesbiologica.edu
Ėý
This document defines acids and bases and discusses their properties. It states that acids produce hydrogen ions in water and have a pH less than 7, while bases are metal oxides or hydroxides that react with acids to form salts and water. Common acids include hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, while common bases include sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide. The document also discusses concentration versus strength, noting that concentration can change but strength depends on the inherent properties of the acid or base.Ph and POH



Ph and POHMuhammad Khan
Ėý
This document provides an overview of acid/base chemistry and pH. It defines pH as a measure of hydrogen ion concentration, describes the pH scale from 0-14, and explains how to calculate pH, pOH, and hydrogen or hydroxide ion concentration from other values. Sample problems demonstrate how to determine pH from concentration and vice versa, as well as the relationship between pH and pOH. Key points are that pH is a log scale measurement of acidity, and that the sum of pH and pOH equals 14 for any aqueous solution.Percent composition



Percent compositionGuerillateacher
Ėý
1. The document discusses calculating percent composition and determining empirical and molecular formulas.
2. To calculate percent composition, the formula mass is determined and the mass of each element is calculated as a percentage of the total mass.
3. An empirical formula shows the lowest whole number ratio of atoms in a compound, while a molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms. Molecular formulas for ionic compounds are always empirical, while molecular formulas for molecular compounds may or may not be empirical.acids and bases



acids and basesRosie Leone
Ėý
1) Acids release H+ ions in water and bases release OH- ions. Strong acids and bases dissociate completely while weak acids and bases only partially dissociate.
2) Acids taste sour, turn litmus red, and react with metals and carbonates. Bases taste bitter and feel slippery.
3) The pH scale measures acidity and alkalinity, with values below 7 being acidic and above 7 being basic. Acid-base indicators change color at specific pH values.Acids and Bases



Acids and BasesSadman Ridoy
Ėý
An acid is a substance that produces hydrogen ions in water and has a pH less than 7. Strong acids, like hydrochloric acid, are completely ionized in water, while weak acids like acetic acid only partially ionize. Acids react with metals to produce salts and hydrogen gas, with carbonates to produce salts, water and carbon dioxide gas, and with bases to produce salts and water. They have sour tastes and are corrosive.Balancing Chemical Equations



Balancing Chemical Equationsjm149499
Ėý
1) A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using element symbols and formulas to show reactants and products.
2) Chemical equations must be balanced so that the same number of each type of atom is on both sides of the reaction arrow.
3) To balance equations, coefficients are placed in front of formulas to adjust the relative numbers of elements and compounds until both sides have equal quantities.Lecture 8.1- Ionic vs. Covalent



Lecture 8.1- Ionic vs. CovalentMary Beth Smith
Ėý
The document provides information about ionic and covalent (molecular) bonding:
- Ionic bonds occur between metals and non-metals and involve the transfer of electrons. Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals and involve the sharing of electrons.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points and conduct electricity when melted or dissolved. Molecular compounds have lower melting and boiling points and do not conduct electricity.
- Ionic compounds exist as crystal lattices of ions, while molecular compounds exist as distinct molecules made of two or more nonmetal atoms bonded together.Acid base reactions



Acid base reactionsknmckee
Ėý
This document defines acids and bases, describing their properties and common uses. Acids have a pH below 7 and taste sour, while bases have a pH above 7 and feel soapy. The document explains that acids and bases react through neutralization, forming less acidic or basic salt mixtures. Common acids include acetic, citric, and sulfuric acids, which are found in vinegar, fruits, and industrial chemicals, while bases are found in soaps, cleaners, and the human body.Isotopes & Atomic Mass



Isotopes & Atomic MassNeQuelle DeFord
Ėý
Magnesium has three naturally occurring isotopes: magnesium-24, magnesium-25, and magnesium-26. They have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons, giving them different atomic masses. Magnesium-24 makes up 79% of magnesium and has the greatest influence in calculating magnesium's average atomic mass of 24.3 amu.3.3 Acids and Bases



3.3 Acids and BasesMelinda MacDonald
Ėý
The pink colour in test tubes #2 and #4 was caused by the basic solution (NaOH) reacting with the phenolphthalein indicator, which turns pink in basic solutions with a pH between 8.2-12.
The colour disappeared in test tube #5 because the acidic solution (HCl) was added, and phenolphthalein is colourless in acidic solutions below pH 8.2.
We could use an acidic solution like HCl to take away the pink colour in test tube #6, as it would neutralize the basic solution and lower the pH below 8.2, making the phenolphthalein colourless again.Shake your acids, bases and salts



Shake your acids, bases and saltsT Arah Kagomi
Ėý
This document discusses acids, bases, and salts. It defines acids as substances that give H+ ions in water and have a sour taste, react with metals, and have a pH less than 7. Bases are defined as substances that give OH- ions in water, usually taste bitter, feel slippery, and have a pH greater than 7. Salts are formed when acids and bases react, combining H+ and OH- ions to form water. Common examples of acids include vinegar and cola, bases include drain cleaner and baking powder, and salts include table salt and toothpaste. The document provides characteristics, examples, and a brief activity to identify household substances as acids, bases or salts.Chemical bonding (UPDATED)



Chemical bonding (UPDATED)Jimnaira Abanto
Ėý
Chemical bonding
valence electrons
electronegativity
ionization energy
Lewis Dot
Octet Rule
Types of Bonding
Ionic bond
Covalent Bond
Metallic Bond
Formation of Ions



Formation of IonsHenry Sergio Jr
Ėý
This document discusses ions and how they are formed. It explains that atoms become ions by gaining or losing electrons to obtain a full outer electron shell. Atoms that gain electrons become negatively charged ions and atoms that lose electrons become positively charged ions. The document also discusses different types of ions including monatomic ions, polyatomic ions, and how to name compound ions that contain multiple atoms like sulfate, nitrate, and hydroxide ions.Acids, bases and salt



Acids, bases and saltJohn Rey Ravago
Ėý
This document defines acids, bases, and salts according to three theories:
1) Arrhenius defines acids as substances that yield hydrogen ions in water and bases as substances that yield hydroxide ions in water. Neutralization produces salt and water.
2) Bronsted-Lowry defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. Neutralization involves the transfer of a proton from an acid to a base.
3) Lewis defines acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors. Neutralization involves the sharing of an electron pair between an acid and base.Chemical Names and Formulas



Chemical Names and FormulasCurrituck County High School
Ėý
This document discusses classifying and naming ionic and covalent compounds, as well as writing their formulas. It provides rules for:
- Classifying compounds as ionic or covalent based on their formula
- Naming ionic compounds using stock systems and identifying polyatomic ions
- Naming covalent compounds using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms
- Writing formulas for ionic compounds by balancing charges and for covalent compounds using prefixes
It also discusses acids, bases, and how to name and write formulas for acids based on their anion name endings.Chemistry GCSE Chapter 8 Acid bases and Salts .pptx



Chemistry GCSE Chapter 8 Acid bases and Salts .pptxAnumToqueer
Ėý
This document discusses acids, bases, and salts. It defines acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solution and bases as substances that produce hydroxide ions in aqueous solution. Examples of strong acids and weak acids are provided. The document also discusses the properties of acids and bases, including their reactions with metals, metal hydroxides, metal carbonates to form salts. It introduces the pH scale for measuring acidity and alkalinity and discusses acid-base indicators. Various types of oxides such as basic, acidic, amphoteric, and neutral oxides are also defined.Intro acids and bases



Intro acids and basestanzmanj
Ėý
This document defines acids and bases and their key characteristics. Acids release H+ ions in water and have sour tastes, while bases release OH- ions in water and feel slippery. Strong acids and bases fully dissociate in water, while weak ones only partially dissociate. Common strong acids include sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid. When acids and bases react, they undergo a neutralization reaction where water and a salt are formed. Indicators are used to test whether a solution is acidic or basic. The pH scale measures the concentration of H+ ions, with lower pH indicating more H+ ions and higher pH less H+ ions.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Properties and Formation of Ionic Compounds Powerpoint



Properties and Formation of Ionic Compounds PowerpointNeQuelle DeFord
Ėý
Ionic compounds form when ions bond through electrostatic attraction. Metals form cations by losing electrons to achieve a full outer shell, while nonmetals form anions by gaining electrons. Cations and anions are attracted due to their opposite charges. Ionic compounds have high melting points, are crystalline solids, and dissolve in water due to the separation of ions. They do not conduct electricity as solids but do so as liquids or dissolved solutions.Introduction to periodic table



Introduction to periodic tableitutor
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to the periodic table, including:
1) It explains how to read the periodic table and what the atomic number, symbol, element name, and atomic weight represent.
2) It describes the main sections and groups of the periodic table, including metals and nonmetals, and how properties change across periods and groups.
3) It provides examples of different types of elements, including alkali metals, alkali earth metals, transition metals, noble gases, halogens, and metalloids.Naming Ionic and Covalent Compounds



Naming Ionic and Covalent CompoundsJohn Canuel
Ėý
1. The document provides an overview of writing formulas and naming ionic and covalent compounds. It reviews the periodic table and properties of metals, nonmetals and metalloids.
2. Key concepts covered include ion formation, the octet rule, polyatomic ions, oxidation numbers, naming conventions for ionic compounds containing metals or transition metals, and prefixes used in naming covalent compounds.
3. The document distinguishes between ionic and covalent bonding, lattice structures, and molecular structures of compounds.Acids and Bases



Acids and BasesKevin Cram
Ėý
This document discusses the chemistry of acids and bases. It outlines three definitions of acids and bases: Arrhenius, BrÃļnsted-Lowry, and Lewis. The Arrhenius definition states that acids produce hydrogen ions in water and bases produce hydroxide ions. The BrÃļnsted-Lowry definition broadened this to include acids as hydrogen ion donors and bases as acceptors. The Lewis definition focuses on electron pair donation and acceptance. Acids react with bases to form salts and water in a neutralization reaction. Common acids include sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and acetic acid.Chapter 15.1 : Properties of Acids and Bases



Chapter 15.1 : Properties of Acids and BasesChris Foltz
Ėý
This document discusses the properties and nomenclature of acids and bases. It defines acids as substances that increase the hydrogen ion concentration in aqueous solutions, and bases as substances that increase the hydroxide ion concentration. Strong acids fully ionize in water, producing hydronium ions, while weak acids only partially ionize. Common strong acids include sulfuric acid and nitric acid. Common bases, such as sodium hydroxide, fully dissociate in water to produce hydroxide ions. The document also provides examples of uses for several acids in industry and food processing.Acids and bases



Acids and basesbiologica.edu
Ėý
This document defines acids and bases and discusses their properties. It states that acids produce hydrogen ions in water and have a pH less than 7, while bases are metal oxides or hydroxides that react with acids to form salts and water. Common acids include hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, while common bases include sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide. The document also discusses concentration versus strength, noting that concentration can change but strength depends on the inherent properties of the acid or base.Ph and POH



Ph and POHMuhammad Khan
Ėý
This document provides an overview of acid/base chemistry and pH. It defines pH as a measure of hydrogen ion concentration, describes the pH scale from 0-14, and explains how to calculate pH, pOH, and hydrogen or hydroxide ion concentration from other values. Sample problems demonstrate how to determine pH from concentration and vice versa, as well as the relationship between pH and pOH. Key points are that pH is a log scale measurement of acidity, and that the sum of pH and pOH equals 14 for any aqueous solution.Percent composition



Percent compositionGuerillateacher
Ėý
1. The document discusses calculating percent composition and determining empirical and molecular formulas.
2. To calculate percent composition, the formula mass is determined and the mass of each element is calculated as a percentage of the total mass.
3. An empirical formula shows the lowest whole number ratio of atoms in a compound, while a molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms. Molecular formulas for ionic compounds are always empirical, while molecular formulas for molecular compounds may or may not be empirical.acids and bases



acids and basesRosie Leone
Ėý
1) Acids release H+ ions in water and bases release OH- ions. Strong acids and bases dissociate completely while weak acids and bases only partially dissociate.
2) Acids taste sour, turn litmus red, and react with metals and carbonates. Bases taste bitter and feel slippery.
3) The pH scale measures acidity and alkalinity, with values below 7 being acidic and above 7 being basic. Acid-base indicators change color at specific pH values.Acids and Bases



Acids and BasesSadman Ridoy
Ėý
An acid is a substance that produces hydrogen ions in water and has a pH less than 7. Strong acids, like hydrochloric acid, are completely ionized in water, while weak acids like acetic acid only partially ionize. Acids react with metals to produce salts and hydrogen gas, with carbonates to produce salts, water and carbon dioxide gas, and with bases to produce salts and water. They have sour tastes and are corrosive.Balancing Chemical Equations



Balancing Chemical Equationsjm149499
Ėý
1) A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using element symbols and formulas to show reactants and products.
2) Chemical equations must be balanced so that the same number of each type of atom is on both sides of the reaction arrow.
3) To balance equations, coefficients are placed in front of formulas to adjust the relative numbers of elements and compounds until both sides have equal quantities.Lecture 8.1- Ionic vs. Covalent



Lecture 8.1- Ionic vs. CovalentMary Beth Smith
Ėý
The document provides information about ionic and covalent (molecular) bonding:
- Ionic bonds occur between metals and non-metals and involve the transfer of electrons. Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals and involve the sharing of electrons.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points and conduct electricity when melted or dissolved. Molecular compounds have lower melting and boiling points and do not conduct electricity.
- Ionic compounds exist as crystal lattices of ions, while molecular compounds exist as distinct molecules made of two or more nonmetal atoms bonded together.Acid base reactions



Acid base reactionsknmckee
Ėý
This document defines acids and bases, describing their properties and common uses. Acids have a pH below 7 and taste sour, while bases have a pH above 7 and feel soapy. The document explains that acids and bases react through neutralization, forming less acidic or basic salt mixtures. Common acids include acetic, citric, and sulfuric acids, which are found in vinegar, fruits, and industrial chemicals, while bases are found in soaps, cleaners, and the human body.Isotopes & Atomic Mass



Isotopes & Atomic MassNeQuelle DeFord
Ėý
Magnesium has three naturally occurring isotopes: magnesium-24, magnesium-25, and magnesium-26. They have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons, giving them different atomic masses. Magnesium-24 makes up 79% of magnesium and has the greatest influence in calculating magnesium's average atomic mass of 24.3 amu.3.3 Acids and Bases



3.3 Acids and BasesMelinda MacDonald
Ėý
The pink colour in test tubes #2 and #4 was caused by the basic solution (NaOH) reacting with the phenolphthalein indicator, which turns pink in basic solutions with a pH between 8.2-12.
The colour disappeared in test tube #5 because the acidic solution (HCl) was added, and phenolphthalein is colourless in acidic solutions below pH 8.2.
We could use an acidic solution like HCl to take away the pink colour in test tube #6, as it would neutralize the basic solution and lower the pH below 8.2, making the phenolphthalein colourless again.Shake your acids, bases and salts



Shake your acids, bases and saltsT Arah Kagomi
Ėý
This document discusses acids, bases, and salts. It defines acids as substances that give H+ ions in water and have a sour taste, react with metals, and have a pH less than 7. Bases are defined as substances that give OH- ions in water, usually taste bitter, feel slippery, and have a pH greater than 7. Salts are formed when acids and bases react, combining H+ and OH- ions to form water. Common examples of acids include vinegar and cola, bases include drain cleaner and baking powder, and salts include table salt and toothpaste. The document provides characteristics, examples, and a brief activity to identify household substances as acids, bases or salts.Chemical bonding (UPDATED)



Chemical bonding (UPDATED)Jimnaira Abanto
Ėý
Chemical bonding
valence electrons
electronegativity
ionization energy
Lewis Dot
Octet Rule
Types of Bonding
Ionic bond
Covalent Bond
Metallic Bond
Formation of Ions



Formation of IonsHenry Sergio Jr
Ėý
This document discusses ions and how they are formed. It explains that atoms become ions by gaining or losing electrons to obtain a full outer electron shell. Atoms that gain electrons become negatively charged ions and atoms that lose electrons become positively charged ions. The document also discusses different types of ions including monatomic ions, polyatomic ions, and how to name compound ions that contain multiple atoms like sulfate, nitrate, and hydroxide ions.Acids, bases and salt



Acids, bases and saltJohn Rey Ravago
Ėý
This document defines acids, bases, and salts according to three theories:
1) Arrhenius defines acids as substances that yield hydrogen ions in water and bases as substances that yield hydroxide ions in water. Neutralization produces salt and water.
2) Bronsted-Lowry defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. Neutralization involves the transfer of a proton from an acid to a base.
3) Lewis defines acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors. Neutralization involves the sharing of an electron pair between an acid and base.Chemical Names and Formulas



Chemical Names and FormulasCurrituck County High School
Ėý
This document discusses classifying and naming ionic and covalent compounds, as well as writing their formulas. It provides rules for:
- Classifying compounds as ionic or covalent based on their formula
- Naming ionic compounds using stock systems and identifying polyatomic ions
- Naming covalent compounds using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms
- Writing formulas for ionic compounds by balancing charges and for covalent compounds using prefixes
It also discusses acids, bases, and how to name and write formulas for acids based on their anion name endings.Similar to Acids & Bases (20)
Chemistry GCSE Chapter 8 Acid bases and Salts .pptx



Chemistry GCSE Chapter 8 Acid bases and Salts .pptxAnumToqueer
Ėý
This document discusses acids, bases, and salts. It defines acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solution and bases as substances that produce hydroxide ions in aqueous solution. Examples of strong acids and weak acids are provided. The document also discusses the properties of acids and bases, including their reactions with metals, metal hydroxides, metal carbonates to form salts. It introduces the pH scale for measuring acidity and alkalinity and discusses acid-base indicators. Various types of oxides such as basic, acidic, amphoteric, and neutral oxides are also defined.Intro acids and bases



Intro acids and basestanzmanj
Ėý
This document defines acids and bases and their key characteristics. Acids release H+ ions in water and have sour tastes, while bases release OH- ions in water and feel slippery. Strong acids and bases fully dissociate in water, while weak ones only partially dissociate. Common strong acids include sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid. When acids and bases react, they undergo a neutralization reaction where water and a salt are formed. Indicators are used to test whether a solution is acidic or basic. The pH scale measures the concentration of H+ ions, with lower pH indicating more H+ ions and higher pH less H+ ions.Introacidsandbases 130416101155-phpapp02



Introacidsandbases 130416101155-phpapp02Cleophas Rwemera
Ėý
This document defines acids and bases and their key characteristics. Acids release H+ ions in water and have sour tastes, react with metals, and contain hydrogen. Strong acids completely dissociate into H+ ions while weak acids only partially dissociate. Common strong acids include sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid. Bases release OH- ions in water and usually taste bitter and feel slippery. Strong bases contain hydroxide ions and are also corrosive. When acids and bases react through neutralization, they form water and a salt like NaCl. The pH scale measures the concentration of H+ ions in a solution, with lower pH indicating more H+ ions.doFGHFHTRHJTRYTRJYLIOYUJTDHRTRwnload.pdf



doFGHFHTRHJTRYTRJYLIOYUJTDHRTRwnload.pdfRahul Radhakrishnan
Ėý
Acids produce hydrogen ions (H+) in water and bases produce hydroxide ions (OH-). Common acids include hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and nitric acid. Common bases include sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide. Acids and bases react through a neutralization reaction where hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions combine to form water and a salt. Indicators are used to determine if a substance is an acid or base by changing color in their presence.Acids-and-Bases (2).pptx



Acids-and-Bases (2).pptxEuannMagtibay
Ėý
This presentation is about acids and bases in chemistry. It is important to study this in order to be knowledgeable. Acids Bases and Salts



Acids Bases and Saltsduncanpatti
Ėý
Acids release H+ ions in water and have sour tastes, while bases release OH- ions in water and feel slippery. Strong acids and bases completely ionize in water, while weak acids and bases only partially ionize. Common strong acids include sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, while strong bases include lithium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide. When acids and bases are mixed, they neutralize each other through a reaction that produces water and a salt. Indicators change color depending on whether the solution is acidic or basic, and can be used to measure the pH of a solution.Acid base notes



Acid base notesFrederick High School
Ėý
This document discusses acids and bases. It defines acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions in water, and bases as substances that produce hydroxide ions in water. Strong acids and bases completely ionize, while weak ones only partially ionize. Neutral substances have equal concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. When acids and bases are mixed, they neutralize to form salts and water through balanced chemical reactions. pH indicators can be used to determine if a solution is acidic, basic, or neutral.Ainun dan winda



Ainun dan windaPaarief Udin
Ėý
This document discusses acid-base theories and properties of acids and bases. It begins by explaining several theories of acids and bases:
1. Arrhenius theory defines acids as compounds producing H+ ions in water and bases as compounds producing OH- ions.
2. Bronsted-Lowry theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors.
3. Lewis theory defines acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors.
It then discusses the properties of acids and bases, including their behavior in water and reactions with metals. The document also explains concepts like pH, acid and base strength, and the relationship between acid and conjugate base dissociation constants.Ainun dan winda



Ainun dan windaPaarief Udin
Ėý
This document discusses acid-base theories and properties of acids and bases. It begins by explaining several theories of acids and bases:
1. Arrhenius theory defines acids as compounds producing H+ ions in water and bases as compounds producing OH- ions.
2. Bronsted-Lowry theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors.
3. Lewis theory defines acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors.
It then discusses the properties of acids and bases, including their behavior in water and reactions with metals. The document also explains concepts like pH, acid and base strength, and the relationship between acid and conjugate base dissociation constants.Acids and Bases Presentation By Asad Ali



Acids and Bases Presentation By Asad AliAsad Ali
Ėý
This document provides information about acids, bases, pH, and neutralization. It defines acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions in solution and have a pH below 7. Bases are defined as substances that accept hydrogen ions and have a pH above 7. It describes how pH is measured and indicates the acidity or alkalinity of a solution on a scale from 0-14. pH indicators are chemicals that change color depending on whether a solution is acidic or basic. The document also discusses acid rain, how it is formed, and some of its harmful effects. Finally, it defines neutralization as the reaction between an acid and base, and provides some examples of uses for neutralization.Acids and Bses 



Acids and Bses armindaortiz
Ėý
This document provides an overview of acid-base theories and properties. It covers the Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis theories of acids and bases. It defines strong and weak acids and bases, and how their strength affects properties like conductivity and reaction rate. It also introduces the pH scale and explains how pH is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution.Acids, bases, & salts



Acids, bases, & saltsabhishekbisht123
Ėý
This document discusses acids, bases, and salts. It defines acids as compounds that produce hydrogen ions (H+) in water, have a pH below 7, and react with metals. Bases are defined as compounds that produce hydroxide ions (OH-) in water and have a pH above 7. Salts are neutral compounds formed by the reaction of acids and bases. Common acids and bases are listed, along with their uses. The pH scale and indicators are also explained.Chemistry unit 7 notes



Chemistry unit 7 notesFrederick High School
Ėý
This document provides information about acids and bases including:
- Acids produce H+ ions in water and bases produce OH- ions. The strength depends on how completely they ionize.
- Examples of acids include vinegar and lemon juice. Examples of bases include soap and ammonia. Neutral substances have equal concentrations of H+ and OH- ions.
- Acids have a sour taste and low pH while bases have a bitter taste, slippery feel and high pH.
- The names and formulas of acids can be determined based on their ionic parts. Neutralization reactions between acids and bases produce salt and water. pH indicators are used to determine if a solution is acidic or basic.quiz_acids and bases



quiz_acids and basesInsel Lei
Ėý
The document provides instructions for a 15 question true/false and multiple choice test on acids and bases. It explains that each question should be answered honestly by selecting the best answer, and that explanations will be provided for each question after it is answered. It also provides directions on how to navigate between questions and pages of the test.ACIDS AND BASES



ACIDS AND BASESAnaliza Secillano
Ėý
Acids and bases are defined by their properties in aqueous solutions. Acids release hydrogen ions (H+) and have a sour taste, while bases release hydroxide ions (OH-) and feel slippery. The pH scale measures acidity and basicity, with values from 0-14 and neutral substances having a pH of 7. Acid-base indicators change color with pH and can test whether a solution is acidic or basic. When acids and bases are mixed, a neutralization reaction occurs where they cancel out each other's properties and form a salt and water.Non aqueous titration- Pharmaceutical Analysis



Non aqueous titration- Pharmaceutical AnalysisSanchit Dhankhar
Ėý
This document discusses non-aqueous acid-base titration. It begins by explaining that non-aqueous titrations are used for substances that are too weakly acidic or basic to give a sharp endpoint in water, or for substances that are insoluble in water. It then covers the major acid-base theories of Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis. The document discusses the effects of different solvent types on acid/base strength and how this enables the titration of weaker acids and bases. It provides examples of titrating benzoic acid with sodium methoxide in n-butylamine and titrating ephedrine alkaloid with perchloric acid in glacial acetic acid or dChapter No 1 : Acids, Bases and Buffers



Chapter No 1 : Acids, Bases and BuffersChetan Jain
Ėý
This is chapter No 1 of Pharmaceutical Chemistry - I for Diploma in Pharmacy (D. Pharmacy)
Details notes for Diploma in Pharmacy (D.Pharmacy) Students. Acids & Bases Gr. 7.pptx



Acids & Bases Gr. 7.pptxAntonio Coloma
Ėý
The document discusses acids and bases. It defines acids as substances that donate hydrogen ions in water, giving them sour tastes and allowing them to conduct electricity and corrode other substances. Bases are defined as substances that form hydroxide ions in water, giving them bitter tastes and allowing them to conduct electricity and feel slippery. The document explains the pH scale and uses of acids and bases, describing properties of strong vs. weak acids and bases and how salts are formed through neutralization reactions of acids and bases.More from OhMiss (20)
bioculact



bioculactOhMiss
Ėý
This biology project document provides ideas for students centered around anatomical apparel, edible models of biological systems, and stationery depicting biological systems. The document lists the topics of anatomical apparel, incredible edibles which are edible models of biological systems, and anatomical accessories which includes ideas for models of the rib cage, lungs, vertebrae, heart, and red blood cells. It also mentions biological systems stationery.Organelles



OrganellesOhMiss
Ėý
This document provides an overview of the main organelles found in eukaryotic cells and their functions. It discusses the cytoplasm, cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vacuoles, and additional organelles specific to plant cells including the cell wall and chloroplasts. Each organelle carries out specialized functions that allow the cell to perform basic activities necessary to stay alive such as using energy, storing materials, transporting substances, and reproducing.Cell division



Cell divisionOhMiss
Ėý
The cell cycle is the repeating series of growth and division that produces new cells. It consists of interphase, where the cell grows and DNA is replicated, and mitosis, where the cell divides into two daughter cells each with identical DNA. Chromosomes, made of DNA and proteins, condense during cell division and separate into each new cell, ensuring genetic continuity. The cycle controls cell growth, division, and death through regulated phases.Cell theory & types of cells



Cell theory & types of cellsOhMiss
Ėý
Cell theory states that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and new cells are produced from existing cells. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic, which lack organelles and a nucleus, or eukaryotic, which contain organelles and a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells can be single-celled or multi-cellular, and multi-cellular organisms contain specialized cells that perform distinct functions like transport, storage, photosynthesis, and more.GHG Sources & Human Activities



GHG Sources & Human ActivitiesOhMiss
Ėý
The document discusses sources and sinks of greenhouse gases and their contribution to climate change. It explains that the main natural greenhouse gas is water vapor, while the main human-caused one is carbon dioxide released from sources like burning fossil fuels. Forests normally act as carbon sinks by absorbing carbon dioxide through photosynthesis, but deforestation has reduced this, increasing atmospheric carbon levels. In addition to large industries, personal lifestyle choices and consumption patterns also generate significant greenhouse gas emissions through activities like waste disposal, manufacturing of disposable products, electricity use, transportation of goods, and more.Greenhouse Gases



Greenhouse GasesOhMiss
Ėý
The document discusses greenhouse gases and their role in the greenhouse effect. It notes that 31% of incoming solar radiation is reflected by clouds, atmosphere and land, while 30% is absorbed by the atmosphere. The remaining radiation warms Earth's surface. Increased greenhouse gas concentrations mean less heat is released to space, increasing average surface temperatures. Tree ring data provides long-term climate records, with thicker rings indicating optimal growth conditions.Earth's Climate



Earth's ClimateOhMiss
Ėý
The document discusses several factors that influence Earth's climate:
1) Solar energy is the main driver of climate, affecting global temperatures as it is absorbed by the atmosphere, oceans, and land.
2) Other factors like Earth's orbit, axial tilt, and rotation influence the distribution of solar radiation and cause seasonal changes.
3) Large bodies of water like oceans influence climate by slowly storing and transferring heat around the world.Lenses and the human eye



Lenses and the human eyeOhMiss
Ėý
There are several types of lenses including double convex, single convex, concavo-convex, convexo-concave, single concave, and double concave. The thin lens equation relates the object distance, image distance, and focal length. A concave lens has a negative focal length while a convex lens has a positive focal length. The image distance is positive for a real image and negative for a virtual image. The eye contains rods and cones, including three types of cones that detect red, green, and blue light. The lens of the eye changes shape to keep close and distant objects in focus by altering how parallel and diverging light rays enter the eye. Common vision problems include nearsightedness whichLenses



LensesOhMiss
Ėý
Lenses are transparent materials that refract light in a predictable way. They are used to magnify or project images. There are two main types of lenses: convex and concave. Convex lenses are thicker in the center and converge light, forming a real image. Concave lenses are thinner in the center and diverge light, forming a virtual upright image that is smaller than the object. The way light rays behave when passing through lenses can be depicted using ray diagrams to show the characteristics of the image formed.Snell's law



Snell's lawOhMiss
Ėý
Total internal reflection occurs when light travels from an optically dense medium to a less dense medium and the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle. At the critical angle, the refracted ray travels along the surface of the dense medium. If the incident ray exceeds the critical angle, total internal reflection occurs and the light ray is reflected back into the dense medium rather than refracting into the less dense medium. Mirages can form due to both total internal reflection and refraction as light passes through layers of air with different densities. Snell's law defines the mathematical relationship between the angle of incidence, angle of refraction, and the indices of refraction of the media.Refraction



RefractionOhMiss
Ėý
Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another. Light travels at different speeds in different media, causing it to change direction at the boundary between the two. The degree to which light is refracted depends on the index of refraction, which is a ratio comparing the speed of light in a medium to the speed of light in a vacuum. White light disperses into the colors of the visible spectrum when refracted due to different wavelengths bending by different amounts.Colour Optics



Colour OpticsOhMiss
Ėý
Additive color theory describes how light combines, stating that white light is composed of red, green, and blue wavelengths, and combining two primary colors produces a secondary color. Subtractive color theory explains how color pigments work by absorbing some light wavelengths and reflecting others, with the primary colors for pigments being cyan, magenta, and yellow which combine to produce the secondary colors red, green, and blue.Curved Mirrors



Curved MirrorsOhMiss
Ėý
The document discusses the characteristics of curved mirrors, including concave and convex mirrors. It defines key terms like focal point, focal length, vertex, and describes the four cases of image formation for concave mirrors based on the object's distance from the mirror. Real images can be projected, virtual images appear behind the mirror. Concave mirrors form inverted and magnified or reduced real images. Convex mirrors always form upright, virtual and reduced images. Ray diagrams illustrate the reflection of light rays for both concave and convex mirrors.Light and the Electromagnetic Spectrum



Light and the Electromagnetic SpectrumOhMiss
Ėý
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that travels in waves made up of electric and magnetic fields. The electromagnetic spectrum includes both visible light and invisible forms of energy across a range of wavelengths. The wavelength of light determines whether it is visible to the human eye or not, with different wavelengths appearing to us as different colors. Objects are visible because they reflect light, with smooth surfaces reflecting light specularly and rough surfaces reflecting it diffusely.Reflections in a Plane Mirror



Reflections in a Plane MirrorOhMiss
Ėý
The document discusses reflection of light off plane mirrors. It explains that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, and provides steps to draw ray diagrams showing the reflection of light off a plane mirror. These include drawing incident and reflected rays, as well as determining the location of the image relative to the object using the law of reflection.asdfgx934



asdfgx934OhMiss
Ėý
The document describes 5 types of chemical reactions:
1. Synthesis reactions combine elements to form compounds.
2. Decomposition reactions break compounds down into their constituent elements.
3. Single displacement reactions occur when one element displaces another in a compound.
4. Double displacement reactions involve the switching of ions between two ionic compounds in aqueous solution.
5. Combustion reactions involve the burning of hydrocarbons in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.Lab equipment



Lab equipmentOhMiss
Ėý
This document describes various pieces of lab equipment including beakers, Erlenmeyer flasks, volumetric flasks, graduated cylinders, test tubes, tongs, test tube holders, test tube brushes, scoopulas, thermometers, forceps, medicine droppers, test tube racks, stirring rods, Bunsen burners, retort stands, C-clamps, burettes, wire mesh, clay triangles, crucibles, funnels, filter paper, mortar and pestles, spot plates, evaporating dishes, Petri dishes, and watch glasses. Each item is briefly described in terms of its common laboratory uses and characteristics.Chemical Reactions



Chemical ReactionsOhMiss
Ėý
A chemical reaction involves the transformation of reactants into different products through rearrangement of atoms. Chemical reactions conserve mass as atoms are not destroyed or created, but instead are reorganized into new substances. Balancing chemical equations ensures the same number and type of atoms are on both sides of the reaction.Molecular Compounds



Molecular CompoundsOhMiss
Ėý
Molecular compounds are formed when two or more different non-metal atoms combine via covalent bonds, sharing electron pairs. Examples include water, which is made of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom. Molecular compounds have properties like being soft and having low melting points. They are named systematically with the first element, the second as an "-ide", and prefixes to indicate atom amounts, like dinitrogen monoxide for N2O.Models of the Atom



Models of the AtomOhMiss
Ėý
The document summarizes the development of atomic models over time from Dalton's model to the current quantum mechanical model. Dalton imagined atoms as spheres that differed in size and mass. Thomson discovered the electron and proposed the "plum pudding" model. Rutherford's gold foil experiment revealed the tiny, dense nucleus. Chadwick discovered neutrons in the nucleus. Bohr incorporated electron shells. The current quantum model depicts electrons as clouds surrounding the nucleus.Acids & Bases
- 1. ACIDS & BASES
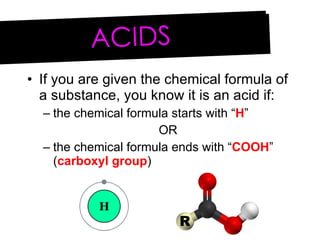
- 2. ACIDS You can identify an acid from its name or chemical formula Usually the name of an acid ends with the word â acid â
- 3. If you are given the chemical formula of a substance, you know it is an acid if: the chemical formula starts with â H â OR the chemical formula ends with â COOH â ( carboxyl group ) ACIDS
- 4. For example: HF (aq) is an acid because it starts with H Hydrofluoric acid is used for etching glass CH 3 COOH (aq) is an acid because it ends with COOH The name of this acid is â acetic acid â Diluted acetic acid is vinegar ACIDS
- 5. NAMING ACIDS When the chemical formula of an acid starts with H and only contains one other non-metallic element, it is named as follows:
- 6. Step 1: Start with the prefix â hydro â Step 2: take the first part of the non-metallic element and add the suffix â ic â and the word â acid â ex.) HCl(aq) = â hydrochloric acid â HF(aq) = â hydrofluoric acid â NAMING ACIDS
- 7. Sometimes the chemical formula of an acid contains a polyatomic ion For example, H 2 SO 4 (aq) contains the polyatomic ion sulphate ( SO 4 2- ) When naming an acid containing a polyatomic ion, do the following: NAMING ACIDS
- 8. Step 1: Start with the name of the element in the polyatomic ion that is not oxygen Step 2: Add the suffix â ic â and the word â acid â ex.) H 2 SO 4 (aq) = sulphuric acid H 3 PO 4 (aq) = phosphoric acid NAMING ACIDS
- 9. BASES Bases can also be identified from their name or chemical formula A substance is a base if its name begins with the name of a metallic ion and ends with the word â hydroxide â
- 10. A substance is also a base if: the chemical formula starts with a metallic ion or with the ammonium ion NH 4 + AND the chemical formula ends with OH ( hydroxyl group) BASES
- 11. For example, NaOH (s) starts with the metallic ion sodium ( Na + ) and ends with OH - Similarly, KOH (s) starts with the metallic ion potassium ( K + ) and ends with OH - NH 4 OH starts with the ammonium ion NH 4 + and ends with OH - BASES
- 12. NAMING BASES Step 1: write the name of the positively charged ion Step 2 : Add the word â hydroxide â ex.) KOH = potassium hydroxide NH 4 OH = ammonium hydroxide
- 13. ACIDS & BASES Thousands of years ago, scientists used taste to distinguish acids from bases Acids taste sour and bases taste bitter Tasting unknown substances is not a safe way of identifying it or its properties
- 14. pH Today you can determine if a substance is an acid or a base by measuring its pH The pH measurement is related to the number of hydrogen ions ( H + ) that are in a solution The abbreviation âpHâ stands for â power of hydrogen â
- 15. The pH scale is a number scale that indicates how acidic or basic a solution is The pH of a substance can only be determined when it is in aqueous solution (dissolved in water ) pH
- 16. Pure water has a pH of 7 Any substance with a pH of 7 when it is in aqueous solution is neutral A neutral substance is neither an acid nor a base pH
- 17. An acid is a substance that has a pH of less than 7 when it is in aqueous solution The more acidic a substance is, the lower the pH pH
- 18. A base is a substance that has a pH greater than 7 when it is in aqueous solution The more basic a substance is, the higher the pH pH
- 19. pH
- 20. One unit of change on the pH scale represents a change by a factor of 10 in how acidic or basic a solution is ex.) stomach acid has a pH of 1 . This is 10 times more acidic than lemon juice, which has a pH of 2 . pH
- 21. Acid-Base Indicators An acid-base indicator is any substance that changes colour in the presence of an acid or a base The most widely known acid-base indicator is litmus
- 22. Litmus is a plant extract that can be blue or red (pink) Litmus turns red/pink in an acidic solution Litmus turns blue in a basic solution Acid-Base Indicators
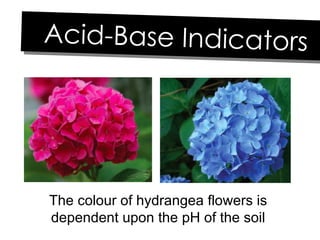
- 23. The colour of hydrangea flowers is dependent upon the pH of the soil Acid-Base Indicators
- 24. It would be impossible to determine the pH of all solutions using just one indicator, such as litmus Several other acid-base indicators exist, each producing a colour change at a specific pH level Acid-Base Indicators
- 25. Ėý
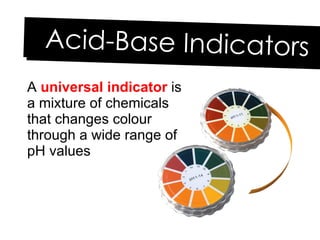
- 26. A universal indicator is a mixture of chemicals that changes colour through a wide range of pH values Acid-Base Indicators
- 27. An even more precise way of determining pH is to use a pH meter
- 28. Properties of Acids & Bases Similarities : dissolve in water conduct electricity in aqueous solution can irritate or burn skin
- 29. Differences : BASES ACIDS turn litmus blue turn litmus red/pink do not react with metals to produce a compound and hydrogen gas react with metals to produce a compound and hydrogen gas do not corrode metals corrode metals release hydroxide ( OH - ) ions in aqueous solution release hydrogen ( H + ) ions in aqueous solution pH > 7 pH < 7 feel slippery do not feel slippery taste bitter taste sour
- 30. Neutralization Reactions Neutralization is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base that produces water (H 2 O) and a salt acid + base ï salt + water
- 31. The salts formed may be soluble in water or can be insoluble If the salt is insoluble, a precipitate will form Recall: a precipitate is a suspension of small, solid particles formed during a chemical reaction Neutralization Reactions
- 32. Applications of neutralization reactions: Pharmaceuticals Agriculture Food industry Neutralization Reactions


