Active suspension-system
- 1. Active Suspension System CHUNCHU DHINESH 18285A0305
- 2. Suspension Systems Conventional suspension system Active suspension system
- 3. A computerized system in automobiles that actively adjusts the suspension in response to driving conditions.
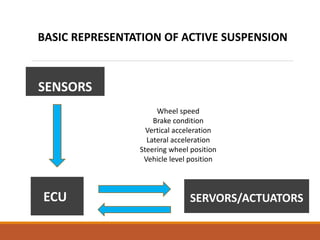
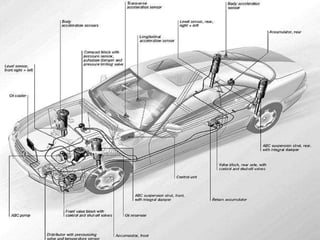
- 5. Wheel speed Brake condition Vertical acceleration Lateral acceleration Steering wheel position Vehicle level position SENSORS ECU SERVORS/ACTUATORS BASIC REPRESENTATION OF ACTIVE SUSPENSION
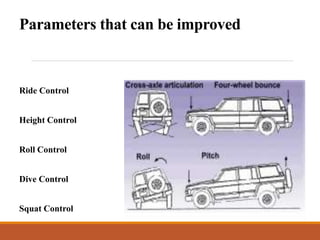
- 6. Parameters that can be improved Ride Control Height Control Roll Control Dive Control Squat Control
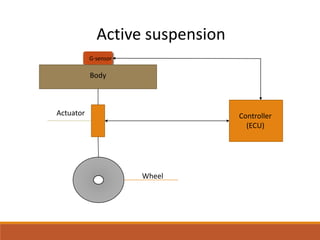
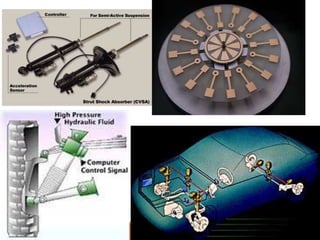
- 7. COMPONENTS ’é¦A Computer or an electronic control unit (ECU) ’é¦Sensors ’é¦Actuator or Servo ’é¦Adjustable shocks and springs
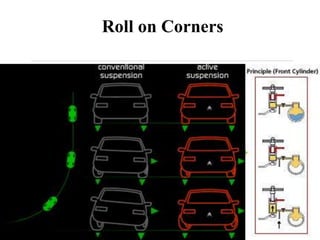
- 10. Functions of Active Suspension Improves driver control, safety and stability, with or without a load . Eliminates sway and reduces roll on corners Reduces axle wrap Maximum safety Absorbs load, rather than resisting it, thereby ensuring a much more comfortable ride Eliminates the need for fitting extra blades which harden the ride Better handling and control in windy and rough road conditions Minimize wear on tires, shocks, shackles and leaf springs
- 11. Roll on Corners
- 13. Active suspension mimics the functions of the human body The sensors are nerve ends The Electronic Control Unit represents our mind Wires connecting the whole thing are the central nervous system The servos and actuators resemble the muso- skelatel portion .
- 16. ADVANTAGES ŌĆóStabilizes the wheel independently. ŌĆóIncreases the overall grip of the vehicle, hence creating a safer ride. ŌĆóIt has soft spring which improves ride quality and passenger comfort. ŌĆóEliminates body role during high speed cornering. ŌĆóAnti role bar is omitted. ŌĆóRide height is not affected by varying static load.
- 17. Draw-backs ’é¦Need for a large external power source ’é¦Complex control algorithms ’é¦Complex closed-loop control systems. ’é¦Requirement of fast-acting devices ’é¦Increased cost
- 18. Conclusion In the case of active suspension system, as in any other innovations of automotive technology, today's innovation is tomorrow's standard feature. In spite of its high initial cost, let us expect to see them in the Indian roads soon. The trickle-down effect will take some time, but it'll happen and when such a time comes we can expect much lesser accidents, less fatalities and more comfort in driving the roads.