Action Research
- 2. CONTENT ïĒ What is Action Research? ïĒ Concept of Action Research ïĒ Types of Action research ïĒ Characteristics of Action research ïĒ Process of Action research ïĒ References
- 3. Kurt Lewin ïĒ Kurt Lewin (1890-1947) ïĒ German social psychologist ïĒ Generally credited as the person who coined the term âaction researchâ in 1944 ïĒ Kurt Lewin define Action research as a process of Planning Action Searching
- 4. WHAT IS ACTION RESEARCH? ï Action research is inquiry or research in the context of focused efforts to improve the quality of an organization and its performance. ï It typically is designed and conducted by practitioners who analyze the data to improve their own practice. ï Action research can be done by individuals or by teams of colleagues. The team approach is called collaborative inquiry.â
- 5. CONCEPT OF ACTION RESEARCH: ïĒ According to (Stephen M. Corey)âs view: âThe process by which practitioners attempt to study their problem scientifically in order to guide, correct and evaluate their decisions and actions in what number of people have called action research.â ïĒ According to (Good)âs view: âAction research is research used by teachers, supervisors and administrators to improve the quality of their decisions and actions.â
- 6. ACTION RESEARCH IN EDUCATION: ïĒ Action research is a systematic process that allow you to try out different way of doing things in your classroom or in your school, until you find something that really works for you and for your students. (Laycock & Long,2009) ïĒ Action research is very popular in the field of education because there is always room for improvement when it comes to teaching and educating others.
- 7. EXAMPLES: 1st Example is: ïĒ Problem: 12th grade students have low performance on applying power and square root. ïĒ Solution from reading: math software, supplement with calculator, role play, games. ïĒ Idea: role play and group presentation. ïĒ Evaluation: using pre-test, quality of project, post- test, students evaluation. ïĒ Based on evaluation â what is going right and what is going wrong ? What is the next action?
- 8. 2nd Example is: ïĒ Problem: 9th grade students cannot write a good sentence. ïĒ Solution from reading: writing workshop, wiki, blog, peer mentor, twitter. ïĒ Idea: students tweet a sentence everyday and peers and instructor give them feedback. ïĒ Evaluate: quality of writing sentence, discussion, interview student, student evaluation. ïĒ Based on evaluation-next action.
- 9. TYPES OF ACTION RESEARCH There are two main types of action research ïĒ participatory action research ïĒ practical action research
- 10. PARTICIPATORY ACTION RESEARCH: ïĒ Participatory action research is an approach to research in communities that emphasizes participation and action ïĒ Members of a group discuss problem. All members approache the topic of research with âcritical intentâ ïĒ Practitioners work together as a group and collectively identify problems and possible solutions. ïĒ There is a strong social element here as well, in that it is expected that participants will emerge with a new view or theory of society
- 11. PRACTICAL ACTION RESEARCH: ïĒ Practitioner identifies the problem or question which he/she want to address and will seek out a facilitator to give collaborateive feedback. ïĒ Concern with practical knowledge or âcraft knowledgeâ ïĒ Here the researcher and the practitioner identify the research problem together and discuss underlying causes and possible interventions.
- 12. CHARACTERISTICS OF ACTION RESEARCH: ïĒ It is about action and research ïĒ It is cyclical and evolves ïĒ Each stage of the cycle is rigorous ïĒ It is critical ïĒ It tends to be collaborative ïĒ It often starts with an engaging question
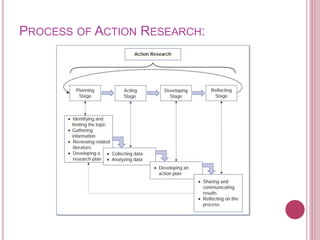
- 13. PROCESS OF ACTION RESEARCH:
- 14. REFERENCES: ïĒ M.M,Manfra.Action Research: Exploring the Theoretical Divide between Practical and Critical Approaches .Journal of Curriculum and Instruction (JoCI), January 2009, Volume 3, Number 1 ïĒ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Action_research ïĒ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2566 051/ ïĒ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Participatory_action_res earch ïĒ http://www.arlecchino.org/ildottore/mwsd/group2fina l-comparison.html ïĒ http://celt.ust.hk/teaching-resources/action- research/models-and-examples