Address translaion 12
Address translation is the process of converting between logical addresses used within a computer system to physical addresses used by memory chips and I/O devices. It involves breaking the logical address into page number and offset, using the page number to index a translation table to find the corresponding physical frame number, and concatenating the frame number and offset to form the physical address. The main types of address translation are network address translation (NAT), port address translation (PAT), dynamic address translation, and static address translation. Address translation provides advantages like conservation of public IP addresses and protection of private resources, but also disadvantages like added delay and difficulty in troubleshooting.











Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to Address translaion 12 (20)
Recently uploaded (20)
Address translaion 12
- 3. CONTENTS ’é× DEFINITION ’é× PROCESS ’é× TYPES ’é× ADVANTAGE ’é× DISADVANTAGE
- 4. DEFINITION
- 5. PROCESS OF ADDRESS TRANSLATION ’é× The address translation process can be described as follows --- 1-Break the logical address down into page number and offset. 2-Use the page number as an index into a page table to find the corresponding page frame. 3-Using the frame number found there generate a physical address by concatenating the frame number and offset from the original address.
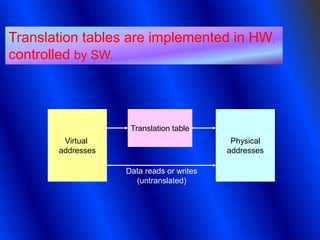
- 6. Translation tables are implemented in HW, controlled by SW. Translation table Virtual Physical addresses addresses Data reads or writes (untranslated)
- 7. Types of address translation ’é× Address translation comes in a variety of types which are given below- 1- NAT (network address translation) 2-PAT (Port address translation) 3- Dynamic address translation 4- Static address translation
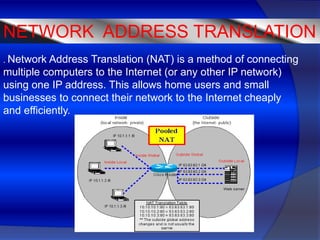
- 8. NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION . Network Address Translation (NAT) is a method of connecting multiple computers to the Internet (or any other IP network) using one IP address. This allows home users and small businesses to connect their network to the Internet cheaply and efficiently.
- 9. Static Address Translations Static address translation establishes a one-to- one mapping between a local and global address or local and global address/port pair. When specifying a static address translation or address/port pair translation, you issue commands to indicate how the translation is applied, along with more specific variables that further define the type of translation
- 10. DYNAMIC ADDRESS TRANSLATION Dynamic address translation, or DAT is the process of translating a virtual address during a storage reference into the corresponding real address.
- 11. PORT ADDRESS TRANSLATION With Port Address Translation (PAT), also known as ŌĆ£overloadŌĆØ and [[Network Address Port Translation (NAPT), the customer may map several internal addresses to one public address. When using PAT, traffic attempts to engage the original source port. If the source port is fully utilized, PAT causes the traffic to find the first available port.
- 12. ADVANTAGE OF ADDRESS TRANSLATION - The advantage of address translation include- 1.Conservation of public addresses. 2.Protection of resources with private addresses from external devices. 3.No need for readdressing of devices when switching from one ISP to another.
- 13. DISADVANTAGES OF ADDESS TRASLATION 1.Each connection has an added delay. 2.Troubleshooting is more difficult. 3.Not all applications work with address translation.