Acids, bases + neutralization
- 1. Acids and Bases Acid-Base Neutralization Buffers Acid-Base Titration
- 2. Neutralization Reactions When acid and bases with equal amounts of hydrogen ion H+ and hydroxide ions OH- are mixed, the resulting solution is neutral. NaOH (aq) + HCl(aq) NaCl + H2O base acid salt water Ca(OH)2 + 2 HCl CaCl2 + 2H2O base acid salt water
- 3. Neutralization H3O+ and OH- combine to produce water H3O+ + OH- → 2 H2O from acid from base neutral Net ionic equation: H+ + OH- → H2O
- 4. Ionic Equations for Neutralization Write strong acids, bases, and salt as ions H+ + Cl- + Na+ + OH- Na+ + Cl- + H2O Cross out matched ions H+ + Cl- + Na+ + OH- Na+ + Cl- + H2O Write a net ionic reaction H+ + OH- H2O
- 5. Balancing Neutralization Equations Write the equation for the neutralization between magnesium hydroxide and nitric acid. 1. Write the formulas of the acid and base Mg(OH)2 + HNO3 2. Balance to give equal OH- and H+ Mg(OH)2 + 2 HNO3
- 6. 3. Write the products: Mg(OH)2 + 2HNO3 Mg(NO3)2 + H2O salt water (metal and nonmetal) 4. Balance products Mg(OH)2 + 2 HNO3 Mg(NO3)2 + 2 H2O
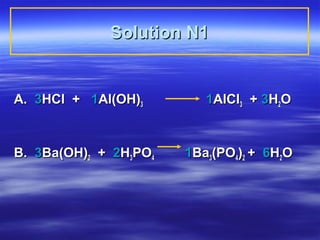
- 7. Learning Check N1 Select the correct group of coefficients for the following neutralization equations A. __ HCl + __ Al(OH)3 __AlCl3 + __ H2O 1) 1, 3, 3, 1 2) 3, 1, 1, 1 3) 3, 1, 1 3 B.__ Ba(OH)2 + __H3PO4 __Ba3(PO4)2 + __ H2O 1) 3, 2, 2, 2 2) 3, 3, 1, 6 3) 2, 3, 1, 6
- 8. Solution N1 A. 3HCl + 1Al(OH)3 1AlCl3 + 3H2O B. 3Ba(OH)2 + 2H3PO4 1Ba3(PO4)2 + 6H2O
- 9. Learning Check N2 Write a balanced equation and calculate the mL of 2.00 M H2SO4 required to neutralize 50.0 mL of 1.00 M KOH? ___H2SO4 + ___KOH ___K2SO4 + H2O 1) 12.5 mL 2) 50.0 mL 3) 200. mL
- 10. Solution N2 How many mL of 2.00 M H2SO4 are required to neutralize 50.0 mL of 1.00 M KOH? H2SO4 + 2KOH K2SO4 + 2H2O 0.0500 L x 1.00 mole KOH x 1 mole H2SO4 x 1L 2 mole KOH 1L x 1000 mL = 12.5 mL 2 mole KOH 1L
- 11. Learning Check N3 A 25 mL sample of phosphoric acid is neutralized by 40. mL of 1.5 M NaOH. What is the molarity of the phosphoric acid solution? 3NaOH + H3PO4 Na3PO4 + 3H2O 1) 0.45 M 2) 0.80 M 3) 7.2 M
- 12. Solution S3 0.040 L x 1.5 mole NaOH x 1 mole H3PO4 1L 3 mole NaOH x 1 = 0.80 mol/L = 0.80 M 0.025 L