Adaptaton to function of the eye
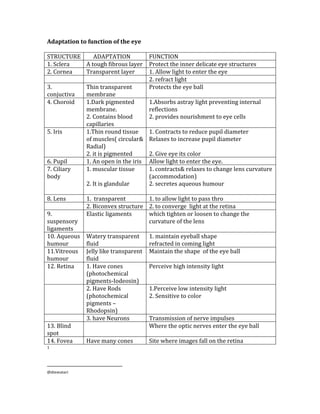
- 1. Adaptation to function of the eye STRUCTURE ADAPTATION FUNCTION 1. Sclera A tough fibrous layer Protect the inner delicate eye structures 2. Cornea Transparent layer 1. Allow light to enter the eye 2. refract light 3. conjuctiva Thin transparent membrane Protects the eye ball 4. Choroid 1.Dark pigmented membrane. 2. Contains blood capillaries 1.Absorbs astray light preventing internal reflections 2. provides nourishment to eye cells 5. Iris 1.Thin round tissue of muscles( circular& Radial) 2. it is pigmented 1. Contracts to reduce pupil diameter Relaxes to increase pupil diameter 2. Give eye its color 6. Pupil 1. An open in the iris Allow light to enter the eye. 7. Ciliary body 1. muscular tissue 2. It is glandular 1. contracts& relaxes to change lens curvature (accommodation) 2. secretes aqueous humour 8. Lens 1. transparent 1. to allow light to pass thro 2. Biconvex structure 2. to converge light at the retina 9. suspensory ligaments Elastic ligaments which tighten or loosen to change the curvature of the lens 10. Aqueous humour Watery transparent fluid 1. maintain eyeball shape refracted in coming light 11.Vitreous humour Jelly like transparent fluid Maintain the shape of the eye ball 12. Retina 1. Have cones (photochemical pigments-Iodeosin) Perceive high intensity light 2. Have Rods (photochemical pigments ¨C Rhodopsin) 1.Perceive low intensity light 2. Sensitive to color 3. have Neurons Transmission of nerve impulses 13. Blind spot Where the optic nerves enter the eye ball 14. Fovea Have many cones Site where images fall on the retina 1 @dmwatari