Adr and-gdr
- 1. Lokesh Dodani â 32 Sunil Gyanchandani â 42 Tripti Kochar â 52 Mukul Ahuja â 05 Akshay Aggarwal â 03 Manish Mahajan â 59 Ritika Gupta â 41
- 2. Depository Receipt ADR - American Depositary Receipt ï AnADR represents ownership in the shares of a non-U.S. company and trades in U.S. financial markets. Advanced Financial Management 2
- 3. GDR - Global Depositary Receipt ï GDRis a certificate issued by a depository bank, which purchases shares of foreign companies. Advanced Financial Management 3
- 4. ISSUER INVESTOR Attractive pricing Diversification No foreign exchange Negotiable instrument free fluctuations from investment restrictions Granting ESOPs Investment opportunities & Less obstacles Less monitoring Trading information and research Enhances image of company Prompt dividend payment globally. in dollars
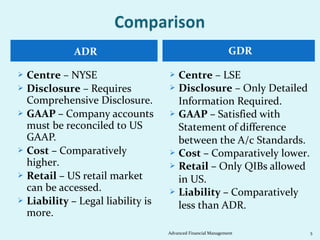
- 5. ADR GDR ï Centre â NYSE ï Centre â LSE ï Disclosure â Requires ï Disclosure â Only Detailed Comprehensive Disclosure. Information Required. ï GAAP â Company accounts ï GAAP â Satisfied with must be reconciled to US Statement of difference GAAP. between the A/c Standards. ï Cost â Comparatively ï Cost â Comparatively lower. higher. ï Retail â Only QIBs allowed ï Retail â US retail market in US. can be accessed. ï Liability â Comparatively ï Liability â Legal liability is less than ADR. more. Advanced Financial Management 5
- 6. ïLead manager ïListing agent ïCo-manager ïLegal advisors ïOverseas ïPrinters Depository Banks ïAuditors ïDomestic ïUnderwriters Custodian Bank
- 8. 5 Company issues Ordinary Shares Kept with Domestic Custodian Transferred to the Overseas Depository Bank ADRâs /GDRâs are issued by ODB Receipts given to the foreign investors
- 9. Appoint Listing Agent / Lead manger Due Diligence Positioning Required financial Valuation statements Deal Structure Prepare prospectus Presentation material and Q & A practice Apply for listing & regulatory approval Analyst Meeting through listing agent Premarketing to Institutions Road shows & marketing to investors List on Eurolist , Start trading
- 10. Types of ADRs Unsponsored Sponsored Level I Level II Level III Private placement
- 11. ï Created in response of investors, brokers - dealers and depository. ï Exempted from reporting requirements of the SEC. ï Not Listed on any exchange. Advantages: Disadvantages: ï Inexpensive. ï No control over the ï Expands investors base. activity. ï Minimal SEC compliance and ï Conversion reporting requirements. becomes costly.
- 12. ï Initiated by Issuer. ï Established jointly by an Issuer and Depository. ï Agreement between Issuer and Depository. ï Depository provides shareholders communication and other information to ADR holders. ï Through Depository ADR holders can exercise voting rights.
- 13. Level I Level II Level III Most Least Expensive More Expensive Expensive Minimal SEC Full SEC SEC reporting registration registration & is more &reporting reporting detailed than requirements. requirements. Level II. Listed on Cannot be listed on Listed on National National National exchange of exchange of US. exchange of US. US. Capital can be Capital Raising is not Capital Raising is raised through permitted. not permitted. Public offering.
- 14. ï Capital can be raised by placing Depositary Receipts with large institutional investors. ï Do not have to conform full SEC reporting and registration requirements. ï Cheaper means of raising equity capital. ï Can only be sold to QIBs.
- 15. ï―Fungibility = Interchangeability of any security One way Two way
- 16. ï Improvement in Liquidity ï Elimination of Arbitrage.
- 17. ï Dividend will be taxed @10 % ï All transactions of trading of the GDRs outside India, among non-resident investors, will be free from any liability of income tax in India. ï Capital gains arising on the redemption of shares will be liable to income tax Section 115AC. ï Long-term capital gains tax @ 10 % ï Short-term capital gains tax@ 15 % (Section 195 and 196 of IT Act). Advanced Financial Management 17
- 18. Eligibility of the issuer Eligibility of the subscriber Approval of Board of Approval of shareholders Directors Listing requirements Approval of FIPB Pricing Reporting requirements of RBI Issue expenses Companies Act
- 19. Private Sector Banking 74% Drugs & Pharmaceuticals 100% Non-Banking Financial 100% Road and highways, Ports and 100% Companies harbours Insurance 26% Hotel & Tourism 100% Telecommunications 74% Mining 74- Services 100% Petroleum Refining- 100% Advertising 100% Private Sector Housing and Real Estate 100% Films 100% Trading 51-100% Airports 74% Coal & Lignite 50-100% Mass Rapid Transport 100% Systems Power 100% Pollution Control & Mng. 100% Air transport Services 100% -NRIs, Special Economic Zones 100% (no foreign airlines) 49% others
Editor's Notes
- Types of ADRs