Activities.pptx
- 1. Android Activities CS 240 – Advanced Programming Concepts
- 2. Activities • Represent the screens in your Android application • Divided into two pieces: 1. The UI layout (normally defined in an xml file with a combination of regular widgets (views) and ViewGroups (containers for other views) 2. The ActivityXXX.java file is where you select and inflate the view for the activity and put your event handling code for the activity and it’s view objects. • Layouts are reusable 2
- 3. Qualified Layouts • Can have separate layouts for different orientations (portrait vs landscape) different screen heights and widths, etc. • Example: – GeoQuiz/QuizActivity 3
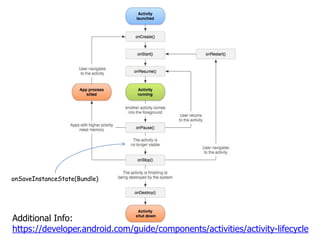
- 4. The Activity Lifecycle • Activities have a lifecycle, controlled by the Android system • Things that cause lifecycle/activity state changes: – Creation of a new activity – Activation (manually or programmatically) of an activity that wasn’t active before – Rotation of the device – Interruptions from other apps (i.e. phone calls) – Low memory – Other 4
- 5. The Six Main Activity Callbacks • protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) – When the system first creates the activity (set the UI/content view here) • protected void onStart() – Makes the activity visible to the user (usually no need to implement) • protected void onResume() – Activity is in the foreground and ready for the user to interact with it • protected void onPause() – First indication that the user is leaving the activity. It is no longer in the foreground. • protected void onStop() – Activity is no longer visible to the user • protected void onDestroy() – Activity is about to be destroyed (either because it is finished or there was a configuration change—most commonly a rotation of the device) 5
- 6. Additional Callbacks • protected void onRestart() – Called if the activity was stopped but not destroyed, and is now being restarted – The activity was not active but is about to become active – onStart() will be called next • protected void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle savedInstanceState) – Called between onPause() and onStop() – Provides an opportunity to save state so it can be restored after a configuration change (i.e. rotation) 6
- 8. Activity Lifecycle Demo • GeoQuiz – Set logcat to “Debug” and filter on “QuizActivity” – Observe the output for the following changes • Initial creation • Rotation • Use of ”recents” button to make another app active • Use of “home” button • Use of “back” button 8
- 9. Saving and Restoring Instance State • Use the onSaveInstanceState(Bundle) callback to save state in an activity record before it is lost due to a configuration or other short-term change – Doesn’t work for long-term storage (activity records are removed when the user hits the ‘back’ button, when an activity is destroyed, when the device is rebooted, or when the activity hasn’t been used for a while) – Default (inherited) implementation saves state for all UI components. Doesn’t save state for instance variables. • Use the Bundle passed to onCreate(Bundle) to restore state – Be sure to check for a null bundle. If it’s null, there’s no saved state to restore. • Example – GeoQuiz/QuizActivity.java 9
- 10. Starting An Activity • Start an activity (from another activity) by creating an instance of the Intent class and passing it to the startActivity(Intent) method – startActivity(Intent) is defined in the Activity class • Example: Intent intent = new Intent(QuizActivity.this, CheatActivity.class); startActivity(intent); 10 We usually create intents from an inner class event handler, so this is a reference to the containing activity. The activity we want to start.
- 11. Starting an Activity and Passing Data boolean answerIsTrue = mQuestionBank[mCurrentIndex].isAnswerTrue(); Intent intent = new Intent(QuizActivity.this, CheatActivity.class); intent.putExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_IS_TRUE, answerIsTrue); intent.putExtra(EXTRA_CHEATS_REMAINING, cheatsRemaining); startActivity(intent); 11
- 12. Retrieving Data from an Intent Intent intent = getIntent(); boolean isAnswerTrue = intent.getBooleanExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_IS_TRUE); • This would be available to the activity that was called 12
- 13. Returning Results from an Activity 1. Calling activity calls startActivityForResult(Intent, int) instead of startActivity(Intent) – See GeoQuiz/QuizActivity (lines 105-110) 2. Called activity creates an Intent, puts result data in the intent as intent extras (if needed), and calls setResult – setResult(int resultCode) – setResult(int resultCode, Intent data) – See GeoQuiz/CheatActivity.setResult(…) 3. Calling activity provides an onActivityResult(…) callback method – See GeoQuiz/QuizActivity.onActivityResult(…) 13
- 14. Applications to Family Map Client • Main Activity (MapFragment) – PersonActivity is started when event info is clicked (person or personId is passed as intent extra) – Search and Settings activities are started when the menu items are clicked • Depending on how you implement them, Settings and Filter activities may return results indicating any changes made by the user • PersonActivity – Clicking a person starts another PersonActivity with the Person or personId passed as an intent extra – Clicking an event starts an EventActivity with the Event or eventId passed as an intent extra 14
- 15. Applications to Family Map Client • SearchActivity – Clicking a person starts a PersonActivity with the Person or personId passed as an intent extra – Clicking an event starts an EventActivity with the Event or eventId passed as an intent extra • SettingsActivity – Logout goes back to MainActivity 15









![Starting an Activity and Passing Data
boolean answerIsTrue =
mQuestionBank[mCurrentIndex].isAnswerTrue();
Intent intent = new Intent(QuizActivity.this,
CheatActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_IS_TRUE, answerIsTrue);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_CHEATS_REMAINING, cheatsRemaining);
startActivity(intent);
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activities-240117065607-c12570d8/85/Activities-pptx-11-320.jpg)