ACLS.pptx
- 2. ACLS Introduction & Rhythm Recognition By Dr. J. Saleem
- 3. What is ACLS âĒ Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) is a systematic approach to resuscitation efforts. âĒ ACLS training gives rescuers a coordinated way to approach critically ill patients, regardless of response team size.
- 4. ACLS Core Concepts 1. Airway management i. You should know how to insert or assist with ETT (Endotracheal Tube). ii. You should also know alternative ventilation techniques, such as how to use a BVM (Bag Valve Mask) device and LMA (Laryngeal Mask Airway). 2. BLS i. You should be proficient in BLS and certified within the last 2 years; or ii. Are a BLS Instructor/Trainer and have conducted workshops in BLS at least once a year for the past 2 years.
- 5. Single Handed E-C Technique Single Handed E-O Technique
- 7. ACLS Core Concepts 3. Early management You should know how to manage the first 30 minutes of emergencies that result from such causes as: âĒ Acute Coronary Syndrome âĒ Cardiac Arrest â medical â associated with trauma â in a pregnant patient âĒ Cardiac Tamponade âĒ Drowning / Near-Drowning âĒ Electrocution / Lightning Strike âĒ Hypothermia âĒ Pneumothorax âĒ (Possible) Drug Overdose âĒ Stroke âĒ Thrombosis
- 8. ACLS Core Concepts 4. Electrical Therapy You should know how to safely use electrical devices like: i. Conventional Defibrillators ii. Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) iii. Temporary Pacemakers (TPM) 5. Emergency conditions i. You should be able to identify indications for ACLS, such as Asystole, PEA, SVTs, VTach, and VFib. ii. You should also be able to administer appropriate treatment.
- 9. ACLS Core Concepts 6. I.V. and Invasive Techniques You should be familiar with: â Peripheral I.V. Line Insertion â Central Line Insertion â Intraosseous Cannulation 7. Pharmacology You should know the action, indication, dosages, and precautions for the major drugs used during ACLS, such as adenosine, amiodarone, and epinephrine.
- 10. 5 Links in Adult Chain of Survival 1. Immediate recognition and activation of the Emergency Medical Services (EMS) â call 1122 2. Early Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) with high-quality chest compressions 3. Rapid Defibrillation 4. Effective Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) 5. Integrated postâcardiac arrest care
- 11. 5 Links in Adult Chain of Survival 1. Immediate recognition and activation of the Emergency Medical Services (EMS) â call 1122 2. Early Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) with high-quality chest compressions 3. Rapid Defibrillation 4. Effective Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) 5. Integrated postâcardiac arrest care
- 12. Step 3 - AED
- 13. Step 4 - ACLS âĒ Advanced Airway Management âĒ Administration of rhythm-appropriate I.V. medications
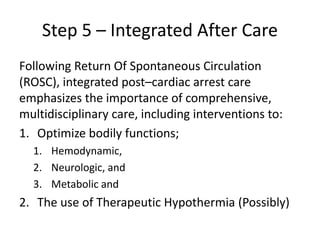
- 14. Step 5 â Integrated After Care Following Return Of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC), integrated postâcardiac arrest care emphasizes the importance of comprehensive, multidisciplinary care, including interventions to: 1. Optimize bodily functions; 1. Hemodynamic, 2. Neurologic, and 3. Metabolic and 2. The use of Therapeutic Hypothermia (Possibly)
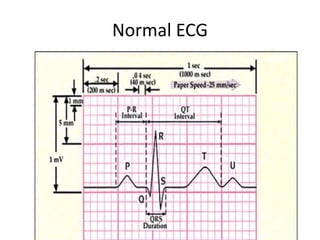
- 16. Normal ECG
- 17. Shocking the Heart Cardioversion âĒ Planned / Scheduled âĒ Synchronized âĒ Low energy settings â 25 to 150 J âĒ Chemical alternative âĒ Rx Atrial Arrhythmias Defibrillation âĒ Unscheduled /Emergency âĒ Asynchronous âĒ High energy settings â 200 â 360 J âĒ No Chemical Alternate âĒ Rx of Ventricular Arrhythmias
- 18. Types of Defibrillators Monophasic Vs. Biphasic Shock âĒ A monophasic shock only travels in one direction from one paddle to another âĒ a biphasic shock travels from one paddle to the other and then back several times. Types 1. Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) 2. Semi-Automated AEDs 3. Standard / Conventional Defibrillators 4. Implanted Defibrillators (eg DDD or DDI)
- 19. Sinus Tachycardia Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial Fibrillation
- 20. Wolfe-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome Multi-Focal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) Junctional Atrial Rhythm
- 21. Ventricular Premature Beats (VPCs) OR Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) Bigeminy Trigeminy
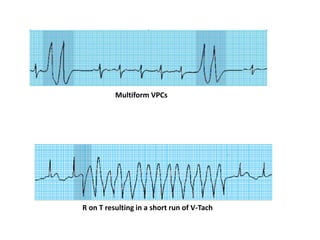
- 22. Multiform VPCs R on T resulting in a short run of V-Tach
- 23. V-Tach
- 24. V-Tach
- 25. V-Tach
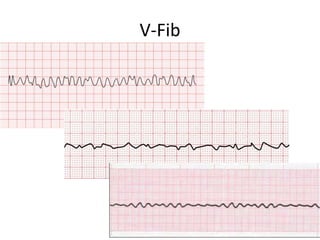
- 26. V-Fib
- 27. Asystole
- 28. PEA